
a)
The question requires us to draw the
a)
Explanation of Solution
In the market for sandals, S1 shows the supply curve, and D1 represents the
At equilibrium,
Quantity supplied = Quantity demanded = Q1 units.
The following graph represents the market for sandals:
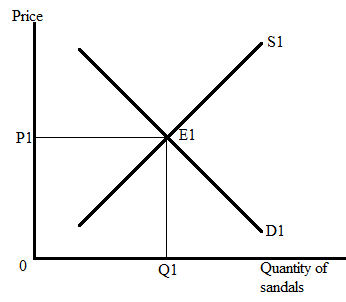
Here, E1 represents the equilibrium point where the supply curve and demand curve intersect each other. The
b)
The question requires us to illustrate the impact of higher income on the equilibrium price and quantity of sandals when sandals are normal goods and label the new equilibrium price and quantity.
b)
Explanation of Solution
The following graph represents the impact of higher income on the equilibrium price and quantity of the sandals:
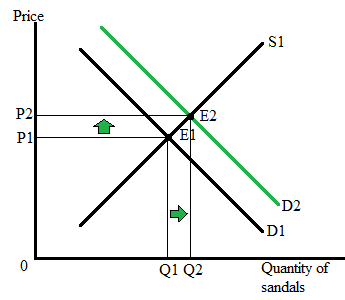
Here, E1 represents the initial equilibrium state in the sandal market, where Q1 is the equilibrium quantity, and P1 is the equilibrium price. Since sandals are normal goods, an increase in the income of consumers will cause the demand for sandals to increase.
A higher demand causes the demand curve to shift rightward from D1 to D2, and results in a higher price (P2) and higher quantity (Q2).
E2 represents the new equilibrium point where P2 is the new market price for the sandals and Q2 represents the new equilibrium quantity of the sandals.
An increase in income level will lead to a higher demand for normal goods.
c)
The question requires us to illustrate the impact of higher income and higher wages on the equilibrium quantity and compare the result with the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
c)
Explanation of Solution
The simultaneous increase in consumers’ income and workers’ wages will increase the price level of sandals, but the impact on equilibrium quantity will depend on the magnitude of change in supply and demand of the sandals so the result will be ambiguous.
Here, three outcomes are possible depending on the magnitude of change in supply and demand:
- When a change in supply is more than the change in demand, the market quantity will fall below the initial equilibrium level (Q3 < Q1
- When a change in supply is less than the change in demand, the market quantity will fall but stay above the initial equilibrium level of quantity (Q1
- When a change in supply is equal to the change in demand, the new market quantity will be equal to the initial equilibrium level of quantity (Q1=Q3
The following graph represents ‘situation 3’ and the combined impact of higher income and higher wages in the market for sandals:
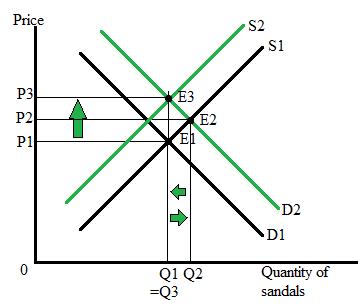
Here, E1 is the initial equilibrium level where P1 is the equilibrium price, and Q1 is the equilibrium quantity. Due to an increase in income level demand for sandals rises from D1 and D2 and causes the price and quantity of sandals to rise. At the same time, an increase in the wage of the sandal-making workers cause the input costs to rise and thus discourages the producer from producing less quantity of the sandals. As a result of higher input costs, the supply of sandals falls and causes the supply curve to shift leftward from S1 to S2.
Finally, the economy reaches new equilibrium point E3 where the market price increases from P1 to P3, and equilibrium quantity falls back to the initial level Q1.
Chapter 2R Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course
- Should Maureen question the family about the history of the home? Can Maureen access public records for proof of repairs?arrow_forward3. Distinguish between a direct democracy and a representative democracy. Use appropriate examples to support your answers. [4] 4. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery [2] 5. A R1000 tax payable by all adults could be viewed as both a proportional tax and a regressive tax. Do you agree? Explain. [4] 6. Briefly explain the displacement effect in Peacock and Wiseman's model of government expenditure growth and provide a relevant example of it in the South African context. [5] 7. Explain how unbalanced productivity growth may affect government expenditure and briefly comment on its relevance to South Africa. [5] 8. South Africa has recently proposed an increase in its value-added tax rate to 15%, sparking much controversy. Why is it argued that value-added tax is inequitable and what can be done to correct the inequity? [5] 9. Briefly explain the difference between access to education and the quality of education, and why we should care about the…arrow_forward20. Factors 01 pro B. the technological innovations available to companies. A. the laws that regulate manufacturers. C. the resources used to create output D. the waste left over after goods are produced. 21. Table 1.1 shows the tradeoff between different combinations of missile production and home construction, ceteris paribus. Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both missiles and houses. Then answer the indicated question(s). Combination Number of houses Opportunity cost of houses in Number of missiles terms of missiles J 0 4 K 10,000 3 L 17,000 2 1 M 21,000 0 N 23,000 Opportunity cost of missiles in terms of houses Tutorials-Principles of Economics m health carearrow_forward
- In a small open economy with a floating exchange rate, the supply of real money balances is fixed and a rise in government spending ______ Group of answer choices Raises the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market Raises the interest rate, so that income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market.arrow_forwardSuppose a country with a fixed exchange rate decides to implement a devaluation of its currency and commits to maintaining the new fixed parity. This implies (A) ______________ in the demand for its goods and a monetary (B) _______________. Group of answer choices (A) expansion ; (B) contraction (A) contraction ; (B) expansion (A) expansion ; (B) expansion (A) contraction ; (B) contractionarrow_forwardAssume a small open country under fixed exchanges rate and full capital mobility. Prices are fixed in the short run and equilibrium is given initially at point A. An exogenous increase in public spending shifts the IS curve to IS'. Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices A new equilibrium is reached at point B. The TR curve will shift down until it passes through point B. A new equilibrium is reached at point C. Point B can only be reached in the absence of capital mobility.arrow_forward
- A decrease in money demand causes the real interest rate to _____ and output to _____ in the short run, before prices adjust to restore equilibrium. Group of answer choices rise; rise fall; fall fall; rise rise; fallarrow_forwardIf a country's policy makers were to continously use expansionary monetary policy in an attempt to hold unemployment below the natural rate , the long urn result would be? Group of answer choices a decrease in the unemployment rate an increase in the level of output All of these an increase in the rate of inflationarrow_forwardA shift in the Aggregate Supply curve to the right will result in a move to a point that is southwest of where the economy is currently at. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forward
- An oil shock can cause stagflation, a period of higher inflation and higher unemployment. When this happens, the economy moves to a point to the northeast of where it currently is. After the economy has moved to the northeast, the Federal Reserve can reduce that inflation without having to worry about causing more unemployment. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forwardThe long-run Phillips Curve is vertical which indicates Group of answer choices that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and the price level. None of these that in the long-run, the economy returns to a 4 percent level of inflation.arrow_forwardSuppose the exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar is £1 = $2.00. The U.S. government implementsU.S. government implements a contractionary fiscal policya contractionary fiscal policy. Illustrate the impact of this change in the market for pounds. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new demand line. 2.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new supply line. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





