
Concept explainers
(a)
To draw: Squares with different sides.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Side of MNPQ = Twice the side of ABCD
Side of FGHJ = Half the side of ABCD
Calculation:
Let the side of ABCD be x meters.
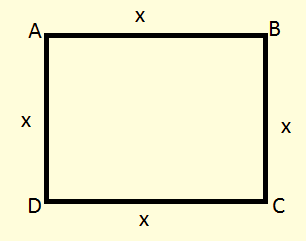
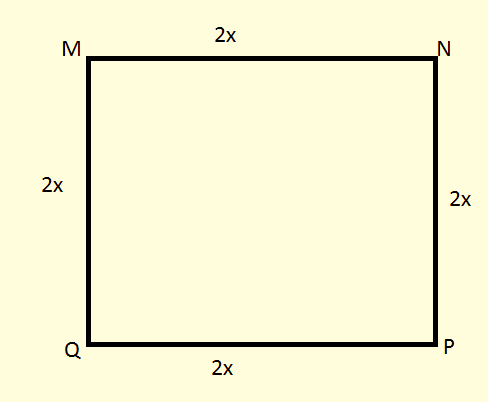
The side of MNPQ will be 2x meters.
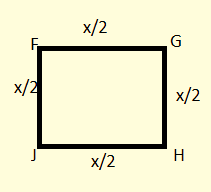
The side of FGHJ will be x/2 meters.
(b)
The blank spaces of the given table.
(b)
Answer to Problem 45PPS

Explanation of Solution
Given:
Side of MNPQ = Twice the side of ABCD
Side of FGHJ = Half the side of ABCD
Calculation:
Let the side of ABCD be x meters.
Perimeter of the square will be:
The side of MNPQ will be 2x meters.
Perimeter of the square will be:
The side of FGHJ will be x/2 meters.
Perimeter of the square will be:
The table will be:

(c)
The relationship between the perimeter and the side length of the square.
(c)
Answer to Problem 45PPS
Directly Proportional.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Side of MNPQ = Twice the side of ABCD
Side of FGHJ = Half the side of ABCD
Calculation:
From the below table:

It can be seen that perimeter is directly proportional to the side length of the square. That is, if the side length is doubled, the perimeter gets doubled and if the side length is halved, the perimeter is halved.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Algebra 1
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- > > > we are hiring Salesforce Admin Location: Remote Key Responsibilities: Administer Salesforce Sales & Revenue Cloud (CPQ & Billing) Configure workflows, validation rules & dashboards Automate processes using Flows & Process Builder Collaborate with Sales, Finance & Marketing teams Manage user roles & security Apply: Hr@forcecraver.comarrow_forwardAnswer this questionarrow_forward1. vector projection. Assume, ER1001 and you know the following: ||||=4, 7=-0.5.7. For each of the following, explicitly compute the value. འབ (a) (b) (c) (d) answer. Explicitly compute ||y7||. Explain your answer. Explicitly compute the cosine similarity of and y. Explain your Explicitly compute (x, y). Explain your answer. Find the projection of onto y and the projection of onto .arrow_forward
- 2. Answer the following questions using vectors u and v. --0-0-0 = find the the cosine similarity and the angle between u and v. འརྒྱ (a) (b) find the scalar projection of u onto v. (c) find the projection of u onto v. (d) (e) (f) find the scalar projection of onto u. find the projection of u onto u. find the projection of u onto and the projection of onto . (Hint: find the inner product and verify the orthogonality)arrow_forwardPlease type out answerarrow_forwardPlease type out answerarrow_forward
- Please type out answerarrow_forwardUsing f(x) = log x, what is the x-intercept of g(x) = log (x + 4)? Explain your reasoning. Please type out answerarrow_forwardThe function f(x) = log x is transformed to produce g(x) = log (x) – 3. Identify the type of transformation and describe the change. Please type out answerarrow_forward
- Each graph below is the graph of a system of three linear equations in three unknowns of the form Ax = b. Determine whether each system has a solution and, if it does, the number of free variables. A. O free variables ✓ B. no solution C. no solution D. no solution E. 1 free variable F. 1 free variablearrow_forwardSolve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5 Please type out answerarrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1 Please type out answerarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





