
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth
Concept introduction: The simpler units which combine to form
Answer to Problem 24P
The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is,
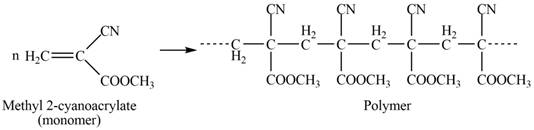
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
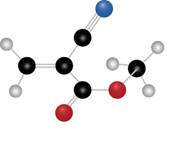
Figure 1
The blue coloured ball has three bonds. So, this is the nitrogen atom. The red coloured ball has two bonds. So, this is the oxygen atom. The black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the compound is,
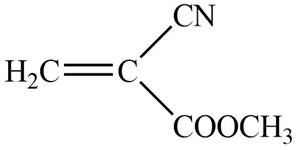
Figure 2
Chain-growth polymerization is formed by the repetitive addition of monomer units containing double or triple bonds. If the monomer units undergoing addition are the same, the polymer is known as
The polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is shown below.
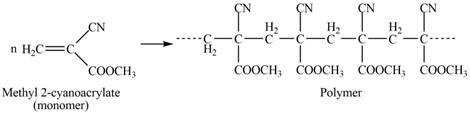
Figure 3
The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is shown in Figure 3.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The simpler units which combine to form polymers are known as monomers. The process by which respective monomers combine to form polymers is known as polymerization.
Answer to Problem 24P
The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is,
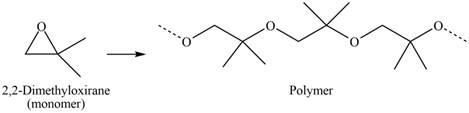
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
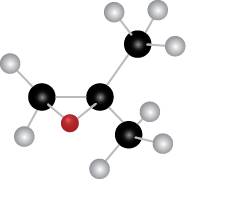
Figure 4
The red coloured ball has two bonds. So, this is the oxygen atom. The black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the compound is,
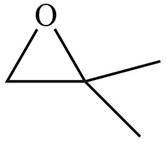
Figure 5
Chain-growth polymerization is formed by the repetitive addition of monomer units containing double or triple bonds. If the monomer units undergoing addition are the same, the polymer is known as homopolymer.
The polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is shown below.
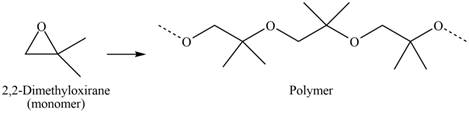
Figure 6
The structure of the polymer formed by chain-growth polymerization of given monomer is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/BIOLOGICAL TOPICS
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





