
Consider heat conduction through a wall of thickness L and area A. Under what conditions will the temperature distributions in the wall be a straight line?
The condition under which the temperature distribution in the wall is a straight line.
Explanation of Solution
The temperature distribution of a wall with thickness L and area A is shown in the figure below:
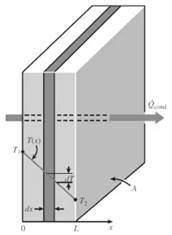
The one-dimensional steady state heat conduction equation without heat generation for the wall is
Here, T is the temperature and x is the direction of flow of heat.
Integrate equation (1) with respect to x.
Where, c1 is the constant of integration.
Further integrate the equation (2) with respect to x.
Now, calculate the constant of integration.
At x = 0, T =T1
Substitute the value in equation (3);
Substitute the value of c2 in equation (3);
Substitute the value of c1 and c2 in equation (3);
The above equation is in the form of a straight line equation y = mx+c. Thus, the distribution of temperature in the plane wall will be a straight line during steady-state one dimensional heat transfer.
Thus, the following are the conditions during which the temperature distribution in the wall is a straight line.
- Heat conduction in one-dimensional steady state direction.
- Thermal conductivity should be constant.
- There is no any internal heat generation in the wall.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
HEAT+MASS TRANSFER:FUND.+APPL.
- What is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple pointarrow_forwardWhat is quality? Does it have any meaning in the superheated vapour region? What is the difference between saturated vapor and superheated vapour? What is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple point?arrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forward
- Describe the principle operation of PEMFC, and role of membrane electrode assembly (MEA).arrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardUsing graphical methods, draw the pressure angle at the position shown in (a) and (b). e |------- R = Cam Base Radius e = Follower Offset ẞ₁ = Section Duration 1 B₁ = Section Duration 2 ẞ₂ = Section Duration 3 В2 B₁ Follower Position ww R ẞ3 (a) Reference Radial (b)arrow_forward
- The figure below illustrates a graph that has a variable load torque and constant drive torque. Each cycle lasts three revolutions (6л radians). Torque (N-m) 600 550 400 1 200 TD= 225 N-m 2 + -T₁ 3 4 1 + 0 In addition, the rotation speed is @o steady-state conditions, determine 1. the average power required, 2πT 4π 5πT 6п Ꮎ = 180° rpm = 18.85 rad/sec, Imachine 125 kg-m². Assuming 2. the maximum and minimum rotational speeds throughout a cycle, 3. the mass of a 0.6-meter-diameter solid disc flywheel to produce Cs = 0.025.arrow_forwardAn elastic cord is stretched between 2 points A and B located 2y = 0.8 m apart in the horizontal plane. When stretched directly between A and B, the tension is P₂ = 40 N. The cord is then stretched as shown until its midpoint C has moved through x = 0.3 m to C', and a force of F = 240 N is required to hold the cord at C'. A pellet (m = 0.1 kg) is placed at C' and the cord is released. Find the speed of the pellet as it passes through C.arrow_forwardA 6305 ball bearing is subjected to a steady 5000-N radial load and a 2000-N thrust load and uses a very clean lubricant throughout its life. If the inner race angular velocity is 500rpm find (a) The equivalent radial load (b) The L10 life (c) The L50 lifearrow_forward
- Slove this the question plearrow_forwardDetermine the Mean Effective Pressure (MEP) in [bar] for a 4-cylinder, 2-Stroke engine with a bore of 85.7 mm, and a stroke of 65.8 mm, that produces 85 hP at 5000 rpm. (Hint: Be careful with units). Note: 1 hP = 0.7457 kW; 100 kPa = 1 bararrow_forwardIbraheem Super Q3: A boiler as shown in the figure below is producing 2 kg/s saturated steam at 240C. The water enters the boiler at 24C. The boiler efficiency is 80%. Patm=1.05 bar .Determine: (10 Marks) 1- The inlet pressure of the turbine. 2- If a gauge pressure connected to the outlet pipe, what is the reading of this gauge? 3- Calculate the required diesel in [kg/s]. Assume the calorific value of the diesel is 45000 kJ/kgf 4- Calculate the equivalent evaporation of the boiler 5- Keeping the same inlet conditions and fuel consumption, determine the turbine efficiency if the produced steam was saturated at 300C. Steam Cut Hot Gasses Out Ts=240C Boiler FURNACE A Water In C 24 Examiner Head of Department Ahmad. A. M. Alsak laniarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
