
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780135245033
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 8CQ
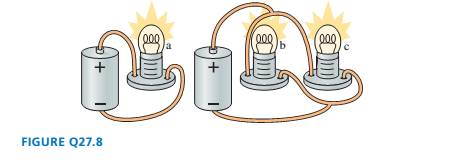
Both batteries in FIGURE Q27.8 are ideal and identical, and all
lightbulbs are the same. Rank in order, from brightest to least
bright, the brightness of bulbs a to c. Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
The kinetic energy of a pendulum is greatest
Question 20Select one:
a.
at the top of its swing.
b.
when its potential energy is greatest.
c.
at the bottom of its swing.
d.
when its total energy is greatest.
Part a-D pl
Chapter 27 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Ch. 27 - Prob. 1CQCh. 27 - Prob. 2CQCh. 27 - The electron drift speed in a wire is exceedingly...Ch. 27 - Prob. 4CQCh. 27 - Prob. 5CQCh. 27 - All the wires in FIGURE Q27.6 are made of the same...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in FIGURE Q27.7 are ideal and...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in FIGURE Q27.8 are ideal and...Ch. 27 - The wire in FIGURE Q27.9 consists of two segments...Ch. 27 - Prob. 10CQ
Ch. 27 - ll. The wires in FIGURE Q27.11 are all made of the...Ch. 27 - Which, if any, of these statements are true? (More...Ch. 27 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 27 - .0 × 1016 electrons flow through a cross section...Ch. 27 - Prob. 4EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 6EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 10EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 27 - The current in an electric hair dryer is 10.0 A....Ch. 27 -
13. When a nerve cell fires, charge is...Ch. 27 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 20EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 27 - 24. The two segments of the wire in FIGURE EX27.24...Ch. 27 - A 1.5 V battery provides 0.50 A of current. a. At...Ch. 27 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 41EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 27 - Variations in the resistivity of blood can give...Ch. 27 - The conducting path between the right hand and the...Ch. 27 - The conductive tissues of the upper leg can be...Ch. 27 - The resistivity of a metal increases slightly with...Ch. 27 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 27 - You need to design a 1.0 A fuse that “blows” if...Ch. 27 - I A hollow metal cylinder has inner radius a....Ch. 27 - A hollow metal sphere has inner radius a, outer...Ch. 27 - The total amount of charge in coulombs that has...Ch. 27 - The total amount of charge that has entered a wire...Ch. 27 - The current in a wire at time t is given by the...Ch. 27 - The current supplied by a battery slowly decreases...Ch. 27 - The two wires in FIGURE P27.62 are made of the...Ch. 27 - What diameter should the nichrome wire in FIGURE...Ch. 27 - An aluminum wire consists of the three segments...Ch. 27 - A wire of radius R has a current density that...Ch. 27 - A 0.60 -mm-diameter wire made from an alloy (a...Ch. 27 - A 20 -cm-long hollow nichrome tube of inner...Ch. 27 - Prob. 68EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 74EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 27 - Prob. 76EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure (Figure 1) shows representations of six thermodynamic states of the same ideal gas sample. Figure 1 of 1 Part A ■Review | Constants Rank the states on the basis of the pressure of the gas sample at each state. Rank pressure from highest to lowest. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) highest 0 ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ Reset Help B F A D E The correct ranking cannot be determined. Submit Previous Answers × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Provide Feedback lowest Next >arrow_forwardPart A m 2πkT ) 3/2 Calculate the integral (v) = f vƒ (v)dv. The function f(v) describing the actual distribution of molecular speeds is called the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, = ƒ(v) = 4π (· v²e-mv²/2kT . (Hint: Make the change of variable v² =x and use the tabulated integral foxne integer and a is a positive constant.) Express your answer in terms of the variables T, m, and appropriate constants. -ax dx n! - an+1 where n is a positive (v) = ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Al Study Tools Looking for some guidance? Let's work through a few related practice questions before you go back to the real thing. This won't impact your score, so stop at anytime and ask for clarification whenever you need it. Ready to give it a try? Startarrow_forwardStarter the rule of significantarrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardCar A starts from rest at t = 0 and travels along a straight road with a constant acceleration of 6 ft/s^2 until it reaches a speed of 60ft/s. Afterwards it maintains the speed. Also, when t = 0, car B located 6000 ft down the road is traveling towards A at a constant speed of 80 ft/s. Determine the distance traveled by Car A when they pass each other.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardIn the given circuit the charge on the plates of 1 μF capacitor, when 100 V battery is connected to the terminals A and B, will be 2 μF A 1 µF B 3 µFarrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed. NOT AI PLSarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
How To Solve Any Resistors In Series and Parallel Combination Circuit Problems in Physics; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eFlJy0cPbsY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY