
Concept explainers
Clearcast Communications Inc. is considering allocating a limited amount of capital investment funds among four proposals. The amount of proposed investment, estimated operating income, and net cash flow for each proposal are as follows:
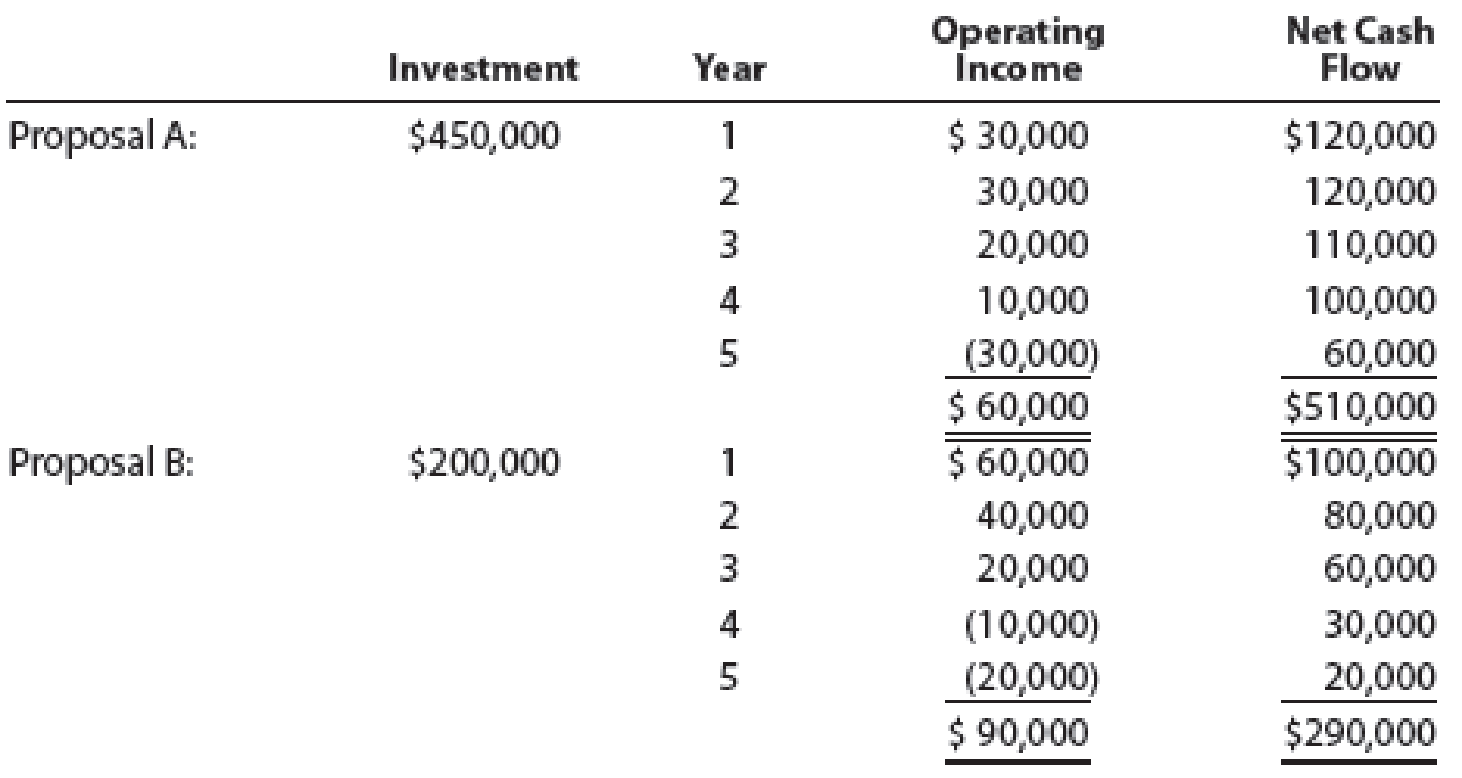
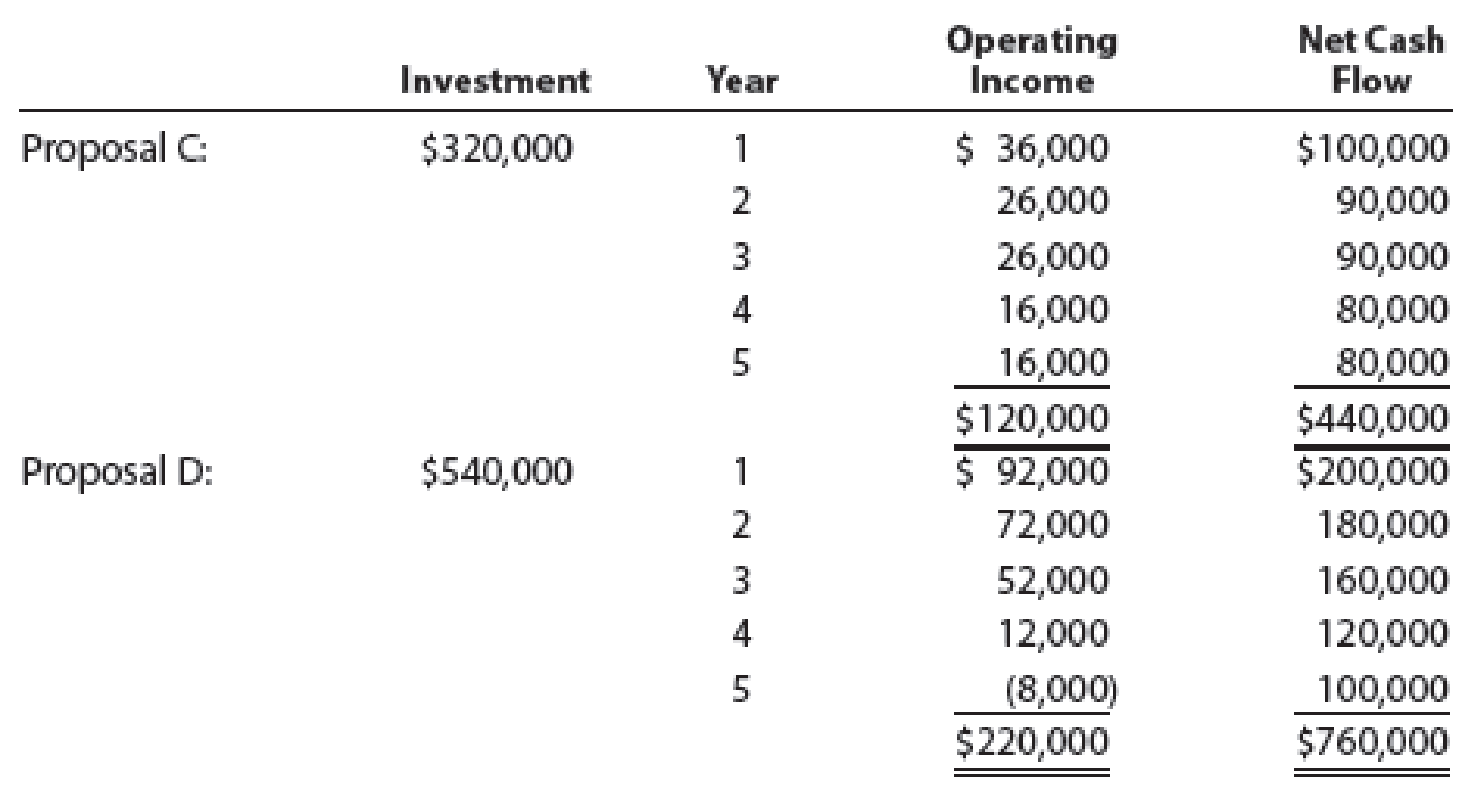
The company’s capital rationing policy requires a maximum cash payback period of three years. In addition, a minimum average
Instructions
- 1. Compute the cash payback period for each of the four proposals.
- 2. Giving effect to straight-line depreciation on the investments and assuming no estimated residual value, compute the average rate of return for each of the four proposals. Round to one decimal place.
- 3. Using the following format, summarize the results of your computations in parts (1) and (2). By placing the computed amounts in the first two columns on the left and by placing a check mark in the appropriate column to the right, indicate which proposals should be accepted for further analysis and which should be rejected.

- 4. For the proposals accepted for further analysis in part (3), compute the net present value. Use a rate of 12% and the present value table appearing in Exhibit 2 of this chapter.
- 5. Compute the present value index for each of the proposals in part (4). Round to two decimal places.
- 6. Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present values of net
cash flows computed in part (4). - 7. Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value indexes computed in part (5).
- 8.
 Based on the analyses, comment on the relative attractiveness of the proposals ranked in parts (6) and (7).
Based on the analyses, comment on the relative attractiveness of the proposals ranked in parts (6) and (7).
1.
Compute the cash payback period for each of the 4 proposals.
Explanation of Solution
Cash payback period: Cash payback period is the time period which the cost of investment is expected to be recovered. It is one of the capital investment methods used by the management to evaluate the long-term investment (fixed assets) of the business.
Calculate the cash payback period:
Proposal A:
Initial investment=$450,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal A | ||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows |
| 1 | $120,000 | $120,000 |
| 2 | $120,000 | $240,000 |
| 3 | $110,000 | $350,000 |
| 4 | $100,000 | $450,000 |
Table (1)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal A is 4 years.
Proposal B:
Initial investment=$200,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal B | ||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows |
| 1 | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| 2 | $80,000 | $180,000 |
| 4 months (1) | $20,000 | $200,000 |
Table (2)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal B is 2 years and 4 months.
Working note 1:
Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
Proposal C:
Initial investment=$320,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal C | ||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows |
| 1 | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| 2 | $90,000 | $190,000 |
| 3 | $90,000 | $280,000 |
| 6 months (2) | $40,000 | $320,000 |
Table (3)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal C is 3 years and 6 months.
Working note 2:
Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
Proposal D:
Initial investment=$540,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal D | ||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows |
| 1 | $200,000 | $200,000 |
| 2 | $180,000 | $380,000 |
| 3 | $180,000 | $560,000 |
Table (4)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal D is 3 years.
2.
Compute the average rate of return for the give proposals.
Explanation of Solution
Average Rate of Return: Average rate of return measures the average earnings of any particular business, as the percentage of the average investment. It is also commonly known as accounting rate of return. The following formula can be used to determine the average rate of return:
Calculate the cash payback period:
Proposal A:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal A is 5.3%.
Proposal B:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal B is 18.0%.
Proposal C:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal C is 15.0%.
Proposal D:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal D is 16.3%.
3.
Summarize the results of the computations in part 1 and 2 in the given table.
Explanation of Solution
The proposals which should be accepted for further analysis, and which should be rejected is as follows:
| Proposal | Cash Payback Period | Average Rate of Return | Accept for Further Analysis | Reject |
| A | 4 years | 5.3% | ✓ | |
| B | 2 years and 4 months | 18.0% | ✓ | |
| C | 3 years and 6 months | 15.0% | ✓ | |
| D | 3 years | 16.3% | ✓ |
Table (5)
Proposals A and C are rejected, because proposal A and C fails to meet the required maximum cash back period of 3 years, and they has less rate of return than the other proposals. Hence, Proposals B and D are preferable.
4.
Compute the net present value for the accepted proposals.
Explanation of Solution
Net present value method: Net present value method is used to compare the initial cash outflow of the investment with the present value of its cash inflows. In the net present value, the interest rate is determined by the business based on the net income received from the investment. This is also called as the discounted cash flow method.
Calculate the net present value:
Proposal B:
| Proposal B | |||
| Year | Present Value of $1 at 12% | Net Cash Flow | Present Value of Net Cash Flow |
| 1 | 0.893 | $100,000 | $89,300 |
| 2 | 0.797 | $80,000 | $63,760 |
| 3 | 0.712 | $60,000 | $42,720 |
| 4 | 0.636 | $30,000 | $19,080 |
| 5 | 0.567 | $20,000 | $11,340 |
| Total | $290,000 | $226,200 | |
| Amount to be invested | ($200,000) | ||
| Net present value | $26,200 | ||
Table (6)
Hence, the net present value of proposal B is $26,200.
Proposal D:
| Proposal D | |||
| Year | Present Value of $1 at 12% | Net Cash Flow | Present Value of Net Cash Flow |
| 1 | 0.893 | $200,000 | $178,600 |
| 2 | 0.797 | $180,000 | $143,460 |
| 3 | 0.712 | $160,000 | $113,920 |
| 4 | 0.636 | $120,000 | $76,320 |
| 5 | 0.567 | $100,000 | $56,700 |
| Total | $760,000 | $569,000 | |
| Amount to be invested | ($540,000) | ||
| Net present value | $29,000 | ||
Table (7)
Hence, the net present value of proposal D is $29,000.
5.
Compute the present value index for each of the proposals in part (4).
Explanation of Solution
Present value index: Present value index is a method, which is used to rank the proposals of the business. It is used by the management when the business has more investment proposals, and limited fund. The present value index is calculated as follows:
Calculate the present value index:
Proposal B:
Hence, the present value index for proposal B is 1.13.
Proposal D:
Hence, the present value index for proposal Dis 1.05.
6.
Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on present values of net cash flows computed in part (4).
Explanation of Solution
Proposals arranged by rank from most attractive to least attractive are as follows:
| Proposals | Net present value | Rank |
| Proposal D | $29,000 | 1 |
| Proposal B | $26,200 | 2 |
Table (8)
7.
Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value indexes computed in part (5).
Explanation of Solution
Proposals arranged by rank from most attractive to least attractive are as follows:
| Proposals | Present value index | Rank |
| Proposal B | 1.13 | 1 |
| Proposal D | 1.05 | 2 |
Table (9)
8.
Comment on the relative attractiveness of the proposals ranked on the basis of analysis in parts (6) and (7).
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of net present value:
The net present value of Proposal B is $26,200, and of Proposal D is $29,000. In this case, the net present value of proposal D is greater than the net present value of proposal B. Hence, investment in Proposal D is recommended.
On the basis of present value index:
The present value index of Proposal B is 1.13, and of Proposal D is 1.05. In this case, Proposal B has a more favorable present value index, because the present value index of Proposal B (1.13) is greater than Proposal D (1.05). Thus, the investment in Proposal B is recommended.
Every business desires to get maximum profit with minimum investment. Thus, the cost of investment in Proposal B is lesser than the proposal D. Hence, investment in Proposal B is most preferable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
FINANCIAL&MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING(LL)W/AC
- I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forwardDevelopment costs in preparing the mine $ 3,400,000 Mining equipment 159,600 Construction of various structures on site 77,900 After the minerals are removed from the mine, the equipment will be sold for an estimated residual value of $12,000. The structures will be torn down. Geologists estimate that 820,000 tons of ore can be extracted from the mine. After the ore is removed, the land will revert back to the state of New Mexico. The contract with the state requires Hecala to restore the land to its original condition after mining operations are completed in approximately four years. Management has provided the following possible outflows for the restoration costs: Cash Outflow Probability $ 620,000 40% 720,000 30% 820,000 30% Hecala’s credit-adjusted risk-free interest rate is 7%. During 2024, Hecala extracted 122,000 tons of ore from the mine. The company’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Required: Determine the amount at which Hecala will record the mine. Calculate the…arrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forward
- what are the Five List of Michael Porter's 5 Force Framework that describes the competitive dynamics of a firm and the industry they are in?arrow_forwardHello tutor i need help I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forwarddefine each item below: A competitive advantage. 2) Data incorporation. 3) Financial Statement Analysis. 4) Product Differentiation. 5) Strategic positioning for a business firmarrow_forward
- Hello tutor i need help I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is true about contra revenue accounts like Sales Returns and Allowances?A. They increase total revenueB. They have a normal credit balanceC. They reduce gross salesD. They increase net income helparrow_forwardWhich of the following is true about contra revenue accounts like Sales Returns and Allowances?A. They increase total revenueB. They have a normal credit balanceC. They reduce gross salesD. They increase net incomearrow_forward
- 7. If inventory is overstated at year-end, which of the following is true?A. Net income is understatedB. Expenses are overstatedC. Net income is overstatedD. Assets are understatedarrow_forward9. In a bank reconciliation, a bank service charge would be:A. Deducted from the book balanceB. Added to the bank balanceC. Deducted from the bank balanceD. Ignoredarrow_forwardWhich statement is prepared first in the accounting cycle?A. Balance SheetB. Statement of Retained EarningsC. Income StatementD. Cash Flow Statement need helparrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



