
Concept explainers
Identify the following bases, and tell whether each is found in DNA, RNA, or both:
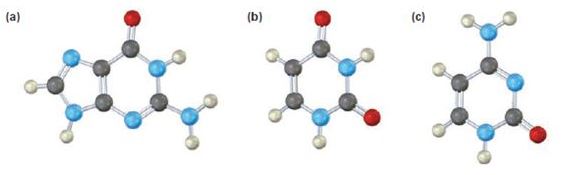
a)
Interpretation:
To identify the following bases and state whether each lie in DNA, RNA or both.
Concept introduction:
Proteins and biopolymers are made up of amino acids, nucleic acids which are joined together to form a long chain. Nucleic acids are the biopolymers of nucleotides, which is composed of a nucleoside. Each nucleoside is bonded to a phosphate group.
Each nucleoside is composed of an aldopentose sugar linked through its anomeric carbon to the nitrogen atom of a heterocyclic purine or pyrimidine base. RNA contains ribose as a sugar component and DNA contains 29-deoxyribose as a sugar component.
DNA contains four different amine bases: two substituted purines (adenine and guanine) and two substituted pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Adenine, guanine, and cytosine also occur in RNA, but thymine is replaced in RNA by a closely related pyrimidine base called uracil.
Answer to Problem 13VC
The base given here is: Guanine (G)
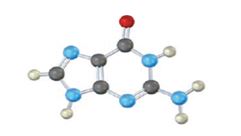
It is found in both DNA and RNA.
Explanation of Solution
In the above diagrams of bases, guanine and cytosine are found in DNA and RNA. Whereas, uracil is found in only RNA. Here the blue atoms are the symbols for nitrogen, red atom represents oxygen, black atom represents carbon and grey atom represnts hydrogen.
The base given here is: Guanine (G)

It is found in both DNA and RNA.
b)
Interpretation:
To identify the following bases and state whether each lie in DNA, RNA or both.
Concept introduction:
Proteins and biopolymers are made up of amino acids, nucleic acids which are joined together to form a long chain. Nucleic acids are the biopolymers of nucleotides, which is composed of a nucleoside. Each nucleoside is bonded to a phosphate group.
Each nucleoside is composed of an aldopentose sugar linked through its anomeric carbon to the nitrogen atom of a heterocyclic purine or pyrimidine base. RNA contains ribose as a sugar component and DNA contains 29-deoxyribose as a sugar component.
DNA contains four different amine bases: two substituted purines (adenine and guanine) and two substituted pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Adenine, guanine, and cytosine also occur in RNA, but thymine is replaced in RNA by a closely related pyrimidine base called uracil.
Answer to Problem 13VC
The base given here is: Uracil (U)
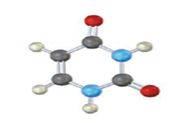
It is found in RNA.
Explanation of Solution
In the above diagrams of bases, guanine and cytosine are found in DNA and RNA. Whereas, uracil is found in only RNA. Here the blue atoms are the symbols for nitrogen, red atom represents oxygen, black atom represents carbon and grey atom represnts hydrogen.
The base given here is: Uracil (U)

It is found in RNA.
c)
Interpretation:
To identify the following bases and state whether each lie in DNA, RNA or both.
Concept introduction:
Proteins and biopolymers are made up of amino acids, nucleic acids which are joined together to form a long chain. Nucleic acids are the biopolymers of nucleotides, which is composed of a nucleoside. Each nucleoside is bonded to a phosphate group.
Each nucleoside is composed of an aldopentose sugar linked through its anomeric carbon to the nitrogen atom of a heterocyclic purine or pyrimidine base. RNA contains ribose as a sugar component and DNA contains 29-deoxyribose as a sugar component.
DNA contains four different amine bases: two substituted purines (adenine and guanine) and two substituted pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Adenine, guanine, and cytosine also occur in RNA, but thymine is replaced in RNA by a closely related pyrimidine base called uracil.
Answer to Problem 13VC
The base given here is: Cytosine (C)
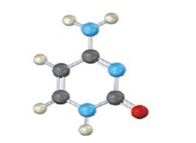
It is found in both DNA and RNA.
Explanation of Solution
In the above diagrams of bases, guanine and cytosine are found in DNA and RNA. Whereas, uracil is found in only RNA. Here the blue atoms are the symbols for nitrogen, red atom represents oxygen, black atom represents carbon and grey atom represnts hydrogen.
The base given here is: Cytosine (C)

It is found in both DNA and RNA.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/OWL
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- H I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forward
- Poly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forward
- Provide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forwardIdentify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





