
Concept explainers
Draw electron-dot structures for the following molecules, indicating any unshared electron pairs. Which of the compounds are likely to act as Lewis acids and which as Lewis bases?
(a) AlBr3
(b) CH3CH2NH2
(c) BH3
(d) HF
(e) CH3SCH3
(f) TiCl4
a) AlBr3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus aluminum has three dots to represent its 3s23p1electrons, bromine has seven dots to represent its 4s24p5 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
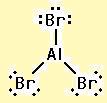
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Aluminum atom has three electrons (3s23p1) in its valence shell. It has used all the three electrons in forming three Al- Br bonds. So it has no lone pair of electrons. The bromine atom has seven electrons in its valence shell (4s24p5). Out of these seven electrons, each bromine has used one electron for forming Al-Br bond and thus has the remaining six electrons as three lone pairs. AlBr3 will act as Lewis acid since the central aluminum atom requires two more electrons to complete its octet.
The electron–dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as

It will act as a Lewis acid.
b) CH3CH2NH2
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron, carbon has four dots to represent its 2s22p2 electrons, and nitrogen has five dots to represent its 2s22p3 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
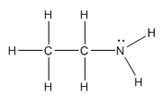
It will act as a Lewis base.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon atom has four electrons (2s22p2) in its valence shell. Both carbons have used all the four electrons in forming four bonds with other atoms. So they do not possess any lone pair of electrons. The nitrogen atom has five electrons in its valence shell (2s22p3). Out of these five electrons, nitrogen has used three electrons for forming one C-N and two N-H bonds and thus has the remaining two electrons as a lone pair. CH3CH2NH2 will act as Lewis base since the nitrogen atom can donate a pair of electrons to other species.
The electron–dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis base.
c) BH3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus boron has three dots to represent its 2s22p1electrons, hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
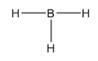
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Boron atom has three electrons (2s22p1) in its valence shell. It has used all the three electrons in forming three B- H bonds. So it has no lone pair of electrons. Each hydrogen atom has one electron in its valence shell (1s1) which they utilize in forming the B-H bonds. BH3 will act as Lewis acid since the central boron atom requires two more electrons to complete its octet.
The electron–dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis acid.
d) HF
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus fluorine has seven dots to represent its 2s22p5 electrons, hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors. To give: The electron dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
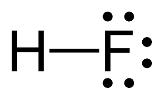
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Fluorine atom is the most electronegative element and hence the H-F bond is highly polarized. The electrons in the bond are more concentrated on F rather than on H. The hydrogen is thus electron deficient and it can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base. Hence HF is likely to behave as Lewis acid.
The electron–dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
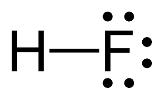
It will act as a Lewis acid.
e) CH3SCH3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron, carbon has four dots to represent its 2s22p2 electrons and sulfur has six dots to represent its 3s23p4 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
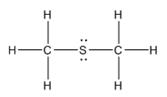
It will act as a Lewis base.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon atom has four electrons (2s22p2) in its valence shell. Both carbons have used all the four electrons in forming four bonds with other atoms. So they do not possess any lone pair of electrons. The sulfur atom has six electrons in its valence shell (3s23p4). Out of these six electrons, sulfur has used two electrons for forming two C-S bonds and thus has the remaining four electrons as two lone pairs. CH3SCH3 will act as Lewis base since the sulfur atom can donate a pair of electrons to other species.
The electron–dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis base.
f) TiCl4
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
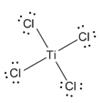
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
The chlorine atom has seven electrons in its valence shell (3s23p5). Out of these seven electrons, each chlorine has used one electron for forming Ti-Cl bond and thus have the remaining six electrons as three lone pairs. Titanium is a transition element. Transition elements utilize the d orbitals in the penultimate shell also along with orbitals of the valence shell during bonding. It has the configuration 3d24s2. It has used all the four electrons in forming four Ti-Cl bonds.
The d orbitals can have a maximum of ten electrons. In TiCl4, the titanium atom has empty d orbitals to accommodate electrons donated by a Lewis base. Hence TiCl4 will act as Lewis acid.
The electron–dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- 13 Consider the "C NMR spectrum below. 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 20 PPM 0 The spectrum belongs to which one of the following constitutional isomers of the compound C,H12? Select the single best answer. Check ✓ G Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe structure of compound 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene) is given below. How many signals would you expect to find in the 'H NMR spectrum of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene)? Check ×arrow_forward1 How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? CI CI Cl Write the answer in the table below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with H atoms shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is highlighted red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: Remember, a multiplet is considered one signal in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. ☐ For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional H atoms to highlight in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at…arrow_forward
- wrtie the balanced equation and find the E° when the following half- reactions are combined Zn2+(aq) + 2e---> Zn(s) E°= -0.763V Ag+(aq) + e---> Ag (s) E°=+0.799Varrow_forwardConsider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal. ☐arrow_forwardStudy this 'H NMR spectrum, and then answer the questions about it in the table below. Check 1.0- 0.5- 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 What unit symbol should be written on the horizontal axis? What is the chemical shift & of the doublet? If there is no doublet, just check the box instead. Give your answer to 2 significant digits. What is the chemical shift of the signal immediately upfield of the doublet? If there is no doublet, or no signal upfield of it, check the box instead. What is the chemical shift & of the least deshielded proton? If you can't tell without more information, check the box instead. 血 8 = ☐ There is no doublet. 8 = ☐ No such signal. 8 = 0 Need more information.arrow_forward
- how many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20arrow_forwardcalculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2arrow_forwardan adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank providearrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





