
(a)
Interpretation:
Styrene can auto initiate free radical
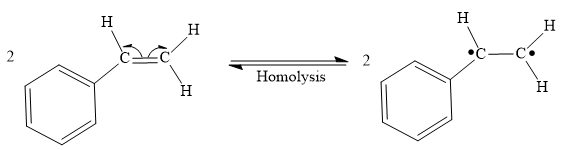
Step 1: Homolysis of the vinyl π bond in a styrene molecule
Step 2: Homolysis of the vinyl π bond in a second styrene molecule
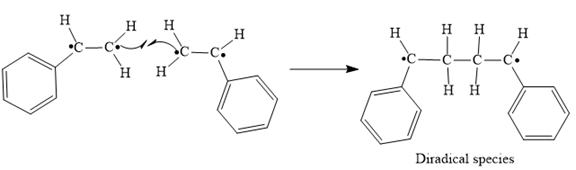
Step 3: Tail-to-tail addition of the radicals from Steps 1 and 2
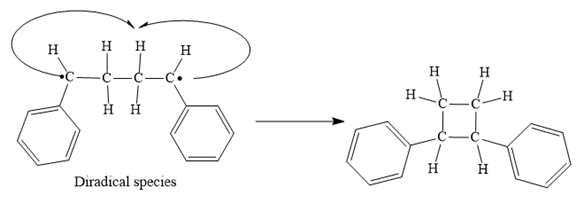
Step 4: Radical coupling of the diradical formed in Step 3.
It as is to be used curved arrow notation to show the steps in a given mechanism.
Concept introduction:
“The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis.” So in homolysis generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is a breakdown equally and each atom acquires a single electron which is called a radical and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest
) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest
Answer to Problem 26.74P
The mechanism for the given steps with curved arrow notation is given below:
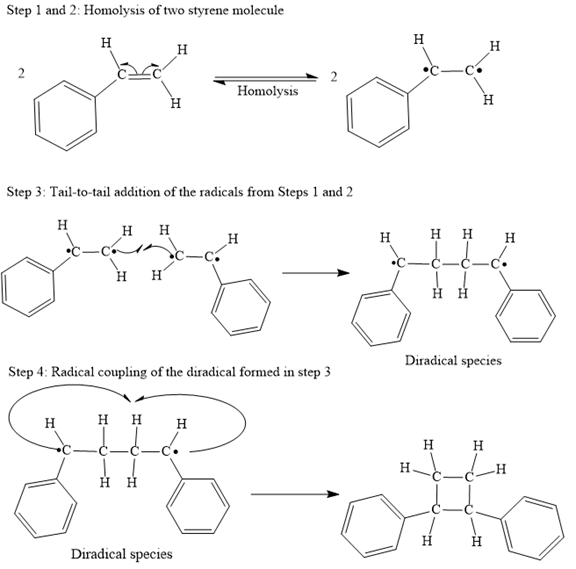
Explanation of Solution
Both steps step 1 and step 2 are same, the homolysis of the vinyl π bond in two styrene molecules.
In step 3 Tail-to-tail addition of the radicals from Steps 1 and 2 takes place as below:
Finally, the radical coupling of the diradical formed in step 3 takes place as below:
A curved arrow notation to show the steps in a given mechanism is used.
(b)
Interpretation:
Styrene can auto initiate free radical polymerization and form polystyrene in the absence of an initiator. At temperatures
Step 1: Homolysis of the vinyl π bond in a styrene molecule
Step 2: Homolysis of the vinyl π bond in a second styrene molecule
Step 3: Tail-to-tail addition of the radicals from Steps 1 and 2
Step 4: Radical coupling of the diradical formed in Step 3.
It is to be explained above steps consistent with those for free radical polymerization.
Concept introduction:
“The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis.” So in homolysis generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is a breakdown equally and each atom acquires a single electron which is called a radical and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest bond dissociation energy. These radials are propagated in the polymerization to elongate the chain of the polymer called a propagation step.
) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest bond dissociation energy. These radials are propagated in the polymerization to elongate the chain of the polymer called a propagation step.
Answer to Problem 26.74P
No, this mechanism is not consistent with a free-radical polymerization, because this mechanism not produces a polymer.
Explanation of Solution
No, this mechanism is not consistent with a free-radical polymerization. In polymerization, the propagation step must occur to elongate the chain of the polymer. But in the given mechanism, the propagation step does not occur thus it not forms polymer, actually, it is a dimer.
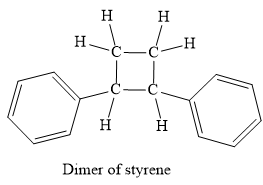
It is explained above steps consistent with those for free radical polymerisation.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained why the use of an initiator such as benzoyl peroxide more efficient in the synthesis of polystyrene than auto initiated polymerization.
Concept introduction:
“The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis.” So in homolysis generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is a breakdown equally and each atom acquires a single electron which is called a radical and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest bond dissociation energy. These radials are propagated in polymerization are elongated to grow the chain of the polymer called a propagation step.
) is used to represents the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, the radicals from a breaking of the weakest bond of the molecule give the major products. The weakest bond possesses the smallest bond dissociation energy. These radials are propagated in polymerization are elongated to grow the chain of the polymer called a propagation step.
Answer to Problem 26.74P
In case of autoinitiator reaction, the reaction can be terminated too rapidly, because the diradicals formed from the two styrene molecule undergoes dimerization to form the 1, 2-phenylcylcobutane as a product, instead of polymerization. Due to the formation of this product, the growth of a long chain of the molecule does not occur. But with benzoyl peroxide, the radical from the initiation step is a monoradical and it will continue the propagation step to build up polymer, through the chain growth.
Explanation of Solution
In case of autoinitiator reaction, the reaction can be terminated too rapidly, because the diradicals formed from the two styrene molecule undergoes dimerization to form the 1, 2-phenylcylcobutane as a product, instead of polymerization. Due to the formation of this product, the growth of a long chain of the molecule does not occur.

But with benzoyl peroxide, the radical from the initiation step is a monoradical and it will continue the propagation step to build up polymer, through the chain growth.
It is explained why the use of an initiator such as benzoyl peroxide more efficient in the synthesis of polystyrene than auto initiated polymerization.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- CHEM2323 E Tt PS CH03 Draw and name all monobromo derivatives of pentane, C5H11Br. Problem 3-33 Name: Draw structures for the following: (a) 2-Methylheptane (d) 2,4,4-Trimethylheptane Problem 3-35 (b) 4-Ethyl-2,2-dimethylhexane (e) 3,3-Diethyl-2,5-dimethylnonane (c) 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane 2 (f) 4-Isopropyl-3-methylheptane KNIE>arrow_forwardProblem 3-42 Consider 2-methylbutane (isopentane). Sighting along the C2-C3 bond: (a) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation. (b) Draw a Newman projection of the least stable conformation. Problem 3-44 Construct a qualitative potential-energy diagram for rotation about the C-C bond of 1,2-dibromoethane. Which conformation would you expect to be most stable? Label the anti and gauche conformations of 1,2- dibromoethane. Problem 3-45 Which conformation of 1,2-dibromoethane (Problem 3-44) would you expect to have the largest dipole moment? The observed dipole moment of 1,2-dibromoethane is µ = 1.0 D. What does this tell you about the actual conformation of the molecule?arrow_forwardGas Law Studies 1. Mass of zinc Determination of 0.899 2) Moles of zinc 0.01361 mol 3.) Moles of hydrogen 00? ← I was told to calculate this number from mole of zinc. 350m So does that mean it will be 0.01361 mol too? 4 Volume of water collected (mL) 5) VL of water collected (Liters) 0.350 L 6) Temp of water collected (°C) 7) Temp of water collected (°K) 8) Atmospheric pressure (mm) 9) Vapor pressure of water (mm) 10) Corrected pressure of hydrogen 20% 29°C 764.0mm Hg (mm) 17.5mm 11) Corrected pressure of hydrogen (atm) 12) Experimentally calculated value of 19 13. Literature value of R 14) % Error 15) Suggest reasons for the % error (#14)arrow_forward
- No wedge or dashes. Do proper structure. Provide steps and explanation.arrow_forward10 Question (1 point) Draw curved arrow notation to indicate the proton transfer between NaOH and CH3CO₂H. 2nd attempt :0- H See Periodic Table See Hint Draw the products of the proton transfer reaction. Don't add a + sign between the products.arrow_forwardProvide steps and explanation please.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





