
Concept explainers
Classifying discontinuities The discontinuities in graphs (a) and (b) are removable discontinuities because they disappear if we define or redefine f at a so that
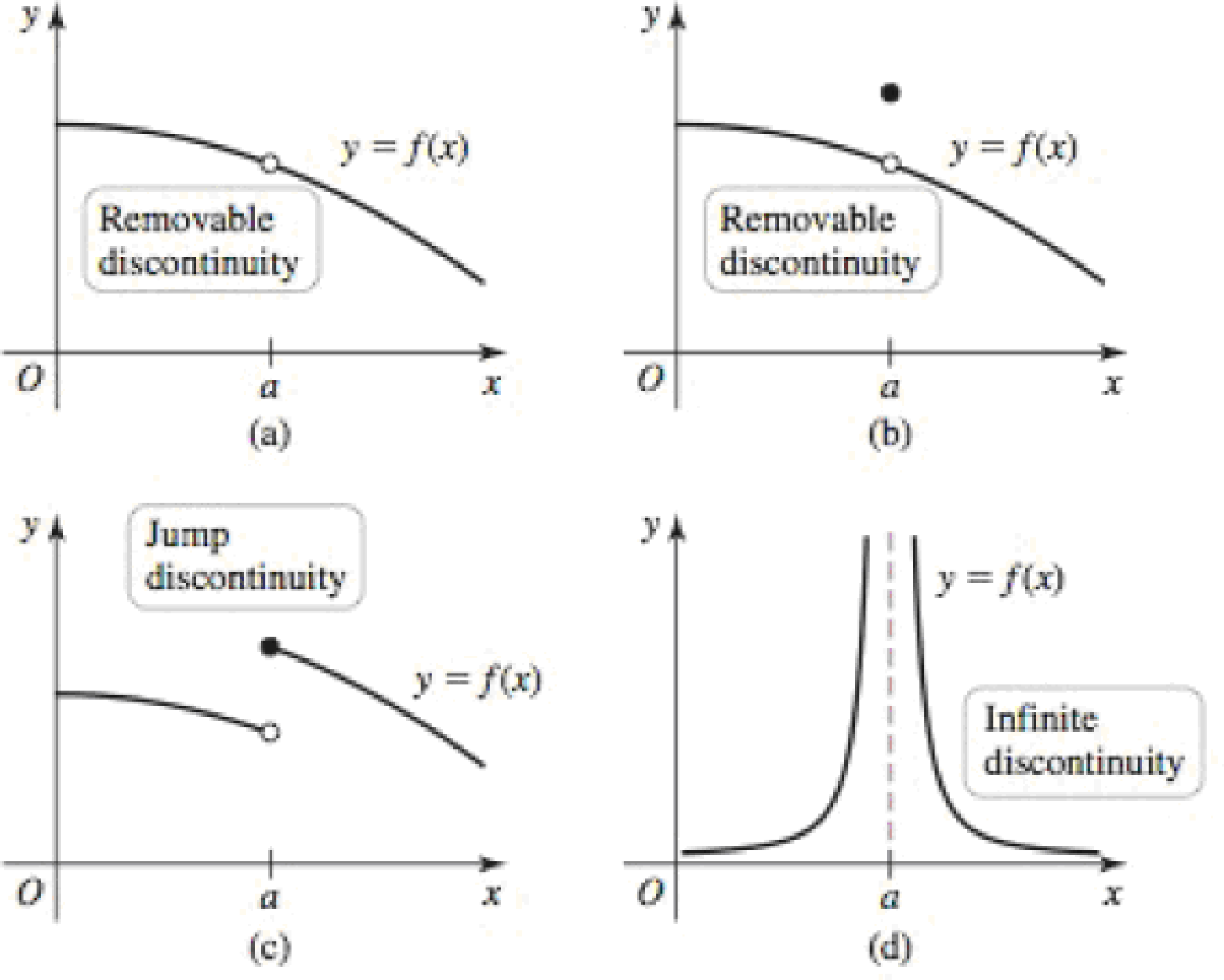 96. Is the discontinuity at a in graph (d) removable? Explain.
96. Is the discontinuity at a in graph (d) removable? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals and MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Title-Specific Access Card Package (3rd Edition) (Briggs, Cochran, Gillett & Schulz, Calculus Series)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- Find the point at which the line (t) = (4, -5,-4)+t(-2, -1,5) intersects the xy plane.arrow_forwardFind the distance from the point (-9, -3, 0) to the line ä(t) = (−4, 1, −1)t + (0, 1, −3) .arrow_forward1 Find a vector parallel to the line defined by the parametric equations (x(t) = -2t y(t) == 1- 9t z(t) = -1-t Additionally, find a point on the line.arrow_forward
- Find the (perpendicular) distance from the line given by the parametric equations (x(t) = 5+9t y(t) = 7t = 2-9t z(t) to the point (-1, 1, −3).arrow_forwardLet ä(t) = (3,-2,-5)t + (7,−1, 2) and (u) = (5,0, 3)u + (−3,−9,3). Find the acute angle (in degrees) between the lines:arrow_forwardA tank initially contains 50 gal of pure water. Brine containing 3 lb of salt per gallon enters the tank at 2 gal/min, and the (perfectly mixed) solution leaves the tank at 3 gal/min. Thus, the tank is empty after exactly 50 min. (a) Find the amount of salt in the tank after t minutes. (b) What is the maximum amount of salt ever in the tank?arrow_forward
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





