
Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the currents
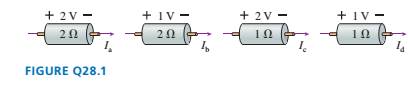
The rank in order of currents from largest to smallest
Answer to Problem 1CQ
Solution:
The rank in order of currents from largest to smallest is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info:
Voltage =
Resistance=
Current =
Voltage =
Resistance=
Current =
Voltage =
Resistance=
Current =
Voltage =
Resistance=
Current =
Formula:
Ohm’s law =>
Applying eqn(1) to all the sets, we get
Calculation:
Substituting the given data in eqn(2)
⇒
Substituting the given data in eqn(3)
⇒
Substituting the given data in eqn(4)
⇒
Substituting the given data in eqn(5)
⇒
On comparing the above values, we get the required relation is
Conclusion:
The rank in order of currents from largest to smallest is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- Please help me with this physics problemarrow_forwardIn a scene from The Avengers (the first one) Black Widow is boosted directly upwards by Captain America, where she then grabs on to a Chitauri speeder that is 15.0 feet above her and hangs on. She is in the air for 1.04 s. A) With what initial velocity was Black Widow launched? 1 m = 3.28 ft B) What was Black Widow’s velocity just before she grabbed the speeder? Assume upwards is the positive direction.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





