
To Label: The muscular artery wall in Fig 29.2.
Introduction: The circulatory system is the vital system in the human body and it is composed of heart, blood vessels, and capillaries. The main function of the circulatory system to provide all the organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and help in the removal of
Answer to Problem 1.2BGL
Pictorial representation:
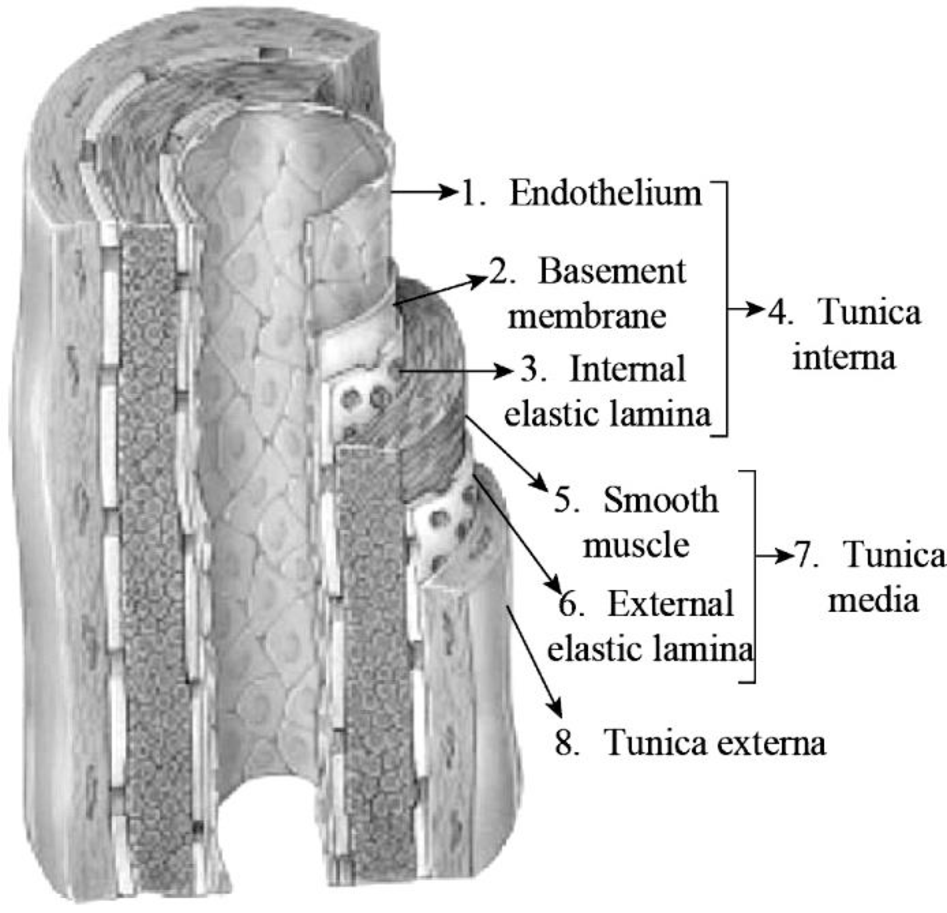
Fig 1: Muscular structure of artery wall
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the muscular arteries is composed of the following:
Tunica interna: The tunica interna or intima is the innermost layer of the arteries which is composed of simple squamous epithelium and inter elastic lamina that provide elasticity to the arteries. The lumen of the arteries is lined up by the endothelium cell that is smooth and helps in smooth blood flow. If there is any damage to the arteries, the endothelium helps the platelets to bind to the walls of the arteries and form plaques to reduce the blood flow, as the arterial blood pressure is high which may cause excessive blood loss.
Tunica media: The tunica media is the middle layer of the arterial wall and it is the thickest of the tunics. The tunica media is composed of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers that regulate the flow of blood by vasodilation and vasoconstriction. The elastic fibers help the artery to retain its original structure after vasodilation and vasoconstriction of the smooth muscle fibers.
Tunica externa: The tunica externa is the outermost layer of the arteries and composed of collagen fibers and elastic fibers. The collagen fibers are the connective tissue which provides the blood vessel with support and protection, while the elastic fibers provide with flexibility and elasticity to constrict, dilate, and to retain its original structure.
Basement membrane: The tunica interna is composed of simple squamous endothelium. The tunica interna is the supported basement membrane which is made up of extracellular matrix that gives structural stability to the endothelium cells of the tunica interna.
External elastic lamina: The external elastic lamina is found between the tunica externa and tunia media. The external elastic lamina is composed of elastic fibers and collagen. The external elastic lamina provides the tunica media with elasticity to vasoconstrict and vasodilate.
Internal elastic lamina: The internal elastic lamina is found between the tunica media and tunia interna. The internal elastic lamina is composed of elastic fibers and collagen. The internal elastic lamina provides the tunica media and tunica interna with elasticity to vasoconstrict and vasodilate.
Smooth muscle: The smooth muscle is present in the tunica media of the arteries, which is the thickest of the three layers of the tunics. The smooth muscle helps in the vasocontrict and vasodilate of the arteries to maintain blood flow.
Endothelium: The endothelium is present in the tunica interna of the arteries, which is composed of simple squamous epithelial cells. The lumen of the arteries is lined up by the endothelium cell that is smooth and helps in smooth blood flow.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion with WileyPLUS Blackboard Card Set
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





