
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
In conjugated triene,
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
In
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
The electron configuration of carbon atom is
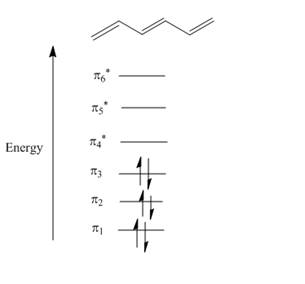
Figure 1
The atomic p orbital of carbon atom overlapped together to form molecular orbital. A total of six molecular orbitals are formed due to six carbon atomic orbital overlapping in
(b)
Interpretation:
Each molecular orbital is to be classified as symmetric and antisymmetric.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbitals
Explanation of Solution
In molecular orbital theory, the MO is said to be symmetric or anti-symmetric is depend on the relative phase of the two terminal carbons. In symmetric MO, the peaks reflect across the reference plane into the peaks and troughs reflect into troughs. On the other hand, in antisymmetric MO, the peaks reflect into troughs and vice versa. According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric. Therefore, the molecular orbitals
The odd number of molecular orbitals is symmetric molecular orbitals that are
(c)
Interpretation:
Bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals are to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbital
Explanation of Solution
In
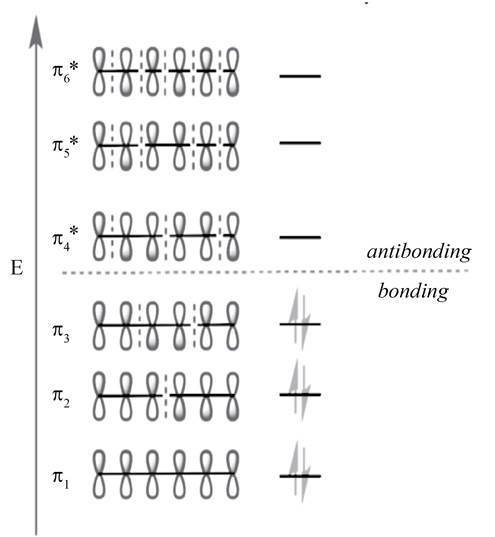
Figure 2
The molecular orbital with lower energy are bonding MO
(d)
Interpretation:
Among the molecular orbitals, the frontier molecular orbital is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbital
Explanation of Solution
The highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) is known as frontier molecular orbitals. In
The molecular orbital
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the phase at terminal carbons in HOMO orbitals is the same or different is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The HOMO orbital that is
Explanation of Solution
According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric or its phase terminal carbons are different and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric or its phase terminal carbons are same. The HOMO orbital is
The HOMO orbital is
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the phase at terminal carbons in LUMO orbitals is the same or different is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The LUMO orbital that is
Explanation of Solution
According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric or its phase terminal carbons are different and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric or its phase terminal carbons are same. The LUMO orbital is
The LUMO orbital is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE AND S
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

