
Concept explainers
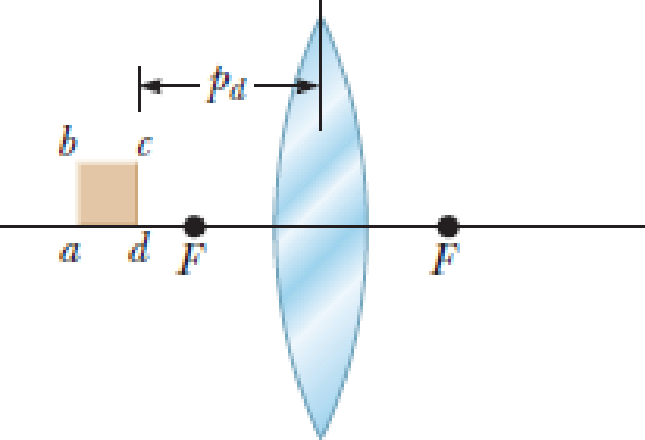
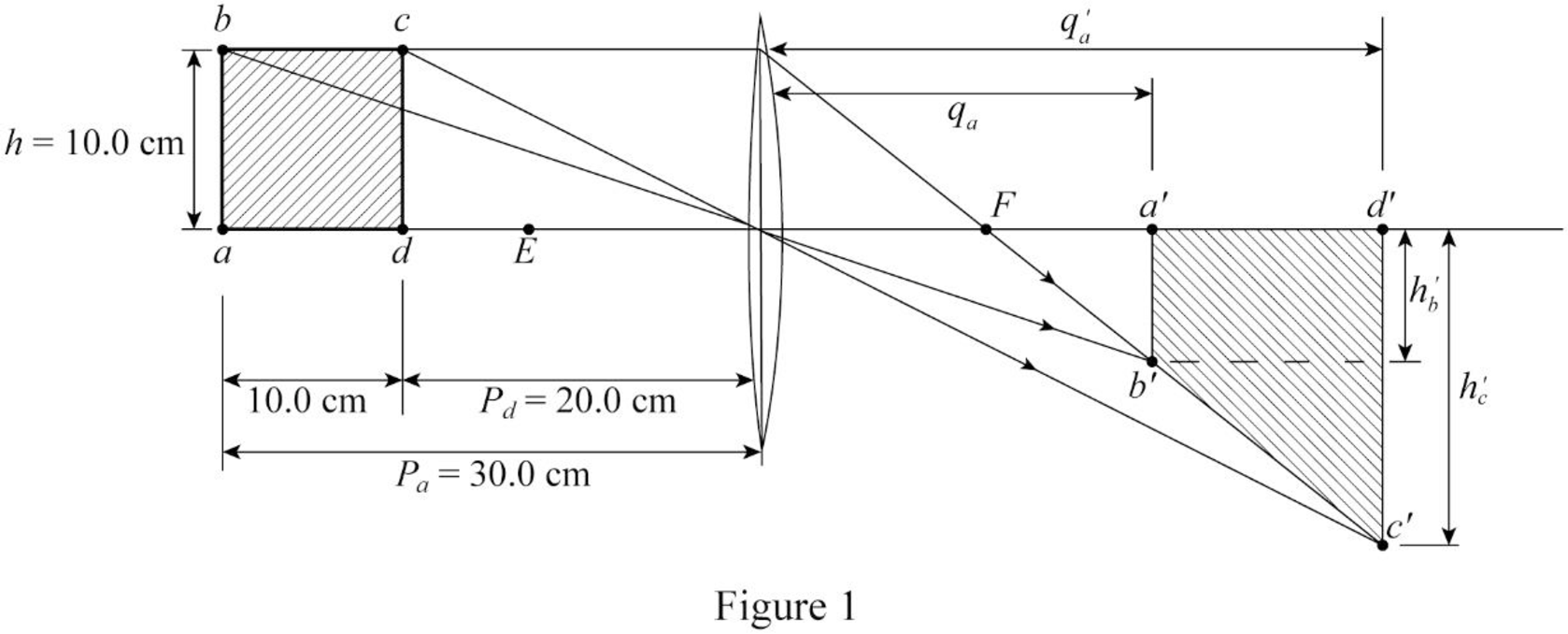
In Figure P26.38, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abcd, which is hc = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a′, b′, c′, and d′ represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a′ and b′, qd represent the image distance for points c′ and d′, h′b represent the distance from point b′ to the axis, and h′c represent the height of c′. (a) Find qa, qd, h′b, and h′c. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a′ and d′, for which the object distance is p. Let h′ represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b′ and c′ at image distance q. Demonstrate that
where h′ and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by
(e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image.
Figure P26.38
(a)
The values of given parameters.
Answer to Problem 38P
The values of the given parameters are
Explanation of Solution
Write the mirror equation for the side a.
Here
Rewrite (I) in terms of
Similarly, write the image distance for side d.
Write the equation for magnification for side b
Here
Rewrite (IV) in terms of
Similarly,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The values of the given parameters are
(b)
Sketch of the image.
Answer to Problem 38P
The image has been drawn
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
The image has been drawn
(c)
Prove the given equation.
Answer to Problem 38P
The equation has been proved.
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for magnification
Rewrite (VII) in terms of
Write the mirror equation in terms of
Substitute (IX) in (VIII)
Conclusion:
Substitute
Hence proved.
(d)
Geometric area of the image.
Answer to Problem 38P
The geometric area of the image is given by
Explanation of Solution
The integral sign suggests that the areas of the small regions are added up to get the whole area. The
Conclusion:
The geometric area of the image is given by
(e)
Area of the image.
Answer to Problem 38P
The area is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for area
Substitute (XI) in (XII)
Conclusion:
The area is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- The 10-lb weight is supported by the cord AC and roller and by the spring that has a stiffness of k = 10 lb/in. and an unstretched length of 12 in. as shown in. Part A Determine the distance d to maintain equilibrium. Express your answer in inches to three significant figures. 節 ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ d = *k J vec 5 t 0 ? d C A in. 12 in. Barrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in . The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Value Submit Request Answer Part B 0 ? Units Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? T₂ = Value Units T₁ Carrow_forwardpls help on botharrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward6. 6. There are 1000 turns on the primary side of a transformer and 200 turns on thesecondary side. If 440 V are supplied to the primary winding, what is the voltageinduced in the secondary winding? Is this a step-up or step-down transformer? 7. 80 V are supplied to the primary winding of a transformer that has 50 turns. If thesecondary side has 50,000 turns, what is the voltage induced on the secondary side?Is this a step-up or step-down transformer? 8. There are 50 turns on the primary side of a transformer and 500 turns on thesecondary side. The current through the primary winding is 6 A. What is the turnsratio of this transformer? What is the current, in milliamps, through the secondarywinding?9. The current through the primary winding on a transformer is 5 A. There are 1000turns on the primary winding and 20 turns on the secondary winding. What is theturns ratio of this transformer? What is the current, in amps, through the secondarywinding?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardWhat is the current, in amps, across a conductor that has a resistance of10 Ω and a voltage of 20 V? 2. A conductor draws a current of 100 A and a resistance of 5 Ω. What is thevoltageacross the conductor? 3. What is the resistance, in ohm’s, of a conductor that has a voltage of 80 kVand acurrent of 200 mA? 4. An x-ray imaging system that draws a current of 90 A is supplied with 220V. What is the power consumed? 5. An x-ray is produced using 800 mA and 100 kV. What is the powerconsumed in kilowatts?arrow_forwardՍՈՈՒ XVirginia Western Community Coll x P Course Home X + astering.pearson.com/?courseld=13289599#/ Figure y (mm) x=0x = 0.0900 m All ✓ Correct For either the time for one full cycle is 0.040 s; this is the period. Part C - ON You are told that the two points x = 0 and x = 0.0900 m are within one wavelength of each other. If the wave is moving in the +x-direction, determine the wavelength. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 t(s) λ = Value m 0.01 0.03 0.05 0.07 Copyright © 2025 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. 日 F3 F4 F5 1775 % F6 F7 B F8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? × Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us | Cookie Settings 28°F Clear 4 9:23 PM 1/20/2025 F9 prt sc F10 home F11 end F12 insert delete 6 7 29 & * ( 8 9 0 t = back Οarrow_forward
- Part C Find the height yi from which the rock was launched. Express your answer in meters to three significant figures. Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 4.1 for projectile motion problems. A rock thrown with speed 12.0 m/s and launch angle 30.0 ∘ (above the horizontal) travels a horizontal distance of d = 19.0 m before hitting the ground. From what height was the rock thrown? Use the value g = 9.800 m/s2 for the free-fall acceleration. PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGY 4.1 Projectile motion problems MODEL: Is it reasonable to ignore air resistance? If so, use the projectile motion model. VISUALIZE: Establish a coordinate system with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical. Define symbols and identify what the problem is trying to find. For a launch at angle θ, the initial velocity components are vix=v0cosθ and viy=v0sinθ. SOLVE: The acceleration is known: ax=0 and ay=−g. Thus, the problem becomes one of…arrow_forwardPhys 25arrow_forwardPhys 22arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax





