
Concept explainers
- (a) Purchased raw materials on account, $44,000.
- (b) Issued direct materials to production:

- (c) Issued indirect materials to production, $5,000.
- (d) Incurred direct labor costs:

- (e) Charged indirect labor to production, $3,300.
- (f) Paid electricity, heating oil, and repair bills for the factory and charged to production, $5,200.
- (g) Applied factory overhead to each of the jobs using a predetermined factory overhead rate as follows:

- (h) Finished Job Nos. 501-504 and transferred to the finished goods inventory account as products W, X, Y, and Z, respectively.
- (i) Sold products W, X, Y, and Z for $17,500, $18,000, $16,900, and $19,000, respectively.
REQUIRED
- 1. Prepare general
journal entries to record transactions (a) through (i). Make compound entries for (b), (d), and (g), with separate debits for each job. - 2.
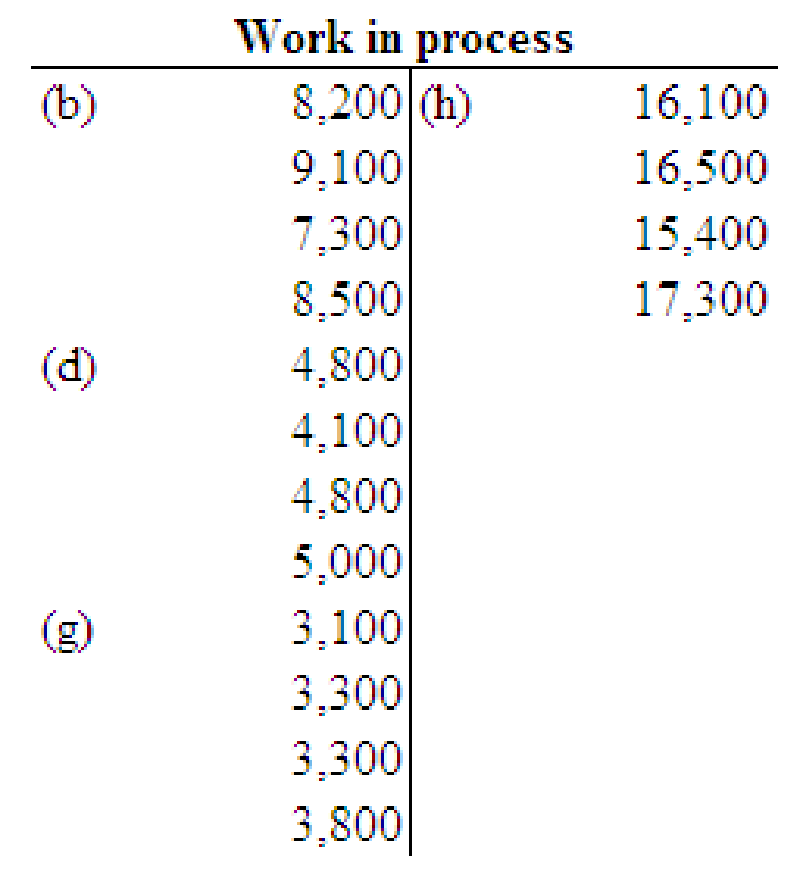
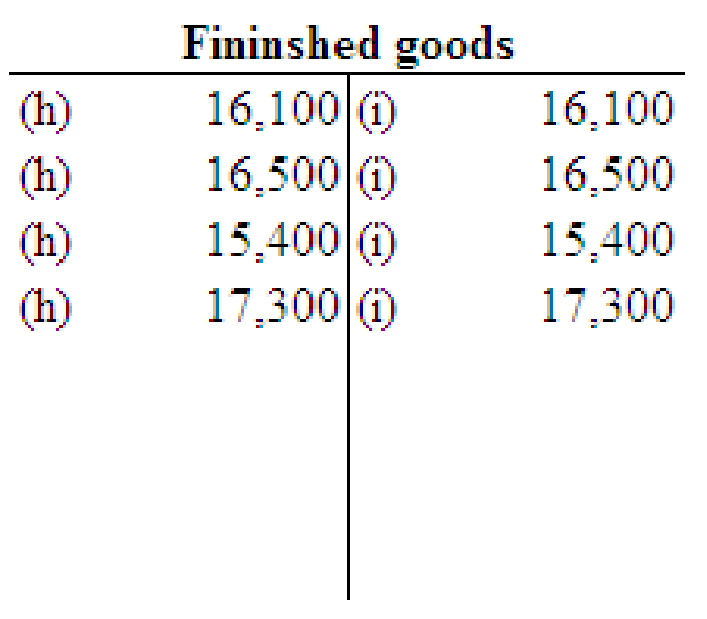
Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts only.
1.
Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (i) and make compound entries for (b), (d), and (g), with separate debits for each job.
Explanation of Solution
Job order costing:
Job order costing is one of the methods of cost accounting under which cost is collected and gathered for each job, work order, or project separately. It is a system by which a factory maintains a separate record of each particular quantity of product that passes through the factory. Job order costing is used when the products produced are significantly different from each other.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Material | 44,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 44,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of materials on account.) | |||
| b. | Work in process | 8,200 | |
| Work in process | 9,100 | ||
| Work in process | 7,300 | ||
| Work in process | 8,500 | ||
| Materials | 33,100 | ||
| (To record direct materials incurred for the job: job no.501, 502,503,504) | |||
| c. | Factory overhead | 5,000 | |
| Materials | 5,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of indirect materials) | |||
| d. | Work in process | 4,800 | |
| Work in process | 4,100 | ||
| Work in process | 4,800 | ||
| Work in process | 5,000 | ||
| Wages payable | 18,700 | ||
| (To record direct labor incurred for the job: job no.501, 502,503,504) | |||
| e. | Factory overhead | 3,300 | |
| Wages payable | 3,300 | ||
| (To record the indirect labor charged to production) | |||
| f. | Factory overhead | 5,200 | |
| Cash | 5,200 | ||
| (To record the payment of electricity bill, heating oil, and repairs bills for the factory and charge made to production) | |||
| g. | Work in process | 3,100 | |
| Work in process | 3,300 | ||
| Work in process | 3,300 | ||
| Work in process | 3,800 | ||
| Factory overhead | 13,500 | ||
| (To record applied factory overhead to the job: job no.501,502,503,504) | |||
| h. | Finished goods (Product W) | 16,100 | |
| Work in process | 16,100 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no. 501 to Product W) | |||
| Finished goods (Product X) | 16,500 | ||
| Work in process | 16,500 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.502 to Product X) | |||
| Finished goods (Product Y) | 15,400 | ||
| Work in process | 15,400 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.503 to Product Y) | |||
| Finished goods (Product Z) | 17,300 | ||
| Work in process | 17,300 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.504 to Product Z) | |||
| i. | Accounts receivable | 17,500 | |
| Sales | 17,500 | ||
| (To record sale of product W) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 16,100 | ||
| Finished goods (Product W) | 16,100 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product W) | |||
| Accounts receivable | 18,000 | ||
| Sales | 18,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product X) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 16,500 | ||
| Finished goods (Product X) | 16,500 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product X) | |||
| Accounts receivable | 16,900 | ||
| Sales | 16,900 | ||
| (To record sale of product Y) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 15,400 | ||
| Finished goods (Product Y) | 15,400 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product Y) | |||
| Accounts receivable | 19,000 | ||
| Sales | 19,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product Z) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 17,300 | ||
| Finished goods (Product Z) | 17,300 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product Z) |
(Table 1)
2.
Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapter 1-15 (Looseleaf) - With Access
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





