
Using Figure 3.1, determine
a. the number of grams of
b. the number of grams of water required to dissolve
c. the number of grams of water required to dissolve
d. the number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
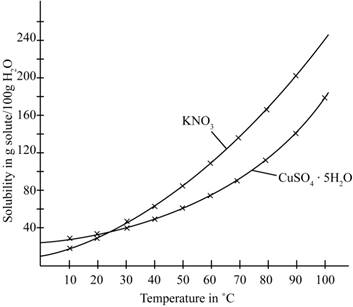
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
The number of grams of
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
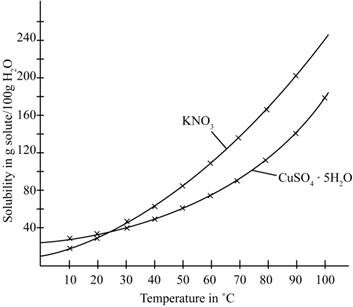
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
Thus, water required to dissolve
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
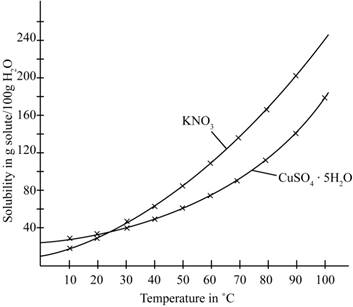
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
Thus, the water required to dissolve
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
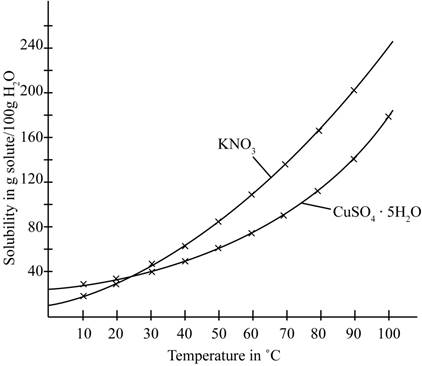
Figure 1
The amount of water required to dissolve
The amount of water required to dissolve
Therefore, the total amount of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES IN THE LABORATO
- Nonearrow_forwardIndicate which option is false(A). Resistivity has a residual component and a thermal component.(B). In some materials resistivity increases with T and in others it decreases.(C). In insulating materials, resistivity is very low.arrow_forwardIn ceramic materials, in relation to polymorphism, the same substance crystallizes differently when external conditions vary. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- Indicate the type of bond that is considered to be a hydrogen bond.(A). Permanent dipole-dipole interaction between polar molecules.(B). Mixed ionic-covalent bond.(C). Principal interatomic bond(D). Van del Waals forces.arrow_forwardRetro aldol: NaOH H₂O H NaOH & d H₂O Harrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H conc. HBr Drawing Qarrow_forward
- Calculate the atomic packing factor of diamond knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are, respectively, 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forwardA pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows. Aldol: NaOH HO H Δ NaOH Δarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Draw structures corresponding to the following names and give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (8 Point) a) b) c) CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CH CH3 C=C H3C H H2C=C=CHCH3 d) CI e) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene f) (Z)-4-bromo-3-methyl-3-penten-1-yne g) cis-1-Bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane h) (5R)-4,4,5-trichloro-3,3-dimethyldecanearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardReview: Design a total total synthesis synthesis of the following compound using methyloxacyclopropane and any other necessary reagents.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





