
(a)
Interpretation:
The way in which the structure of the given compound differs from the structure of fats and oils has to be described.
Fats: Glycerol is a part of the structure of fat and is made up of three Carbon atoms. fats are made up of fatty acids, having a long carbon chain with one end of the chain possessing a carbonyl (COOH) groups.
Triglycerides: The major molecule which starts the structure of a triglyceride is glycerol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with three hydroxyl groups on them. These hydroxyl groups are the sites of an ester reaction with three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can be different, and are long chains of carbons.
Formation of triglyceride:
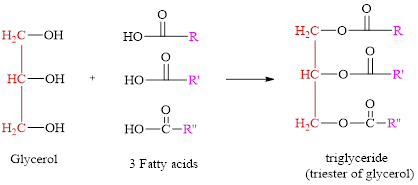
General structure of triglyceride is,
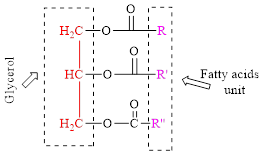
(b)
Interpretation:
The three products obtained when the given compound is hydrolyzed with aqueous Sodium hydroxide has to be drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Four compounds are obtained when the given compound is hydrolyzed with aqueous acid; all the possible structures have to be drawn.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 26 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (LL)
- Heating an alcohol in the presence of sulfuric or phosphoric acid will cause a dehydration to occur: the removal of the elements of water from a molecule, forming an alkene. The reaction usually follows an E1 mechanism. The SN1 pathway is suppressed by using a strong acid whose conjugate base is a poor nucleophile. Further, heating the reaction mixture causes a greater increase in the rate of E1 compared to the rate of S№1. 2nd attempt 0 See Periodic Table See Hint Draw the organic intermediate from the first step (no byproducts) and draw curved arrow(s) to show how it reacts. TH +11: 1st attempt Feedback H H H C F F See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardThis molecule undergoes an E1 mechanism when stirred in methanol. 3rd attempt CH₂OH CH₂OH 6148 O See Periodic Table. See Hint Draw 3 chemical species including formal charges and lone pairs of electrons. Add the missing curved arrow notation. H N O O SA 3 Br Iarrow_forwardComplete the mechanism for the E1 reaction below by following the directions written above each of the five boxes. Be sure to include lone pair electrons and nonzero formal charges. 1st attempt Y 0 + Provide the missing curved arrow notation. 01: See Periodic Table See Hint H C Br Iarrow_forward
- Please help answer number 2. Thanks in advance.arrow_forwardHow do I explain this? Thank you!arrow_forwardWhen an unknown amine reacts with an unknown acid chloride, an amide with a molecular mass of 163 g/mol (M* = 163 m/z) is formed. In the infrared spectrum, important absorptions appear at 1661, 750 and 690 cm. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra are provided. Draw the structure of the product as the resonance contributor lacking any formal charges. 13C NMR DEPT 90 200 160 120 80 40 0 200 160 120 80 40 0 DEPT 135 T 200 160 120 80 40 0 Draw the unknown amide. Select Dow Templates More Fragearrow_forward
- Identify the unknown compound from its IR and proton NMR spectra. C4H6O: 'H NMR: 82.43 (1H, t, J = 2 Hz); 8 3.41 (3H, s); 8 4.10 (2H, d, J = 2 Hz) IR: 2125, 3300 cm¹ The C4H6O compound liberates a gas when treated with C2H5 MgBr. Draw the unknown compound. Select Draw с H Templates Morearrow_forwardPlease help with number 6 I got a negative number could that be right?arrow_forward1,4-Dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene can undergo 1,2- or 1,4-addition with hydrogen halides. (a) 1,2-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,2-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,2-addition product formed during the reaction in (i)? (b) 1,4-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,4-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,4-addition product formed from the reaction in (i)? (c) What is the kinetic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobromic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (d) What is the thermodynamic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobro-mic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (e) What major product will result when 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of hydrobromic acid at - 78 deg * C ? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Give the product of the bimolecular elimination from each of the isomeric halogenated compounds. Reaction A Reaction B. КОВ CH₂ HotBu +B+ ко HOIBU +Br+ Templates More QQQ Select Cv Templates More Cras QQQ One of these compounds undergoes elimination 50x faster than the other. Which one and why? Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups and to each other Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gauche to each other. ◇ Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gach to each other. Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups anti to each other.arrow_forwardFive isomeric alkenes. A through each undergo catalytic hydrogenation to give 2-methylpentane The IR spectra of these five alkenes have the key absorptions (in cm Compound Compound A –912. (§), 994 (5), 1643 (%), 3077 (1) Compound B 833 (3), 1667 (W), 3050 (weak shoulder on C-Habsorption) Compound C Compound D) –714 (5), 1665 (w), 3010 (m) 885 (3), 1650 (m), 3086 (m) 967 (5), no aharption 1600 to 1700, 3040 (m) Compound K Match each compound to the data presented. Compound A Compound B Compound C Compound D Compoundarrow_forward7. The three sets of replicate results below were accumulated for the analysis of the same sample. Pool these data to obtain the most efficient estimate of the mean analyte content and the standard deviation. Lead content/ppm: Set 1 Set 2 Set 3 1. 9.76 9.87 9.85 2. 9.42 9.64 9.91 3. 9.53 9.71 9.42 9.81 9.49arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





