
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Cash (+A) | $9,500 | |
| Consulting fees revenue (+R) (+SE) | $9,500 | ||
| (To record the fees earned) | |||
| b | Cash (+A) | $1,200 | |
| Common stock (+SE) | $10 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital (+SE) | $1,190 | ||
| (To record the purchase of building) | |||
| c | Office equipment (+A) | $640 | |
| Cash (-A) | $160 | ||
| Short-term notes payable (+L) | $480 | ||
| (To record the purchase of equipment on account) | |||
| d | Cash (+A) | $890 | |
| Unearned revenue (+L) | $890 | ||
| (To record the unearned revenue) | |||
| e | Supplies (+A) | $470 | |
| Accounts payable (-L) | $470 | ||
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | |||
| f | Utilities expense (+E) (-SE) | $1,800 | |
| Cash (-A) | $1,800 | ||
| (To record the utilities expense) | |||
| g | $1,620 | ||
| Consulting fees revenue (+R) (+SE) | $1,620 | ||
| (To record the fees earned) | |||
| h | Cash (+A) | $2,980 | |
| Accounts receivable (-A) | $2,980 | ||
| (To record the cash receivable from customer) | |||
| i | Salaries expense (+E) (-SE) | $6,210 | |
| Cash (-A) | $5,300 | ||
| Salaries payable (+L) | $910 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash for accounts payable) | |||
| j | Short term investments (+A) | $1,230 | |
| Prepaid expenses (+A) | $800 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $2,030 | ||
| (To record the cash receivable from customer) | |||
| k | Cash (+A) | $10 | |
| Interest revenue (+R) (-SE) | $10 | ||
| (To record the interest revenue) |
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
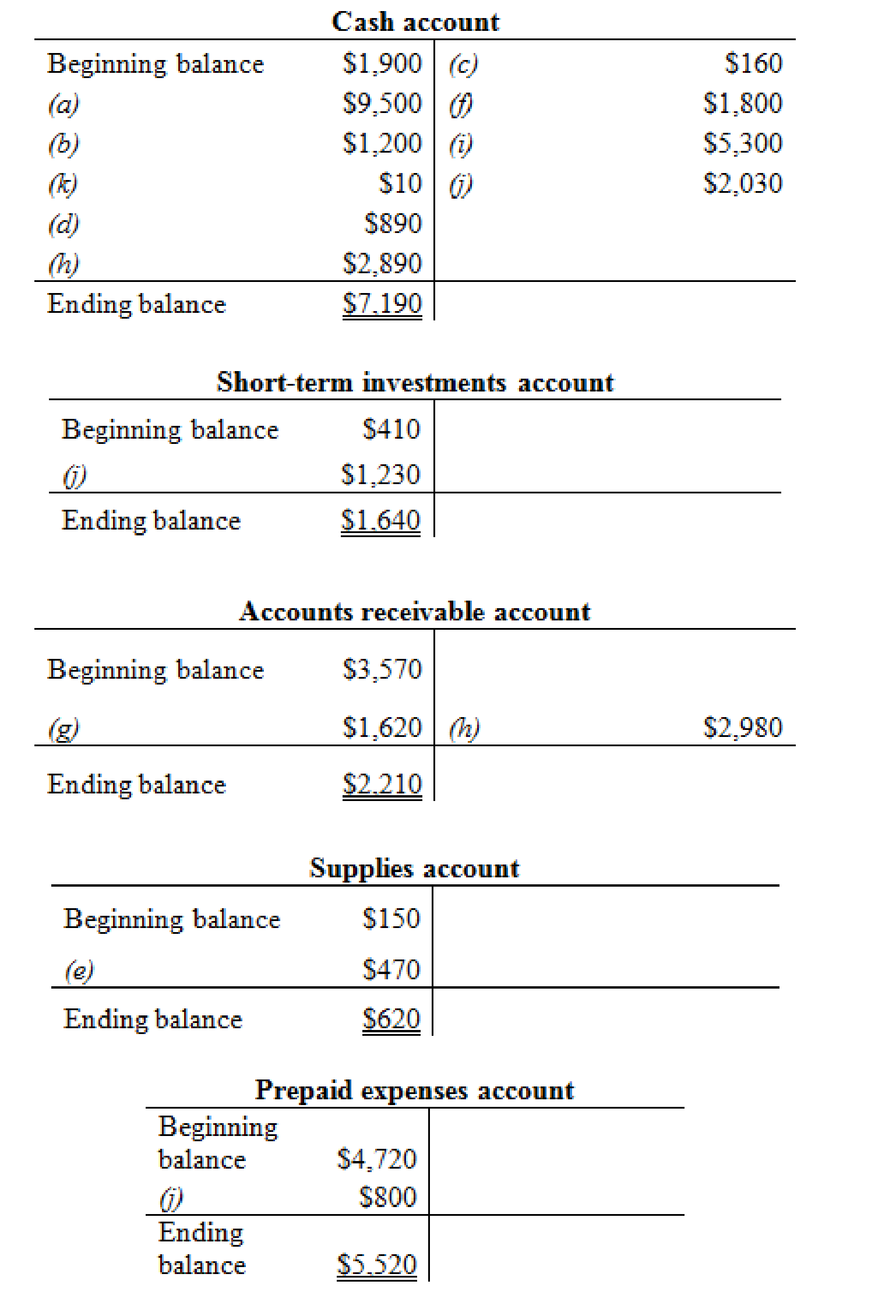
Figure (1)
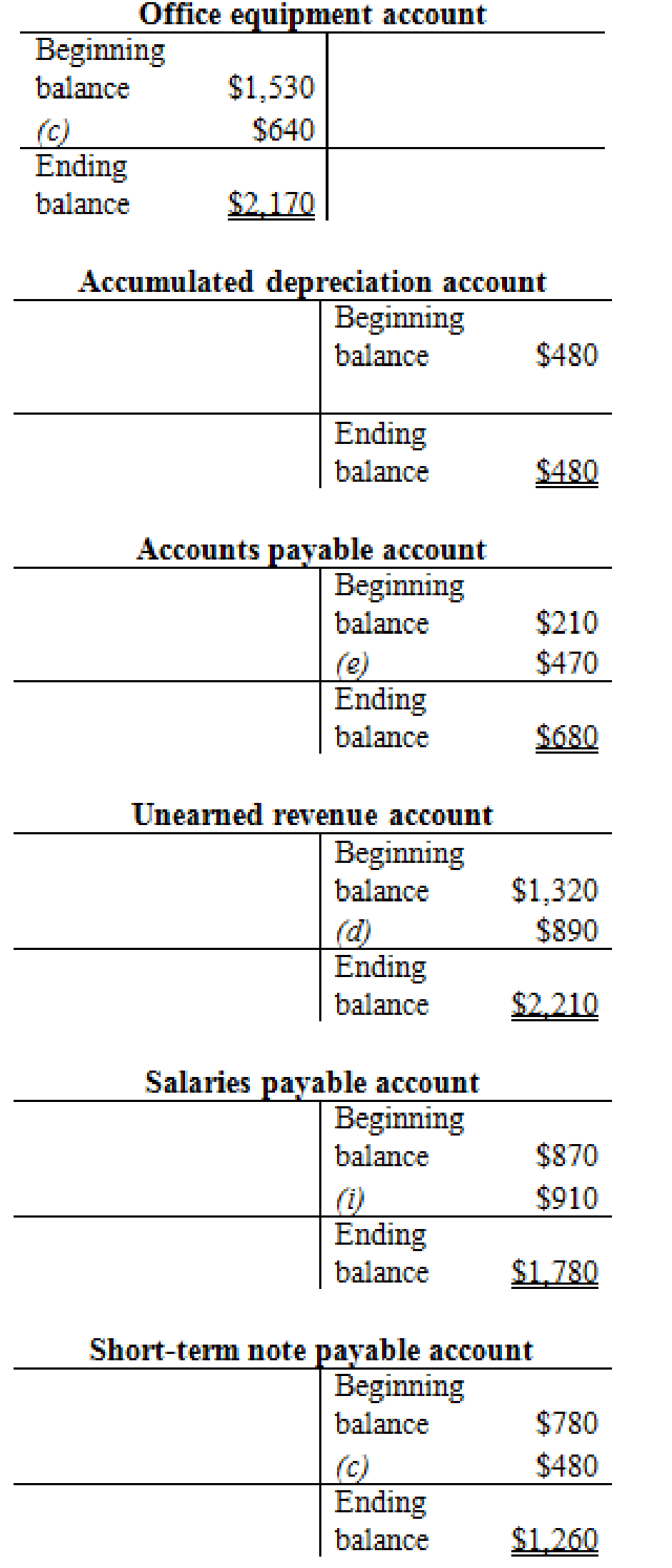
Figure (2)
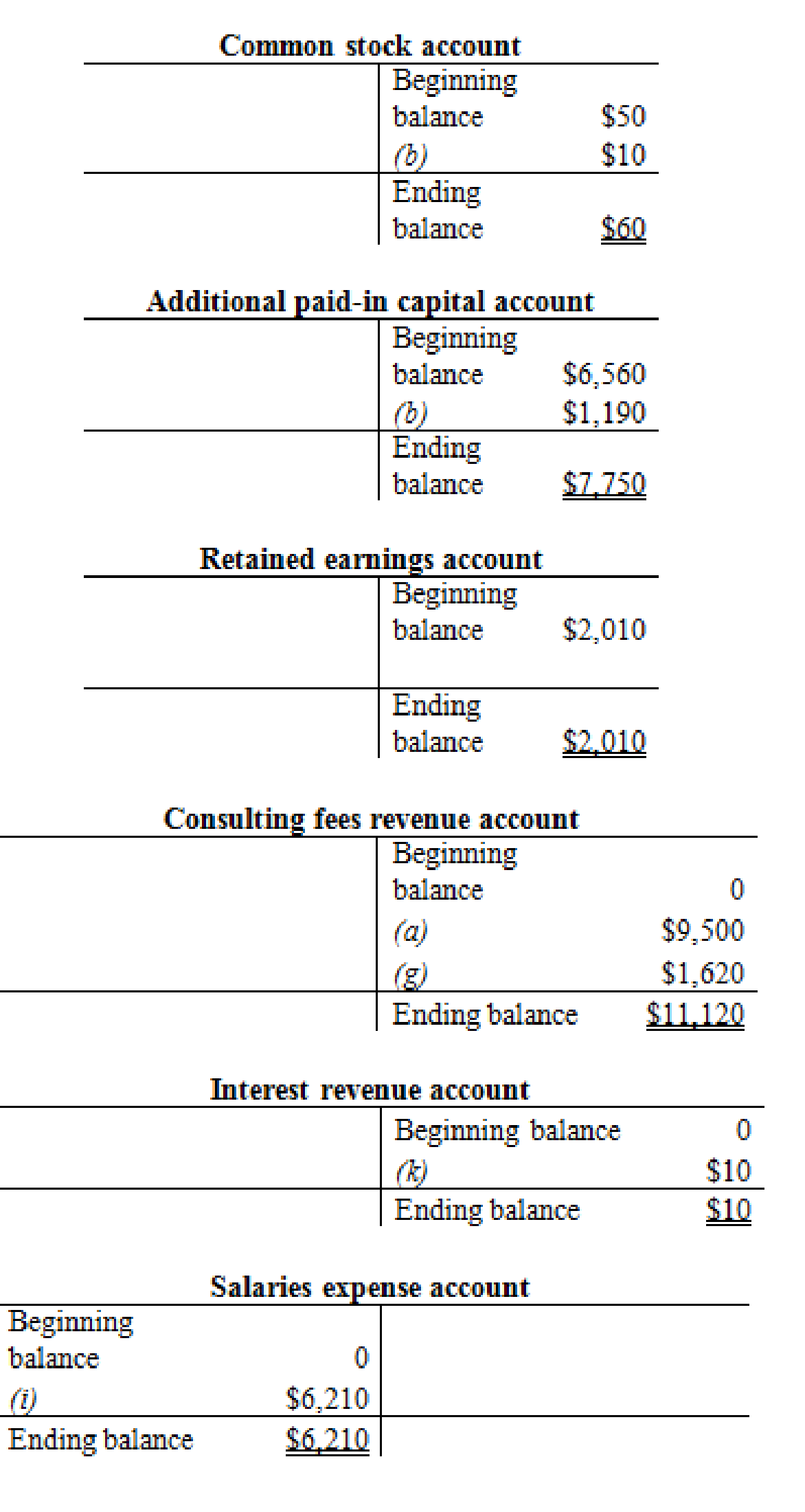
Figure (3)
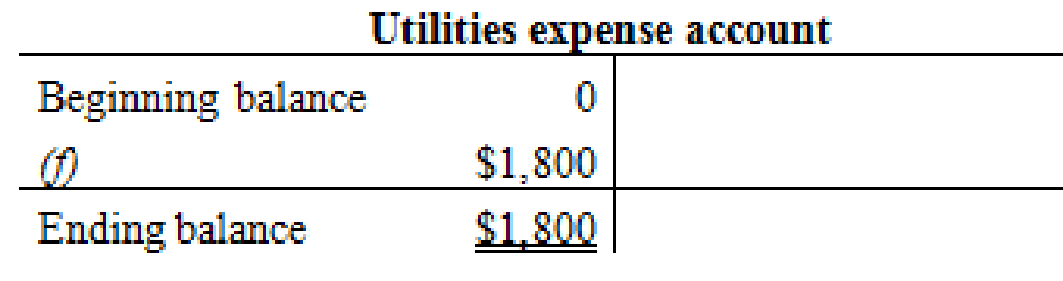
Figure (4)
Thus, the T-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Ascertain the amount for the given equations at the end of the January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
For the equation
For the equation
Working note (1):
Calculate the revenues:
Working note (2):
Calculate the expenses:
Working note (3):
Calculate the net income:
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues | (1) 11,130 | |
| Less: Expenses | (2) 8,010 | |
| Net income | $3,120 |
Table (2)
4.
Calculate the net income under cash basis of accounting and explain the reason in which manner the net income differs from accrual basis of accounting.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the net income under cash basis accounting:
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash receipts | (4) 14,580 | |
| Less: Cash payments | (5) 9,290 | |
| Net income | $5,290 |
Table (3)
Net income of Incorporation C under cash basis of accounting is $5,290.
Working note (4):
Calculate the cash receipts:
Working note (5):
Calculate the cash payments:
- According to the cash basis of accounting, the net income is $5,290 which higher than the accrual basis of accounting.
- The recording of the expenses and revenues differ from the accrual basis of accounting.
- Hence, the net income is different for the accrual basis of accounting and cash basis of accounting.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTRO TO FIN ACCT (LL W/ ACCESS-1 SMSTR
- Titan Manufacturing has total maintenance department expenses of $35,600. The maintenance costs are allocated based on square footage, where the Molding department occupies 5,500 square feet, and the Finishing department occupies 2,500 square feet. Compute the amount of maintenance department expense allocated to Molding.arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the net realizable value of accounts receivable after the write off entry on these financial accounting question?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





