
Concept explainers
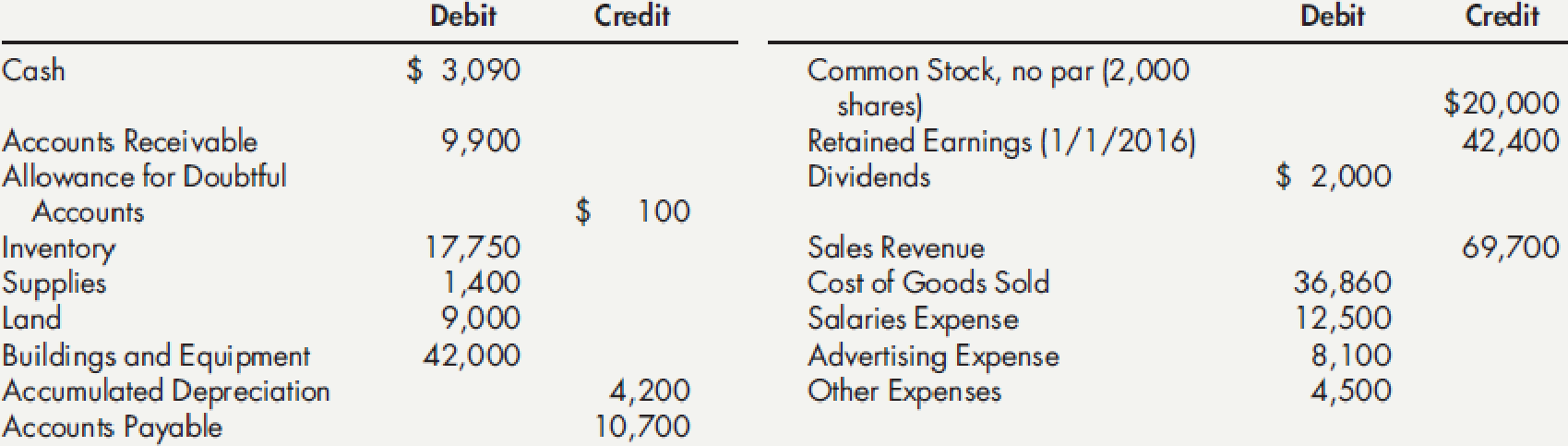
Comprehensive On November 30, 2016, Davis Company had the following account balances:
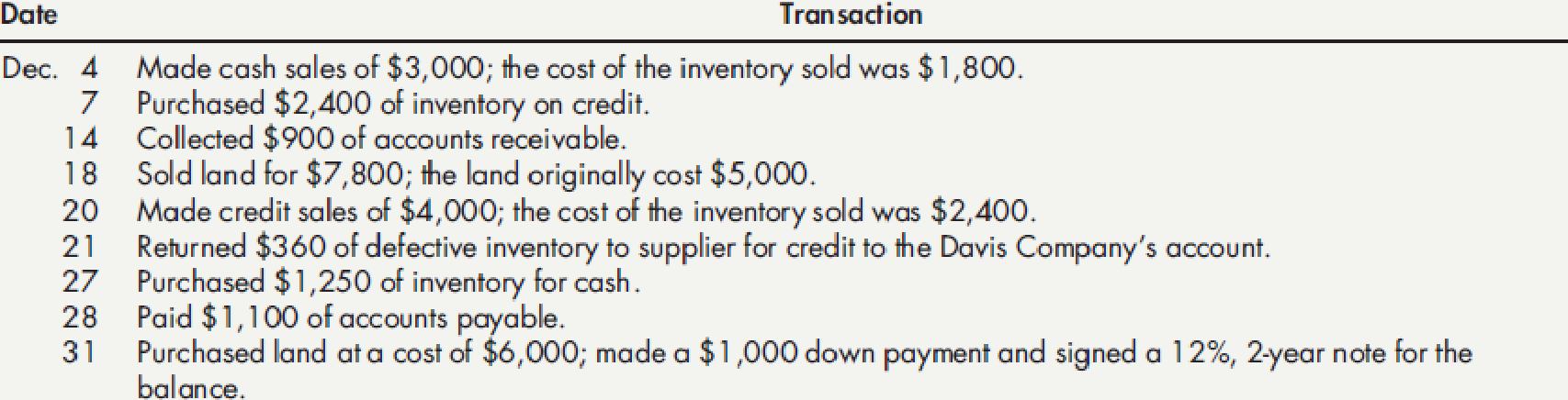
During the month of December, Davis entered into the following transactions:
Required:
- 1. Prepare general journal entries to record the preceding transactions.
- 2. Post to general ledger T-accounts.
- 3. Prepare a year-end
trial balance on a worksheet and complete the worksheet using the following information: (a) accrued salaries at year-end total $1,200; (b) for simplicity, the building and equipment are beingdepreciated using the straight-line method over an estimated life of 20 years with no residual value; (c) supplies on hand at the end of the year total $630; (d)bad debts expense for the year totals $830; and (e) the income tax rate is 30%; income taxes are payable in the first quarter of 2017. - 4. Prepare the company’s financial statements for 2016.
- 5. Prepare the 2016 (a) adjusting and (b) closing entries in the general journal.
1.
Prepare the journal entries to record the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To record the increase of balance in account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record the decrease of balance in account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare the journal entries to record the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 4 | Cash | 3,000 | |
| Sales Revenue | 3,000 | ||
| (To record the cash sales) | |||
| December 4 | Cost of Goods Sold | 1,800 | |
| Inventory | 1,800 | ||
| (To record the cost of ale) | |||
| December 7 | Inventory | 2,400 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,400 | ||
| (To record the purchase of inventory on account) | |||
| December 14 | Cash | 900 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 900 | ||
| (To record amount of accounts receivable collected) | |||
| December 18 | Cash | 7,800 | |
| Gain on sale of land | 2,800 | ||
| Land | 5,000 | ||
| (To record the gain on sale of land) | |||
| December 20 | Accounts Receivable | 4,000 | |
| Sales Revenue | 4,000 | ||
| (To record the credit sales) | |||
| December 20 | Cost of goods sold | 2,400 | |
| Inventory | 2,400 | ||
| (To record the cost of goods sold) | |||
| December 21 | Accounts Payable | 360 | |
| Inventory | 360 | ||
| (To record the returned defective merchandise for credit) | |||
| December 27 | Inventory | 1,250 | |
| Cash | 1,250 | ||
| (To record purchased inventory for cash) | |||
| December 28 | Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Cash | 1,100 | ||
| (To record accounts payable amount paid) | |||
| December 31 | Land | 6,000 | |
| Cash | 1,000 | ||
| Notes Payable | 5,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of land by paying cash and issuing 12% of note) |
Table (1)
2.
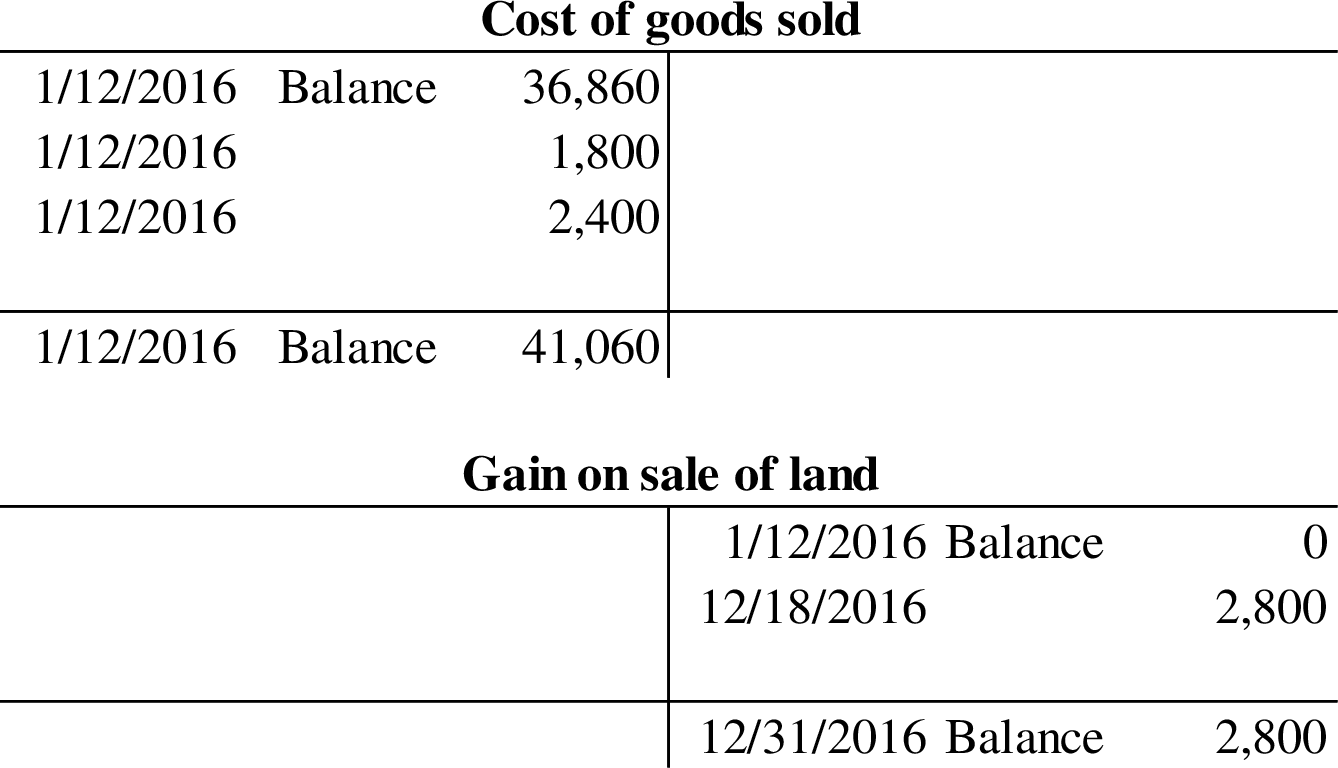
Post the part 1 entries to general ledger T-Accounts.
Explanation of Solution
T-account: T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
Post the part 1 entries to general ledger T-Accounts:
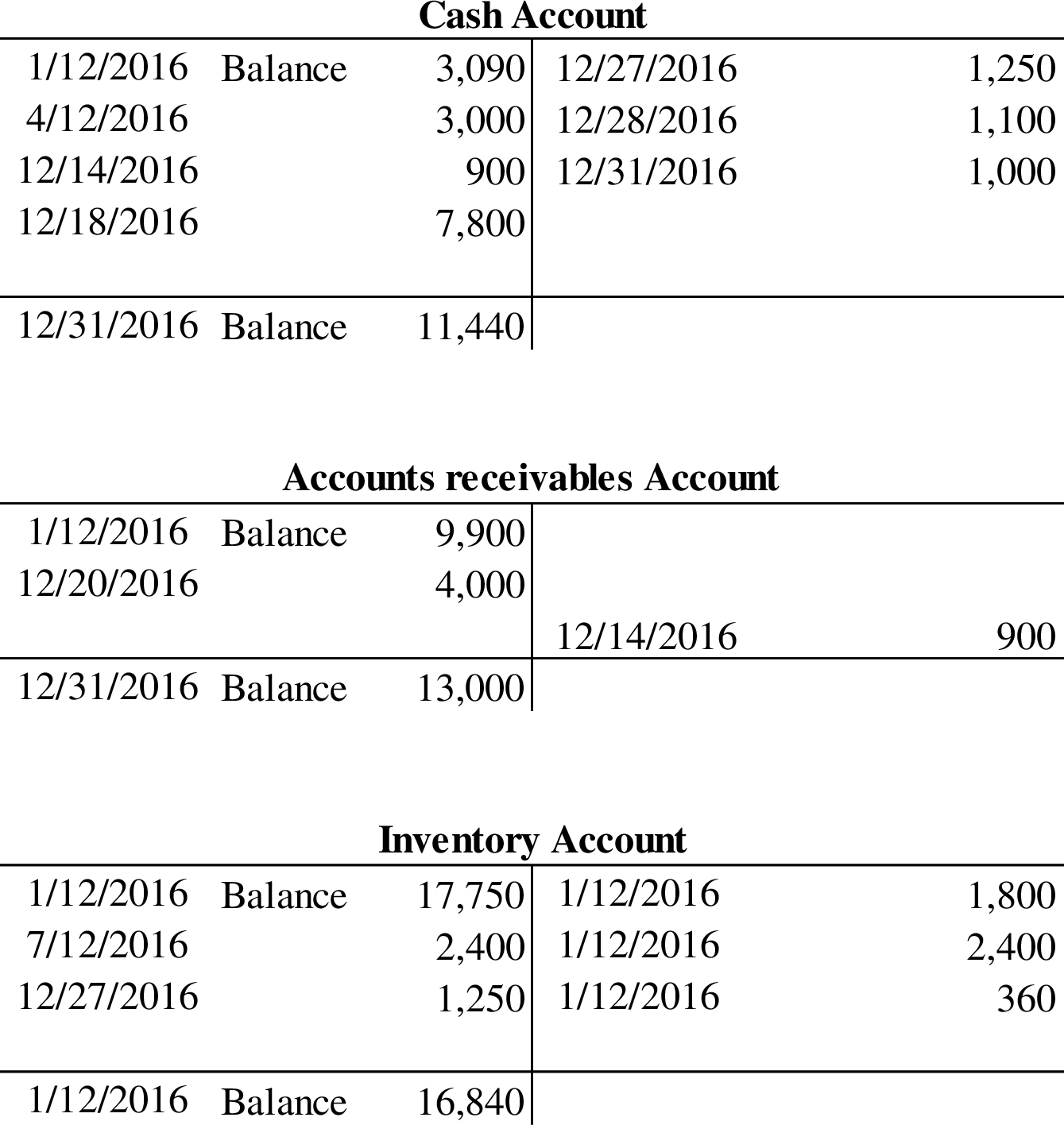
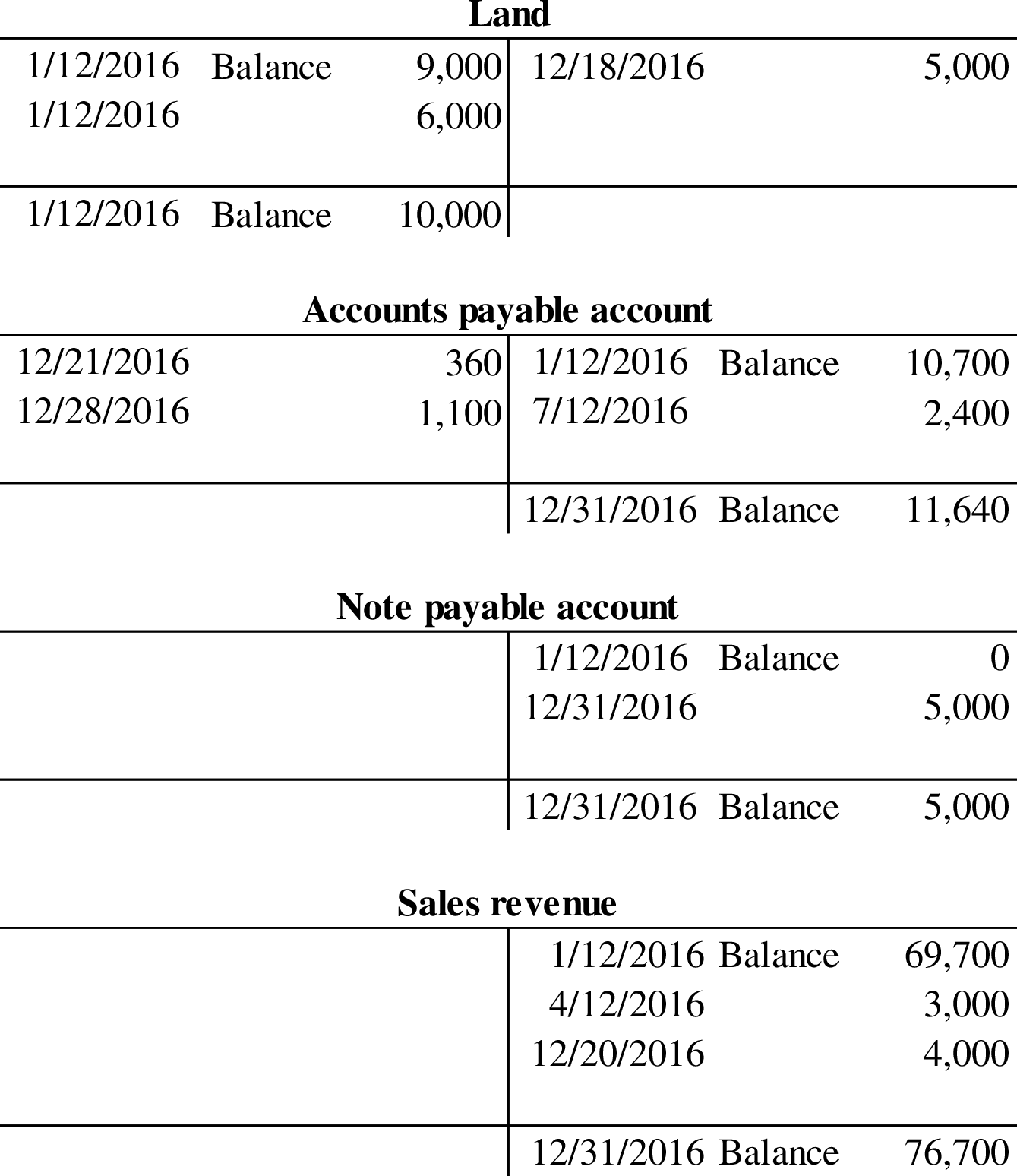
3.
Prepare the worksheet with the given information.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the worksheet with the given information:
Worksheet: A worksheet is a tool that is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form, having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process.
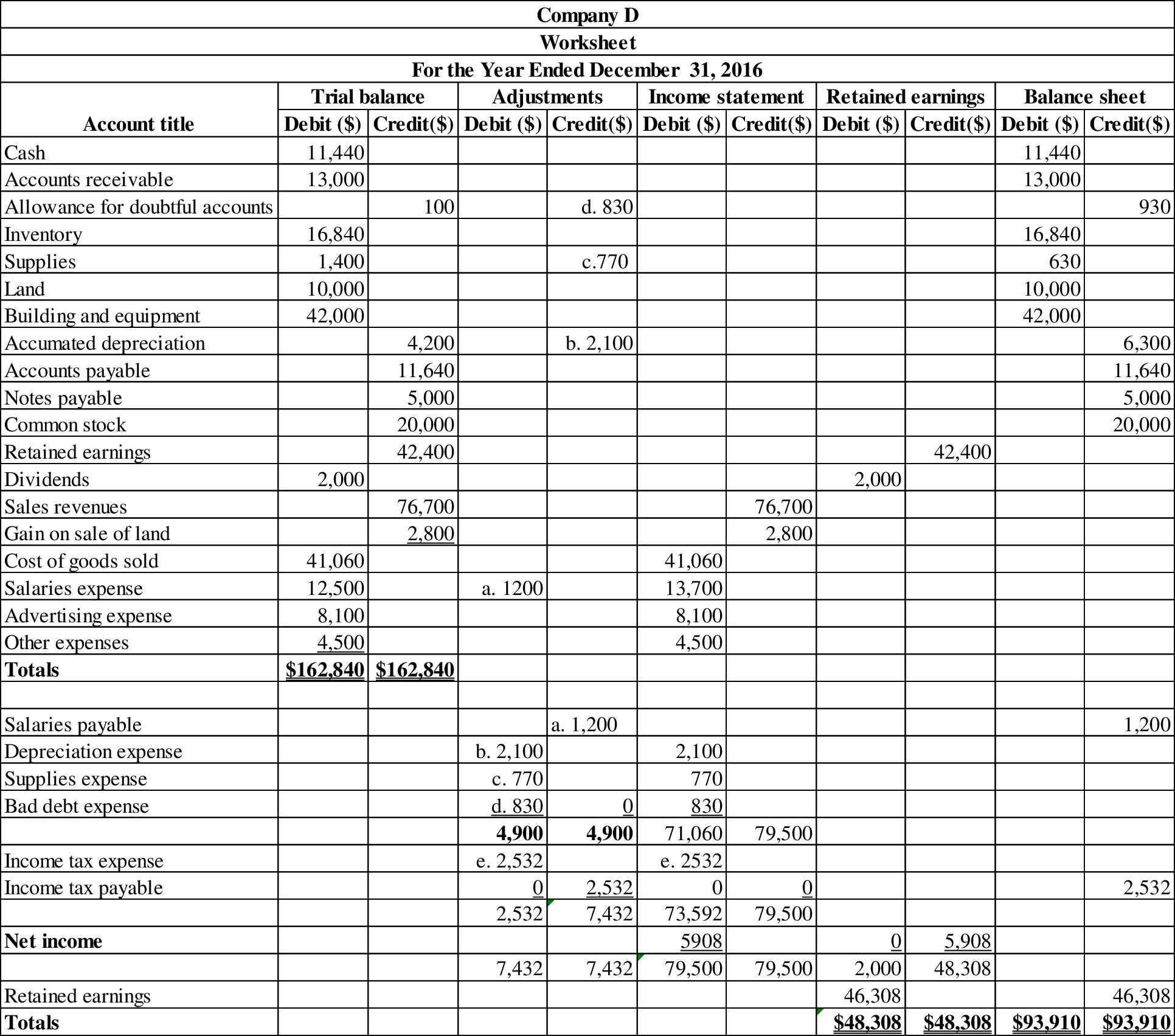
Table (2)
4.
Prepare the financial statements of Company D.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare income statement:
| Company D | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Sales revenue | 76,700 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (41,060) | |
| Gross profit | 35,640 | |
| Less: Operating expenses: | ||
| Salaries expense | 13,700 | |
| Advertising expense | 8,100 | |
| Depreciation expense | 2,100 | |
| Supplies expense | 770 | |
| Bad debt expense | 830 | |
| Other expenses | 4,500 | |
| Total operating expense | (30,000) | |
| Income from operations | 5,640 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Gain on sale of land | 2,800 | |
| Income before income taxes | 8,440 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | (2,532) | |
| Net income | $5,908 | |
| Earnings per share | $2.95 | |
Table (3)
Statement of Retained Earnings: Statement of retained earnings shows, the changes in the retained earnings, and the income left in the company after payment of the dividends, for the accounting period.
Prepare statement of retained earnings:
| D Company | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, January 1, 2016 | 42,400 | |
| Add: Net income | 5,908 | |
| Subtotal | 48,308 | |
| Less: Dividends | (2,000) | |
| Retained earnings at December 31, 2016 | $46,308 | |
Table (4)
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements which summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet:
| Company D | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| At December 31, 2016 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 11,440 | |
| Accounts receivable | 13,000 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubt accounts | (930) | 12,070 |
| Inventory | 16,840 | |
| Supplies | 630 | |
| Total current assets | 40,980 | |
| Property, plant and equipment: | ||
| Land | 10,000 | |
| Building and equipment | 42,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (6,300) | 35,700 |
| Net property, plant and equipment | 45,700 | |
| Total assets | $86,680 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 11,640 | |
| Salaries payable | 1,200 | |
| Income taxes payable | 2,532 | |
| Total liabilities | ||
| Long-term liabilities: | 15,372 | |
| Notes payable due 31/12/18 | 5,000 | |
| Shareholders’ Equity | ||
| Contributed Capital: | ||
| Common stock | 20,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 46,308 | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | 66,308 | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $86,680 | |
Table (5)
5 (a)
Prepare adjusting entries for the year 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are the journal entries which are recorded at the end of the accounting period to correct or adjust the revenue and expense accounts, to concede with the accrual principle of accounting.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Prepare adjusting entries for the year 2016:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| 2016 | Salaries Expense | 1,200 | |
| December 31 | Salaries Payable | 1,200 | |
| (To record the amount of accrued salaries for the period) | |||
| 2016 | Depreciation Expense | 2,100 | |
| December 31 | Accumulated Depreciation - Building and Equipment | 2,100 | |
| (To record the amount of depreciation expense for the period) | |||
| 2016 | Supplies Expense | 770 | |
| December 31 | Supplies | 770 | |
| (To record the amount of supplies used during the period) | |||
| 2016 | Bad debt expense | 830 | |
| December 31 | Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | 830 | |
| (To record the bad debt expense for the period) | |||
| 2016 | Income Tax Expense | 2,532 | |
| December 31 | Income Tax Payable | 2,532 | |
| (To record the income tax liability on earnings |
Table (6)
5 (b)
Prepare the closing entries for December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts such as revenues account, expenses account and dividend account to the retained earnings account. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Prepare the closing entries for December 31, 2016.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Debit | Credit |
| ($) | ($) | ||
| December 31, 2016 | Sales Revenue | 76,700 | |
| Gain on Sale of Land | 2,800 | ||
| Income Summary | 79,500 | ||
| (To close the revenue accounts) | |||
|
December 31, 2016 | Income Summary | 73,592 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 41,060 | ||
| Salaries Expense | 13,700 | ||
| Advertising Expense | 8,100 | ||
| Depreciation Expense | 2,100 | ||
| Supplies Expense | 770 | ||
| Bad Debt Expense | 830 | ||
| Other Expense | 4,500 | ||
| Income Tax Expense | 2,532 | ||
| (To close the expense accounts) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Income Summary | 5,908 | |
| Retained Earnings | 5,908 | ||
| (To close the income summary account) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Retained Earnings | 2,000 | |
| Dividends | 2,000 | ||
| (To close the dividends account) |
Table (7)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Whats a good response and question to this post? Choosing Canada to grow a business and would be a great idea do to the same similarities that the United States has within their politics, legal system, and their economics POLITICS Even though Canada is ruled by a monarchy the legislature and monarchy still work together, making very similar to the US government.The Canadian government also has a constitution that states “system of fundamental laws and principles that outline the nature, functions, and limits of Canada’s system of government, both federal and provincial”.Canada has a reputation of having a very welcoming business platform throughout their politics. Legal System Canada's legal system used both civil and common law based on French and English laws.These ideas were brought to them in the 17th century by the columnist.Canada is one of the only countries that has common law and civil law at the same stature. Throughout Canada everyone from common people to government…arrow_forwardWhat is a good response to this post? The Hofstede Country Comparison tool provides an analytical framework for comprehending cultural subtleties via variables such as power distance, individualism, masculinity, uncertainty avoidance, long-term orientation, and indulgence. The comparison of Russia, China, and the United States unveils unique cultural landscapes. The United States exhibits a low Power Distance score of 40, indicating a social inclination towards equality and dispersed power systems. This starkly contrasts with Russia's score of 93, which signifies a strong acceptance of hierarchical order, and China's score of 80, where power is similarly consolidated, demonstrating a society that prioritizes authority and hierarchy. The United States gets 91 in individualism, highlighting the importance of personal rights and accomplishments. Russia, scoring 39 and China, scoring 20, exhibit a collectivist inclination where group allegiance and communal interests frequently take…arrow_forwardWhats a good response to this post? Comparing USA to Germany and Japan Hofstede's dimensions include Power, Distance, Individualism, Masculinity, Uncertainty Avoidance, Long-Term Orientation and Indulgence. Power: USA 40, Germany 35, Japan 54 The USA and Germany have relatively low scores, indicating a preference for equality and decentralized power structures. Japan's score suggests a more Hierarchical society with greater acceptance of unequal power distribution. IDV: USA 91, Germany 67, Japan 46 The USA scores very very high, reflecting a strong emphasis on individual rights. Germany also values IDV but to a lesser extent while Japan has the lowers store, showing more collectivism, emphasizing group harmony and loyalty. MAS, USA 62, Germany 66, Japan 95 All three have pretty high scores but Japan outranks. Indicating a strong focus on competition, achievement and success. UAI: USA 46, Germany 65, Japan 92 The USA has a low score, suggesting a higher tolerance for ambiguity and…arrow_forward
- Whats a good response and question to ask to this post? The county that I am choosing to expand to is Denmark. Below is a brief overview of their political, economic, and legal systems. Political System Denmark is a Constitutional Monarchy. Their chief of state is the Queen and their head of government is the Prime Minister. The government is broken up into three branches, the executive branch, judicial branch, and legislative branch. Economic System Denmark is a developed country with a high income. Not much is able to sway Denmark. Unlike most countries, when Covid was wreaking havoc all over the world, their economy recessed by only 2% in 2020 and continued on to jump back up by 3.8% by 2022. They also have a very low unemployment rate of only 2.7%. Legal System Denmark operates by a civil law system with roots in Germanic Law. They have a medium corruption score of 88 out of 200. Denmark has a great business perspective overall. The only part that I would question is, how would the…arrow_forwardProblem 3-2B Preparing adjusting and subsequent journal entries P1 P2 P3 P4 Natsu Company's annual accounting period ends on October 31. The following information concerns the adjusting entries that need to be recorded as of that date. Entries can draw from the following partial chart of accounts: Cash; Accounts Receivable; Office Supplies; Prepaid Insurance; Building; Accumulated Depreciation- Building; Salaries Payable; Unearned Revenue; Rent Revenue; Salaries Expense; Office Supplies Expense; Insurance Expense; and Depreciation Expense-Building. a. b. c. d. e. f. The Office Supplies account started the fiscal year with a $600 balance. During the fiscal year, the company purchased supplies for $4,570, which was added to the Office Supplies account. The supplies available at October 31 totaled $800. The Prepaid Insurance account had a $12,000 debit balance at October 31 before adjusting for the costs of any expired coverage for the fiscal year. An analysis of prepaid insurance shows…arrow_forwardProblem 3-1B Identifying adjusting entries with explanations P1 P2 P3 P4 For journal entries 1 through 12, indicate the explanation that most closely describes it. You can use explanations more than once. A. To record payment of a prepaid expense. B. To record this period's use of a prepaid expense. C. To record this period's depreciation expense. D. To record receipt of unearned revenue. E. To record this period's earning of prior unearned revenue. F. To record an accrued expense. G. To record payment of an accrued expense. H. To record an accrued revenue. I. To record receipt of accrued revenue. 1. Interest Receivable 3,500 7. Cash 1,500 Interest Revenue 3,500 Accounts Receivable (from services) 1,500 2. Salaries Payable 9,000 8. Salaries Expense 7,000 Cash 9,000 Salaries Payable 7,000 3. Depreciation Expense 8,000 9. Cash 1,000 Accumulated Depreciation. 8,000 Interest Receivable 1,000 4. Cash 9,000 10. Unearned Revenue 9,000 Prepaid Rent Cash 3,000 3,000 5. Insurance Expense 4,000…arrow_forward
- ???arrow_forward$240 Assume that a company produced 10,000 units and sold 8,000 units during its first year of operations. It has also provided the following information: Particulars Selling price Per unit per year Direct materials $85 Direct labor $57 Variable manufacturing overhead $10 Sales commission $11 Fixed manufacturing overhead P Fixed selling and administrative expense $250,000 If the company's unit product cost under absorption costing is $197, then what is the amount of fixed manufacturing overhead per year?arrow_forwardI need help with accounting questionarrow_forward
 Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





