
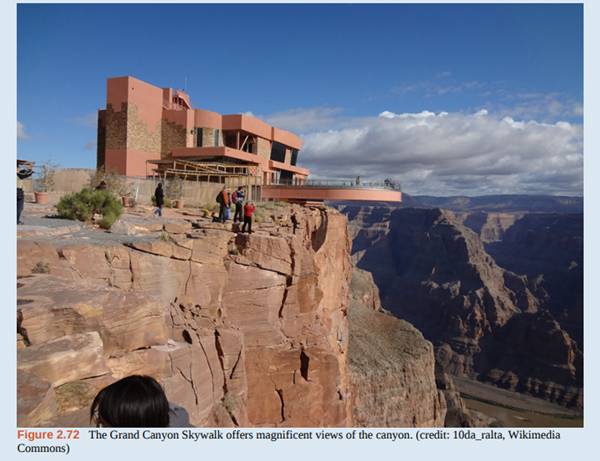
The Grand Canyon Skywalk opened to the public on March 28, 2007. This engineering marvel is a horseshoe-shaped observation platform suspended 4000 ft above the Colorado River on the West Rim of the Grand Canyon. Its crystal-clear glass floor allows stunning views of the canyon below (see the following figure).
The Skywalk is a cantilever design, meaning that the observation platform extends over the rim of the canyon, with no visible means of support below it. Despite the lack of visible support posts or struts, cantilever structures are engineered to be very stable and the Skywalk is no exception. The observation platform is attached firmly to support posts that extend 46 ft down into bedrock. The structure was built to withstand 100-mph winds and an 8.0-magnitude earthquake within 50 mi, and is capable of supporting more than 70,000,000 lb.
One factor affecting the stability of the Skywalk is the center of gravity of the structure. We are going to calculate the center of gravity of the Skywalk, and examine how the center of gravity changes when tourists walk out onto the observation platform.
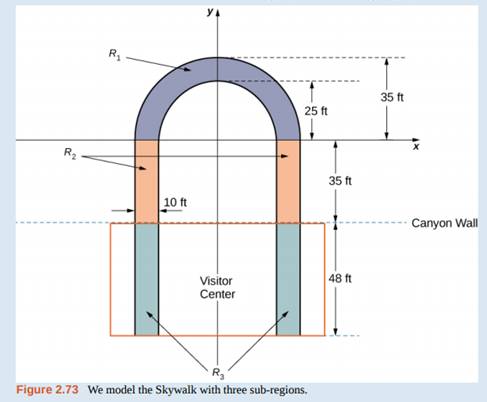
The observation platform is U-shaped. The legs of the U are 10 ft wide and begin on land, under the visitors' center, 48 ft from the edge of the canyon. The platform extends 70 ft over the edge of the canyon.
To calculate the center of mass of the structure, we treat it as a lamina and use a two-dimensional region in the xy-plane to represent the platform. We begin by dividing the region into three subregions so we can consider each subregion separately. The first region, denoted R1, consists of the curved part of the U. We model R1as a semicircular annulus, with inner radius 25 ft and outer radius 35 ft, centered at the origin (see the following figure).
The legs of the platform, extending 35 ft between R1and the canyon wall, comprise the second sub-region, R2, Last, the ends of the legs, which extend 48 ft under the visitor center, comprise the third sub-region, R3. Assume the density of the lamina is constant and assume the total weight of the platform is 1,200,000 lb (not including the weight of the visitor center; we will consider that later). Use g = 32 ft/sec2.
5.Assume the visitor center weighs 2,200,000 lb, with a center of mass corresponding to the center of mass of R3. Treating the visitor center as a point mass, recalculate the center of mass of the system. How does the center of mass change?

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Calculus Volume 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward4 In the integral dxf1dy (7)², make the change of variables x = ½(r− s), y = ½(r + s), and evaluate the integral. Hint: Find the limits on r and s by sketching the area of integration in the (x, y) plane along with the r and s axes, and then show that the same area can be covered by s from 0 to r and r from 0 to 1.arrow_forward7. What are all values of 0, for 0≤0<2л, where 2 sin² 0=-sin? - 5π 6 π (A) 0, л, and 6 7π (B) 0,л, 11π , and 6 6 π 3π π (C) 5π 2 2 3 , and π 3π 2π (D) 2' 2'3 , and 3 4元 3 1 די } I -2m 3 1 -3 บ 1 # 1 I 3# 3m 8. The graph of g is shown above. Which of the following is an expression for g(x)? (A) 1+ tan(x) (B) 1-tan (x) (C) 1-tan (2x) (D) 1-tan + X - 9. The function j is given by j(x)=2(sin x)(cos x)-cos x. Solve j(x) = 0 for values of x in the interval Quiz A: Topic 3.10 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities Created by Bryan Passwaterarrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward-xx0. B2 If Xfx(x) find the MGF in the case that fx(x) = - 1 28 exp{-|x − a\/ẞ}, Use the MGF to compute E(X) and Var(X).arrow_forwardName Assume there is the following simplified grade book: Homework Labs | Final Exam | Project Avery 95 98 90 100 Blake 90 96 Carlos 83 79 Dax 55 30 228 92 95 79 90 65 60 Assume that the weights used to compute the final grades are homework 0.3, labs 0.2, the final 0.35, and the project 0.15. | Write an explicit formula to compute Avery's final grade using a single inner product. Write an explicit formula to compute everyone's final grade simultane- ously using a single matrix-vector product.arrow_forward
- 1. Explicitly compute by hand (with work shown) the following Frobenius inner products 00 4.56 3.12 (a) ((º º º). (156 (b) 10.9 -1 0 2)), Fro 5')) Froarrow_forward3. Let 4 0 0 00 0 0 1.2 0 00 0 0 0 -10.1 0 0 0 D = 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 05 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.8 Either explicitly compute D-¹ or explain why it doesn't exist.arrow_forward4. [9 points] Assume that B, C, E are all 3 x 3 matrices such that BC == -64 -1 0 3 4 4 4 -2 2 CB=-1-2 4 BE -2 1 3 EC = 1 3 2 -7, 1 6 -6 2-5 -7 -2 Explicitly compute the following by hand. (I.e., write out the entries of the 3 × 3 matrix.) (a) [3 points] B(E+C) (b) [3 points] (E+B)C (c) [3 points] ETBTarrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,





