
In Figure P28.28, the cube is 40.0 cm on each edge. Four straight segments of wire—ab, bc, cd, and da—form a closed loop that carries a current I = 5.00 A in the direction shown. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.020 0 T is in the positive y direction. Determine the magnetic force vector on (a) ab, (b) bc, (c) cd, and (d) da. (c) Explain how you could find the force exerted on the fourth of these segments from the forces on the other three, without further calculation involving the magnetic field.
Figure P28.28
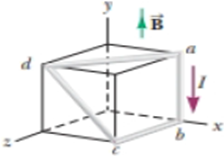
(a)
Answer to Problem 28P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
As the current flows down and the magnetic from point
Substitute
The magnitude of the force is zero because an equal and opposite force cancels it due to which the magnetic force of
Conclusion:
Therefore, magnetic force vector on
(b)
Answer to Problem 28P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
As the current flows down and the magnetic from point
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the x axis direction. Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is in
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(c)
Answer to Problem 28P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
Use Pythagoras theorem to find
Substitute
As the current flows at an angle and the magnetic from point b is perpendicular so the angle
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the z axis direction. Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is in z direction.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(d)
Answer to Problem 28P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
Use Pythagoras theorem to find
Substitute
As the current flows vertically and the magnetic from point b is perpendicular so the angle
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the direction d
The direction of the force is,
Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(e)
Answer to Problem 28P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
By the parallelogram law of forces, when the forces on three of the arms of a parallelogram are provided then the magnitude of force on the forth arm is equal to the resultant of the other three forces.
According to the parallelogram law of vectors,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted on the forth segment from the forces on the other three can be calculated by the parallelogram law of vectors.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Single-Term
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





