
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The given reaction is to be classified as an electrocyclic reaction, cycloaddition, or a sigmatropic rearrangement. The sigma bonds that are broken or formed in the given reaction are to be labeled.
Concept introduction: A
Answer to Problem 27.1P
The reaction is classified as an electrocyclic reaction. The sigma bond broken or formed in the given reaction is,
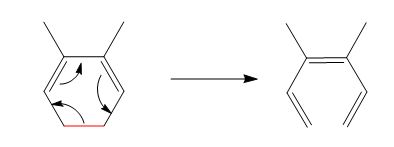
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The sigma bond that is broken during the conversion of reactant into product is shown in red. The new bonds formed during the conversion are shown by curved arrows in the reactant. In the product, the ring is opened due to the rearrangement of
The reaction is classified as an electrocyclic reaction. The sigma bond that is broken or formed in the given reaction is labeled in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The given reaction is to be classified as an electrocyclic reaction, cycloaddition, or a sigmatropic rearrangement. The sigma bonds that are broken or formed in the given reaction are to be labeled.
Concept introduction: A chemical reaction that involves
Answer to Problem 27.1P
The reaction is classified as a cycloaddition reaction. The sigma bonds broken or formed in the given reaction are,
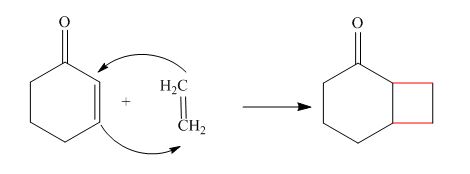
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 2
The sigma bonds that are formed during the conversion of reactant into a product are shown in red. In the reaction,
The reaction is classified as a cycloaddition reaction. The sigma bonds broken or formed in the given reaction are labeled in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The given reaction is to be classified as an electrocyclic reaction, cycloaddition, or a sigmatropic rearrangement. The sigma bonds that are broken or formed in the given reaction are to be labeled.
Concept introduction: A chemical reaction that involves
Answer to Problem 27.1P
The reaction is classified as an electrocyclic reaction. The sigma bond broken or formed in the given reaction is,
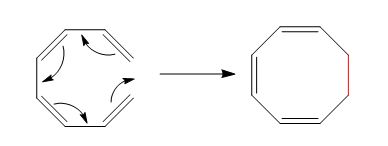
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
The sigma bond that is formed during the conversion of reactant into product is shown in red. The new bonds formed during the conversion are shown by curved arrows in the reactant. In the product, the ring gets closed due to the rearrangement of
The reaction is classified as an electrocyclic reaction. The sigma bond broken or formed in the given reaction is labeled in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The given reaction is to be classified as an electrocyclic reaction, cycloaddition, or a sigmatropic rearrangement. The sigma bonds that are broken or formed in the given reaction are to be labeled.
Concept introduction: A chemical reaction that involves
Answer to Problem 27.1P
The reaction is classified as a sigmatropic reaction. The sigma bonds broken or formed in the given reaction are,
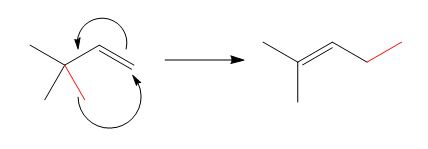
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
The sigma bond that is broken and formed during the conversion of reactant into product is shown in red. The product indicates that
The reaction is classified as a sigmatropic reaction. The sigma bonds broken or formed in the given reaction are labeled in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- b. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





