
Concept explainers
(a).
To find: The real values of
The real value of
Given information:
Consider the given function.
Calculation:
When the given function
And
Thus, the real values of
(b).
To find: The real values of
The real values of
Given information:
Consider the given function.
Calculation:
When the given function
Therefore, the real values of
(c).
To find: The real values of
The real values of
Given information:
Consider the given function.
Calculation:
The given function
First find the boundary points of the function
Substitute the numerator and the denominator equal to zero, then calculate the values of
And
So, the boundary points of the function
Now, locate these boundary points on the number line (or sign chart) and dividing the number line into intervals and check the function
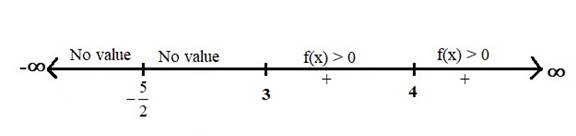
Therefore, the given function
Hence, the real values of
(d).
To find: The real values of
No real values of
Given information:
Consider the given function.
Calculation:
The given function
First find the boundary points of the function
Substitute the numerator and the denominator equal to zero, then calculate the values of
And
So, the boundary points of the function
Now, locate these boundary points on the number line (or sign chart) and dividing the number line into intervals and check the function
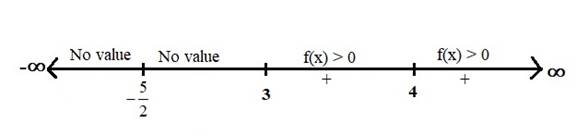
Therefore, no value of
Hence, there is no real values of
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRECALCULUS:GRAPH...-NASTA ED.(FLORIDA)
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward9. a) Determie values of a and b so that the function is continuous. ax - 2b f(x) 2 x≤-2 -2x+a, x ≥2 \-ax² - bx + 1, −2 < x < 2) 9b) Consider f(x): = 2x²+x-3 x-b and determine all the values of b such that f(x) does not have a vertical asymptote. Show work.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- 3. True False. If false create functions that prove it is false. Note: f(x) = g(x). a) If_lim ƒ(x) = ∞ and_lim g(x) = ∞,then_lim [ƒ(x) − g(x)] = 0 x→ 0+ x→0+ x→0+ b) If h(x) and g(x) are continuous at x = c, and if h(c) > 0 and g(c) = 0, then h(x) lim. will = x→c g(x) c) If lim f(x) = 0 and lim g(x) = 0 then lim f(x) does not exist. x-a x-a x→a g(x)arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward15. a) Consider f(x) = x-1 3x+2 and use the difference quotient to determine the simplified expression in terms of x, for the slope of any tangent to y = f(x). Also, determine the slope at x = 2. 15 b) Determine the equation of the tangent to f(x) at x = 2. Final answer in Standard Form Ax + By + C = 0, A ≥ 0, with no fractions or decimals.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





