
Physics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134051802
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 12PCE
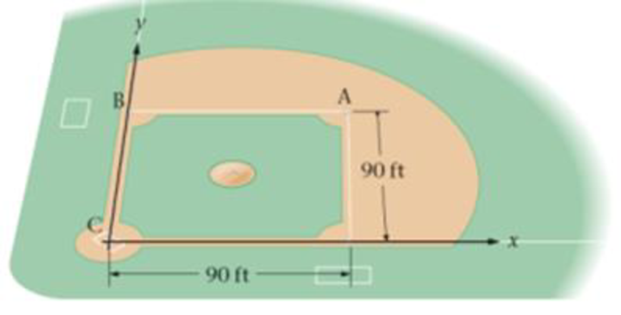
A baseball “diamond” (Figure 3-38) is a square with sides 90 ft in length. If the positive x axis points from home plate to first base, and the positive y axis points from home plate to third base find the displacement vector of a base runner who has just hit (a) a double (b) a triple, or (c) a home run.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
"looks" like a particle.)
...32 GO
In Fig. 22-55, positive
charge q = 7.81 pC is spread uni-
formly along a thin nonconducting
rod of length L = 14.5 cm. What are
the (a) magnitude and (b) direction
(relative to the positive direction
of the x axis) of the electric field
produced at point P, at distance
R = 6.00 cm from the rod along its
perpendicular bisector?
R
y
Р
+ + + + + + + + +-×
L
Figure 22-55 Problem 32.
1) A horizontal wire carrying current I in +x direction on the x-axis from x=0 to x=2
2) A vertical wire carrying current I upward at along the x=2 line from y=0 to y=8
3) A diagonal straight wire started at the origin and it ends at y=8 x=2 carrying a current in SE direction ( diagonally downward); y=4x
In a regional magnetic field that is given in vector notation by
B = ( y i - x j )/(x^2+y^2+25)
As components
Bx = (y+1)/x^2+y^2+25)
By = (1- x )/(x^2+y^2+25)
Find the integral expression for the net force for each branch carrying 5 ampere current.
An electric power station that operates at 30 KV and uses
a 15:1 set step-up ideal transformer is producing 400MW
(Mega-Watt) of power that is to be sent to a big city
with only 2.0% loss. What
which is located 270 km
away
is the resistance of the Two wires that are
being used?
52
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Ch. 3.1 - Is it possible for two vectors to be different...Ch. 3.2 - A vector has the components Ax = 5 m and Ay = 3 m....Ch. 3.3 - Several vectors are shown in Figure 3-16. The red...Ch. 3.4 - Which of the vectors shown in Figure 3-20 has the...Ch. 3.5 - An object moves along the brown path in Figure...Ch. 3.6 - Suppose the speed of the boat is increased in part...Ch. 3 - For the following quantities, indicate which is a...Ch. 3 - Which, if any of the vectors shown in Figure 3-36...Ch. 3 - Given that A+B=0, (a) how does the magnitude of B...Ch. 3 - Can a component of a vector be greater than the...
Ch. 3 - Prob. 5CQCh. 3 - Can a vector with zero magnitude heve one or more...Ch. 3 - Prob. 7CQCh. 3 - Prob. 8CQCh. 3 - Prob. 9CQCh. 3 - Prob. 10CQCh. 3 - Prob. 11CQCh. 3 - Use a sketch to show that two vectors of unequal...Ch. 3 - Rain is falling vertically downward and you are...Ch. 3 - When sailing, the wind feels stronger when you...Ch. 3 - Suppose that each component ot a certain vector is...Ch. 3 - Rank the vectors in Figure 3-37 in order of...Ch. 3 - Rank the vectors in Figure 3-37 in order of...Ch. 3 - Rank the vectors in Figure 3-37 in order of...Ch. 3 - The press box at a baseball park is 44.5 ft above...Ch. 3 - You are driving up a long, inclined road. After...Ch. 3 - A One-Percent Grade A road that rises 1 ft for...Ch. 3 - You walk in a straight line tor 95 m at an angle...Ch. 3 - Find the x and y components of a position vector r...Ch. 3 - A vector has the components Az = 22 m and Ay = 13...Ch. 3 - A vector has the components Az = 36 m and Ay = 43...Ch. 3 - A baseball diamond (Figure 3-38) is a square with...Ch. 3 - A lighthouse that rises 49 ft above the surface of...Ch. 3 - H2O A water molecule is shown schematically in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 15PCECh. 3 - You drive a car 660 ft to the east, then 340 ft to...Ch. 3 - Vector A has a magnitude of 50 units and points in...Ch. 3 - A treasure map directs you to start at a palm tree...Ch. 3 - A whale comes to the surface to breathe and then...Ch. 3 - Consider the vectors A and B shown in Figure 3-42....Ch. 3 - Refer to Figure 3-42 for the following questions...Ch. 3 - A vector A has a magnitude of 40.0 m and points in...Ch. 3 - An air traffic controller observes two airplanes...Ch. 3 - The initial velocity of a car, vi, is 45 km/h in...Ch. 3 - Vector A points in the positive x direction and...Ch. 3 - Vector A points in the negative x direction and...Ch. 3 - Vector A points in the negative y direction and...Ch. 3 - A basketball player runs down the court, following...Ch. 3 - A particle undergoes a displacement r of magnitude...Ch. 3 - A vector has a magnitude of 3.50 m and points in a...Ch. 3 - A vector A has a length of 6.1 m and points in the...Ch. 3 - The vector 5 2 A has a magnitude of 34 m and...Ch. 3 - Find the direction and magnitude of the vectors....Ch. 3 - Find the direction and magnitude of the vectors....Ch. 3 - For the vectors given in Problem 34, express (a)...Ch. 3 - Express each of the vectors in Figure 3-44 in unit...Ch. 3 - Referring to the vectors in Figure 3-44, express...Ch. 3 - The blue curves shown in Figure 3-45 display the...Ch. 3 - What are the direction and magnitude of your total...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate Moving the Knight Two of the...Ch. 3 - To visit your favorite ice cream shop, you must...Ch. 3 - Referring to Problem 41, suppose you lake 44 s to...Ch. 3 - You drive a car 1500 ft to the east, then 2500 ft...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate A jogger runs with a speed of...Ch. 3 - You throw a ball upward with an initial speed of...Ch. 3 - Consider a skateboarder who starts from rest at...Ch. 3 - In a soccer game a midfielder kicks the ball from...Ch. 3 - The accompanying photo shows a KC-10A Extender...Ch. 3 - As an airplane taxied on the runway with a speed...Ch. 3 - Referring to part (a) of Example 3-11, find the...Ch. 3 - A police car travels at 38.0 m/s due east while in...Ch. 3 - Consider the river crossing problem in Example...Ch. 3 - As you hurry to catch your flight at the local...Ch. 3 - In Problem 53, how much lime would it take you to...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate The pilot of an airplane wishes...Ch. 3 - A passenger walks from one side of a ferry to the...Ch. 3 - You are riding on a Jet Ski at an angle of 35...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate In Problem 57, suppose the Jet...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate Two people take identical Jet...Ch. 3 - CE Predict/Explain Consider the vectors A=(1.2m)x...Ch. 3 - CE Predict/Explain Two vectors are defined as...Ch. 3 - To be compliant with regulations the inclination...Ch. 3 - Find the direction and magnitude of the vector...Ch. 3 - Prob. 64GPCh. 3 - Prob. 65GPCh. 3 - Prob. 66GPCh. 3 - You pilot an airplane with the intent to fly 392...Ch. 3 - Find the x, y, and z components of the vector A...Ch. 3 - Observer 1 rides in a car and drops a ball from...Ch. 3 - A person riding in a subway train drops a ball...Ch. 3 - A football is thrown horizontally with an initial...Ch. 3 - As a function of time, the velocity of the...Ch. 3 - Two airplanes taxi as they approach the terminal....Ch. 3 - A shopper at the supermarket follows the path...Ch. 3 - BIO A food particle from your breakfast takes a...Ch. 3 - Initially a particle is moving at 4.10 m/s at an...Ch. 3 - A passenger on a stopped bus notices that rain is...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate Suppose we orient the x axis of...Ch. 3 - Predict/Calculate The Longitude Problem In 1759,...Ch. 3 - Referring to Example 3-11, (a) what heading must...Ch. 3 - Vector A points in the negative x direction....Ch. 3 - As two boats approach the marina, the velocity of...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...Ch. 3 - BIO Motion Camouflage in Dragonflies Dragonflies,...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. 1.Measurement of how orbital aur vital...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Why is living epithelial tissue limited to a certain thickness?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
What dipeptides would be formed by heating a mixture of valine and N-protected leucine?
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Examine the graph in Figure 6.3. Note that the growth rate increases slowly until the optimum is reached and th...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Slink, from Toy Story, is a slinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed (as shown in figure A) with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again (as shown in figure C).arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardCalculate the energy needed to melt 50 g of 0°C icearrow_forward
- Two very long line charges are set up along lines that areparallel to the z-axis, so they set up Electric fields strictly in the xy plane. One goes throughthe x-axis at x = −0.40 m and has charge a density λ1 = +12.0 μC/m, the other goesthrough the x-axis at x = +0.40 m has charge density λ2 = −8.0 μC/m.A. Find the Electric field at point A: (0.40, 0.80) (distances in meters). Give answersin unit vector notation and draw a graph of the x-y plane with the E-fields you justfound.B. Find a point on the x-axis at which the total E-field is 0.arrow_forwardIn order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight. (a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car? ] (b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb? ] (c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system? Eburned Δυarrow_forwardA 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact? Narrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.) a m ha 3.20 m 2.00 m i (a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and point B ©. m/s m/s point (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J A to pointarrow_forwardA 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forwardReport on the percentage errors (with uncertainty) between the value of 'k' from the F vs displacement plot and each of the values of 'k' from the period measurements. Please comment on the goodness of the results. Value of k = Spring constant k = 50.00 N/m Each of the values of k from period measurements: Six Measurements of time for 5 osccilations: t1 = 7.76s, t2=8.00s, t3=7.40s, t4=7.00s, t5=6.90s, t6=7.10s (t1-tavg)^2 = (7.76-7.36)^2 = 0.16%(t2-tavg)^2 =(8.00-7.36)^2 = 0.4096%(t3-tavg)^2 =(7.40-7.36)^2 = 0.0016%(t4-tavg)^2 =(7.00-7.36)^2 = 0.1296%(t5-tavg)^2 =(6.90-7.36)^2 = 0.2116%(t6-tavg)^2 =(7.10-7.36)^2 = 0.0676arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardBased on the two periods (from hand timed and ultrasonic sensor), find the value of 'k' they suggest from the physics and from the value of the hanging mass. hand time period is 1.472s and ultrasonic sensor time period is 1.44sarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to Vectors and Their Operations; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KBSCMTYaH1s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY