
Concept explainers
Cost of production report
The debits to Work in Process—Roasting Department for Morning Brew Coffee Company for August, together with information concerning production, are as follows:
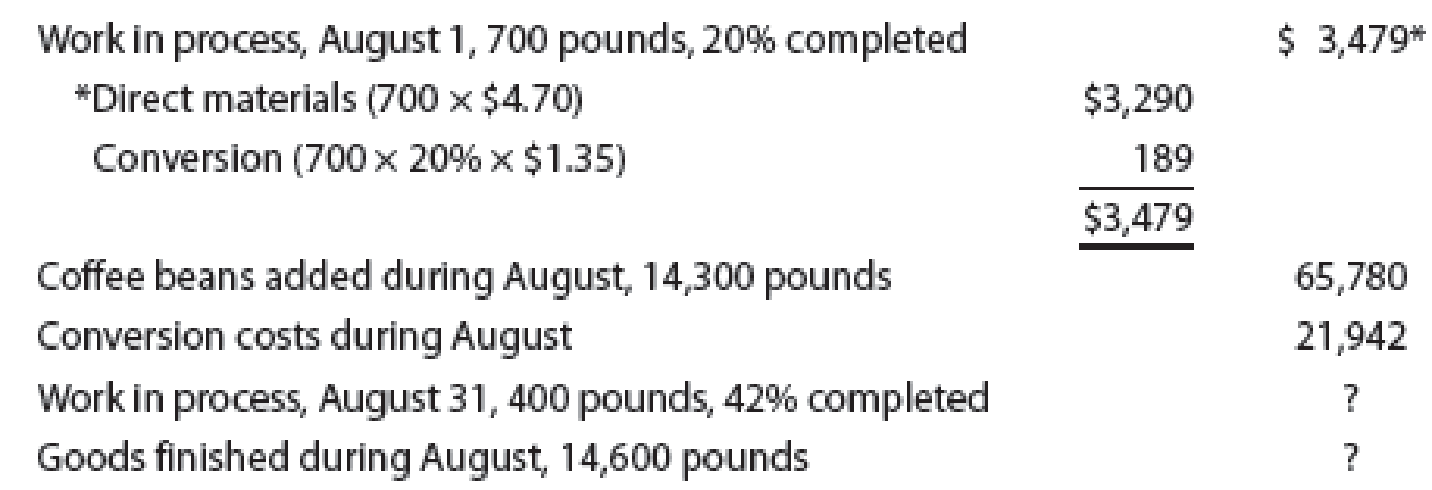
All direct materials are placed in process at the beginning of production.
- A. Prepare a cost of production report, presenting the following computations:
- 1. Direct materials and conversion equivalent units of production for August
- 2. Direct materials and conversion costs per equivalent unit for August
- 3. Cost of goods finished during August
- 4. Cost of work in process at August 31
- B. Compute and evaluate the change in cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion from the previous month (July).
A. (1)
Calculate the equivalents units for production of direct materials and conversion costs for the month of August for Company MBC.
Explanation of Solution
Process costs
It is a method of cost accounting, which is used where the production is continuous, and the product needs various processes to complete. This method is used to ascertain the cost of the product at each process or stage of production.
Equivalents units for production
The activity of a processing department in terms of fully completed units is known as equivalent units. It includes the completed units of direct materials and conversion cost of beginning work in process, units completed and transferred out, and ending work in process.
Production cost report
A production cost report is a comprehensive report prepared for each department separately at the end of a particular period, which represents the physical flow and cost flow of product for the concerned department.
Calculate the equivalents units for production of direct materials and conversion costs for the month of August for Company MBC as shown below:
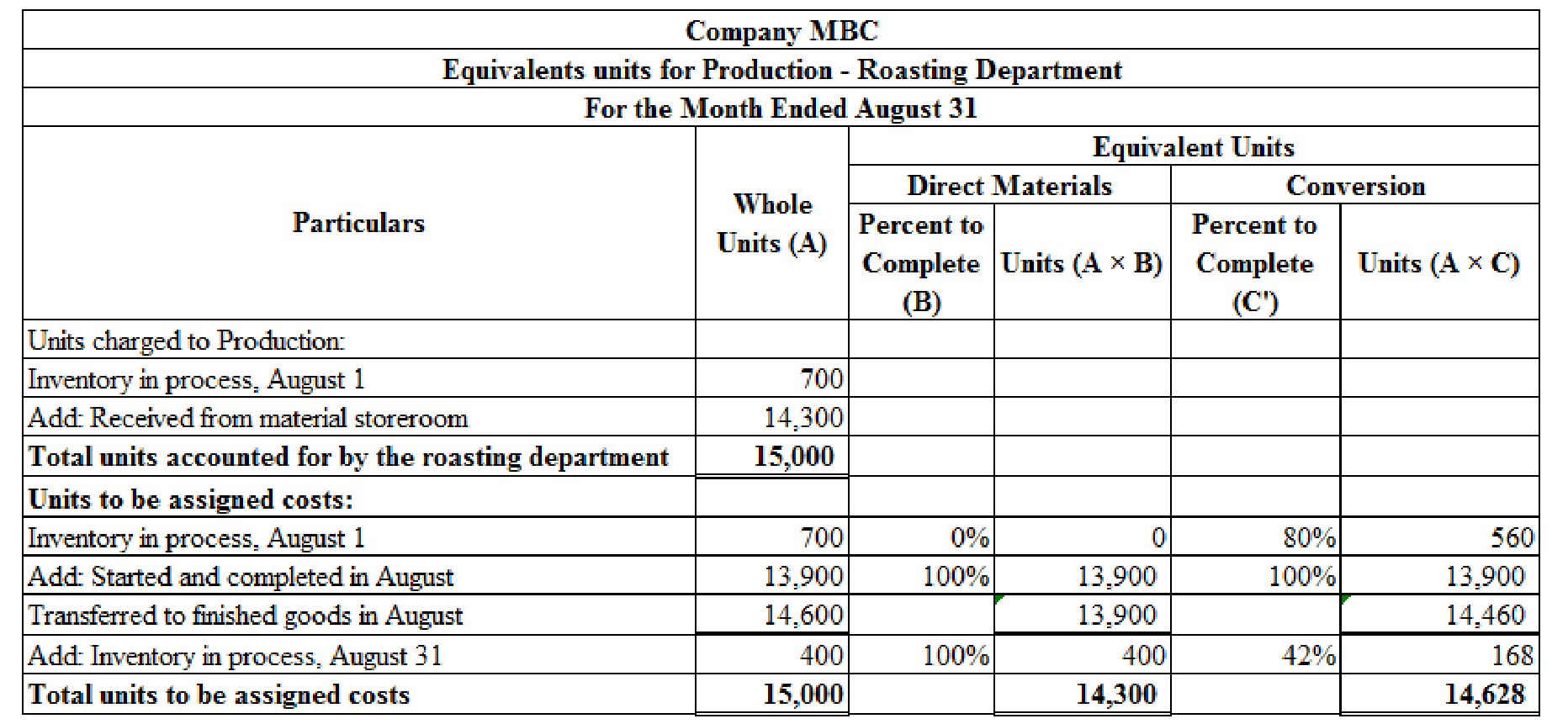
Figure (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate opening work in process inventory for conversion costs as shown below:
Working note (2):
Calculate units started and completed in August as shown below:
Working note (3):
Calculate ending work in process inventory for conversion costs as shown below:
Equivalent units for production is calculated by adding units of opening work in process inventory, transferred to finished goods in august, and units for ending work in process inventory. Therefore, an equivalents unit for production for direct materials is 14,300 units and equivalent units for production for conversion costs is 14,628 units.
A. (2)
Calculate the direct materials and conversion cost equivalent cost per unit for August.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate direct materials and conversion cost equivalent cost per unit for August as shown below:
Direct material cost per unit is calculated by dividing total direct materials cost by equivalent units for direct materials. Hence, direct material cost per unit is $4.60 per unit. Conversion cost per unit is calculated by dividing total conversion costs by equivalent units for conversion. Hence, conversion cost per unit is $1.50 per unit.
A. (3)
Calculate the cost of goods finished during the month of august.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of goods finished during the month of August as shown below:
| Particulars | Units (A) | Per unit (B) | Amount (A × B) |
| Inventory in process, August 1 balance | $3,479 | ||
| Add: Cost of completed August 1, Work in process | |||
| Direct materials | 0 | $4.60 | $0 |
| Conversion | 560 | $1.50 | $840 |
| Add: Transferred to finished goods in August: | |||
| Direct materials | 13,900 | $4.60 | $63,940 |
| Conversion | 13,900 | $1.50 | $20,850 |
| Cost of Goods finished during August | $89,109 |
Table (1)
Cost of goods finished during the month of august is calculated by adding opening inventory balance, cost of opening work in process inventory, and transferred to finished goods during the period of August. Therefore, cost of goods finished during the august is $89,109.
A. (4)
Calculate the cost of ending work in process inventory during the month of August.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of ending work in process inventory during the month of August as shown below:
| Particulars | Units (A) | Per unit (B) | Amount (A × B) |
| Inventory in process, August 31, balance | |||
| Direct materials | 400 | $4.60 | $1,840 |
| Conversion | 168 | $1.50 | $252 |
| Cost of ending work in process inventory | $2,092 |
Table (2)
Cost of ending work in process inventory is calculated by adding ending work in process inventory for both direct materials and conversion costs. Hence, cost of ending work in process inventory is $2,092.
Cost of production report for Company MBC as shown below:
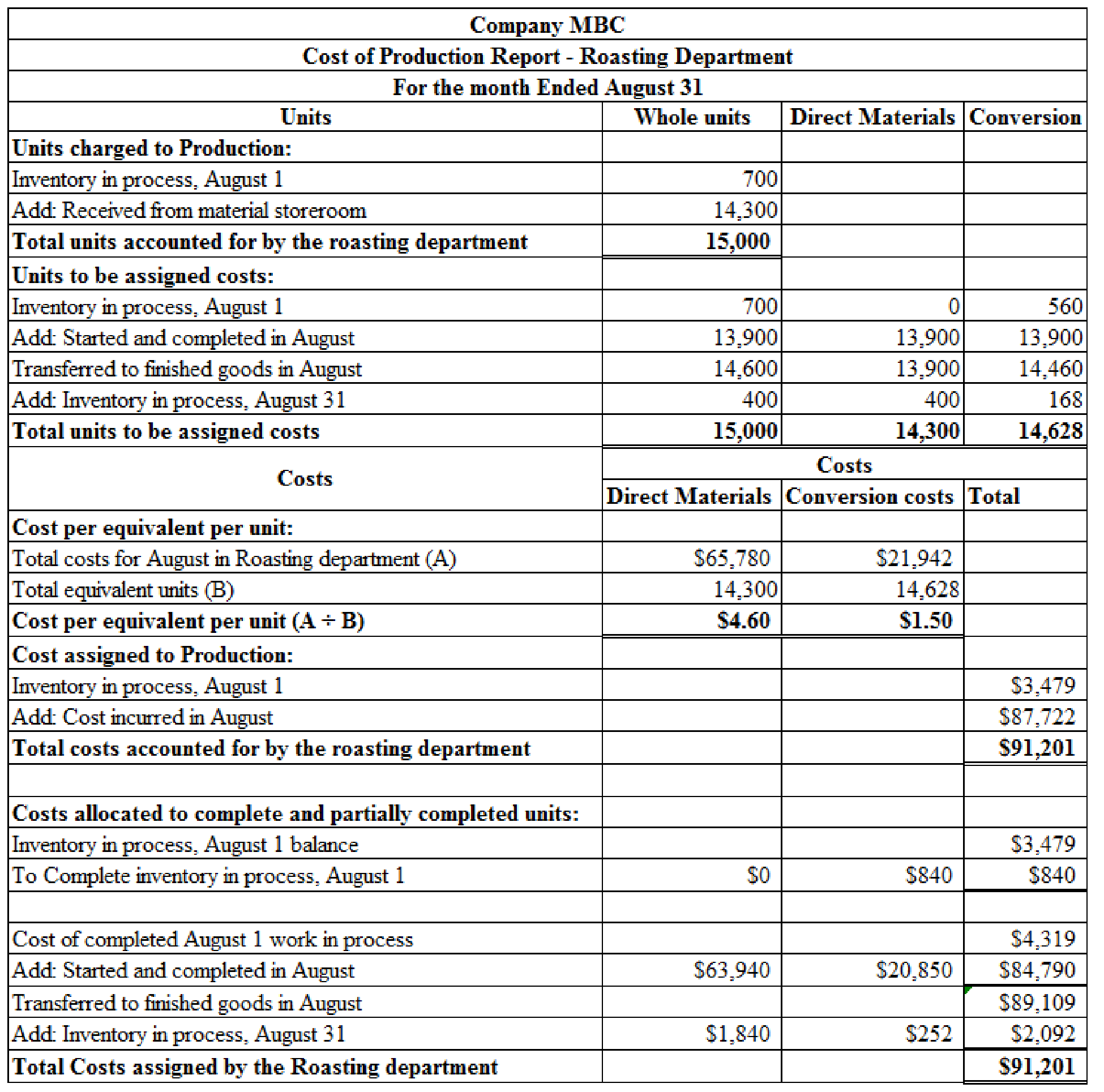
Figure (2)
B.
Calculate the change in cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost comparing with July month.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate change in cost per equivalent unit for direct material and conversion cost during the month of July as shown below:
| Particulars | Per unit |
| Cost per unit for August | $4.60 |
| Less: Cost per unit for July | $4.70 |
| Decrease in direct material per unit | ($0.10) |
Table (3)
| Particulars | Per unit |
| Cost per unit for August | $1.50 |
| Less: Cost per unit for July | $1.35 |
| Increase in conversion cost per unit | $0.15 |
Table (4)
Change in cost per equivalent unit is calculated by deducting previous month cost per unit from current month cost per unit. Direct material is decreased by $0.10. Conversion cost per unit is increased by $0.15 per unit. Company MBC might be asking to scrutinize the reasons for the rise in the conversion cost in the current month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting, Loose-leaf Version, 14th - Book Only
- Samuel Entertainment Inc. was organized on March 1, 2018. During 2021, Samuel Entertainment issued 18,000 shares at $22 per share, purchased 2,500 shares of treasury stock at $25 per share, and had a net income of $240,000. What is the total amount of stockholders' equity at December 31, 2021?arrow_forwardWhat will be the firm's operating cyclearrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning





