
Concept explainers
Draw a phylogenetic tree illustrating our current understanding of plant phylogeny; label the common ancestor of plants and the origins of multicellular gametangia, vascular tissue, and seeds.
To draw: A phylogenetic tree that describes the relationship between the common ancestor of plants and the origins of multicellular gametangia, vascular tissue, and seeds.
Introduction: About 1.2 billion years ago, the microorganisms colonized on the land surface. The microscopic fossils are the shreds of evidence of life on the Earth. These spore fossils are estimated to be 450 million years old. These spores are different from spores of algae and fungi of the present day in terms of their chemical composition. Cooksonia sporangium is one of the biggest fossils of the larger plants that occurred about 435 million years ago. Then a third clade of seed plants occurred that is defined today as the gymnosperm and the angiosperm.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the phylogenetic tree drawn to represent the relationship between different groups of land plants.
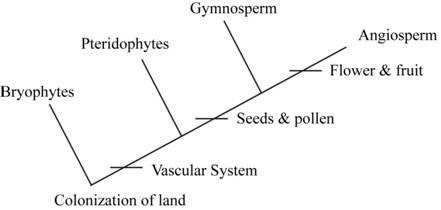
Fig.1 Phylogenetic tree
Fossils show that the origin of plants occurred about various million years ago. Plants then divided into various groups like the Bryophytes (non-vascular plants), which include liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Then about 430 million years ago the origin of seedless vascular plants occurred, which includes lycophytes (spike mosses, and quillworts) and monilophytes (fern, horsetail, and whiskfern). Around 360 million years ago various seed plants originate that including angiosperm as well as the gymnosperm, occurred. The Fig.1 shows the phylogenetic relationship between the four groups of the plant.
There are some characteristics that differentiate these four groups of plants are as follows:
- Bryophytes (mosses): The vascular system is absent, the gametophyte stage is dominant, having spores, and have motile sperm
- Pteridophytes (ferns): Vascular system present, dominant sporophyte system, reproduction through spores, and motile sperm is present.
- Gymnosperm (Pines, Spruce, and Gingko): They also have a vascular system with sporophyte as the dominant stage and the reproduction occurs by either heterospory, cones, pollen, eggs, or seeds.
- Angiosperm (monocot and dicots): The vascular system is present and the sporophyte stage is dominant in sporophytes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Campbell Biology (10th Edition)
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





