
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
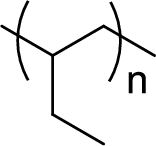
The name of the above polymer is poly(1-butene) because it is formed by the
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
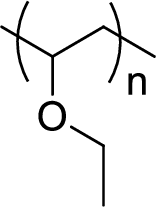
The name of the above polymer is poly(ethyl vinyl ether) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of ethyl vinyl ether.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
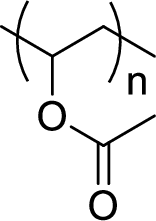
The name of the above polymer is poly(vinyl acetate) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of vinyl acetate.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
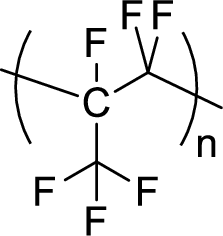
The name of the above polymer is poly(perfluoropropylene) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of perfluoropropylene.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
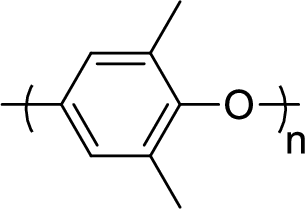
The name of the above polymer is poly(2,6-dimethylphenylene oxide) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of 2,6-dimethylphenol.
(f)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
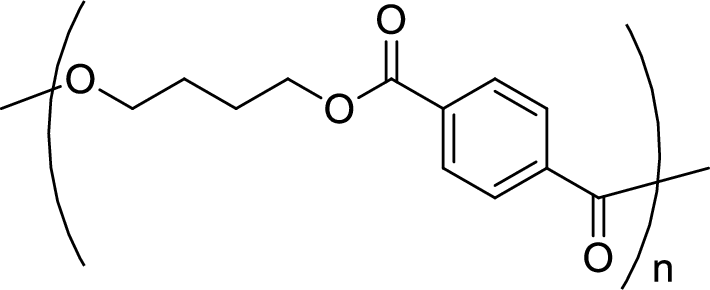
The name of the above polymer is poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of 1,4-butanediol with terephthalic acid.
(g)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
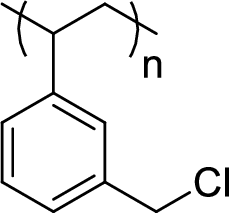
The name of the above polymer is poly(3-chloromethylphenylethylene) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of 3-chloromethylstyrene.
(h)
Interpretation:
For the given polymer structure, name has to be given.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Given polymer structure,
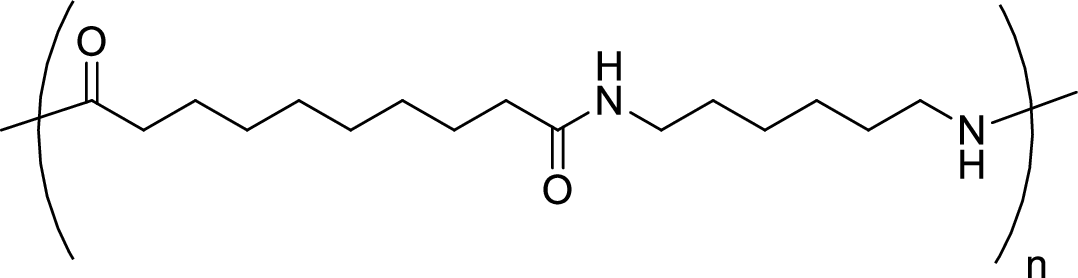
The name of the above polymer is poly(hexamethylene sebacamide) because it is formed by the polymerization reaction of hexamethylenediamine with sebacoyl chloride.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





