
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
17th Edition
ISBN: 9780137319497
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 9CQ
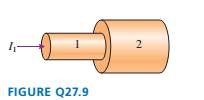
The wire in FIGURE Q27.9 consists of
two segments of different diameters
but made from the same metal. The
current in segment I is Il.
a. Compare the currents in the two
segments. That is, is I2 greater than, less than, or equal to Il ?
Explain.
b. Compare the current densities Jl and in the two segments.
c. Compare the electric field strengths El and E2 in the two
segments.
d. Compare the drift speeds (Vd)l and (Vd)2 in the two segments.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Cam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust.
The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a
rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide
through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the
motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and
move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 27 Solutions
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
Ch. 27 - Prob. 1CQCh. 27 - Prob. 2CQCh. 27 - The electron drift speed in a wire is exceedingly...Ch. 27 - Prob. 4CQCh. 27 - Prob. 5CQCh. 27 - All the wires in FIGURE Q27.6 are made of the same...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in FIGURE Q27.7 are ideal and...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in FIGURE Q27.8 are ideal and...Ch. 27 - The wire in FIGURE Q27.9 consists of two segments...Ch. 27 - Prob. 10CQ
Ch. 27 - ll. The wires in FIGURE Q27.11 are all made of the...Ch. 27 - Which, if any, of these statements are true? (More...Ch. 27 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 27 - .0 × 1016 electrons flow through a cross section...Ch. 27 - Prob. 4EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 6EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 10EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 27 - The current in an electric hair dryer is 10.0 A....Ch. 27 -
13. When a nerve cell fires, charge is...Ch. 27 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 20EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 27 - 24. The two segments of the wire in FIGURE EX27.24...Ch. 27 - A 1.5 V battery provides 0.50 A of current. a. At...Ch. 27 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 41EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 27 - Variations in the resistivity of blood can give...Ch. 27 - The conducting path between the right hand and the...Ch. 27 - The conductive tissues of the upper leg can be...Ch. 27 - The resistivity of a metal increases slightly with...Ch. 27 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 27 - You need to design a 1.0 A fuse that “blows” if...Ch. 27 - I A hollow metal cylinder has inner radius a....Ch. 27 - A hollow metal sphere has inner radius a, outer...Ch. 27 - The total amount of charge in coulombs that has...Ch. 27 - The total amount of charge that has entered a wire...Ch. 27 - The current in a wire at time t is given by the...Ch. 27 - The current supplied by a battery slowly decreases...Ch. 27 - The two wires in FIGURE P27.62 are made of the...Ch. 27 - What diameter should the nichrome wire in FIGURE...Ch. 27 - An aluminum wire consists of the three segments...Ch. 27 - A wire of radius R has a current density that...Ch. 27 - A 0.60 -mm-diameter wire made from an alloy (a...Ch. 27 - A 20 -cm-long hollow nichrome tube of inner...Ch. 27 - Prob. 68EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 74EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 76EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
- I tried to solve this question, and I had an "expert" answer it and they got it wrong. I cannot answer this questionarrow_forwardEddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forwardsolve for (_) Narrow_forward
- Two boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forwardAll correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forwardThree long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forward
- Number There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 2.38 μC. Two are positive and two are negative. The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.132-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge. ips que Mi Units estic re harrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forwardThank you in advance, image with question is attached below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Circuits, Voltage, Resistance, Current - Physics 101 / AP Physics Review with Dianna Cowern; Author: Physics Girl;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8X2gcPVwO0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY