
Concept explainers
Devise a synthesis of each of the following compounds. Besides inorganic reagents, you may use hydrocarbons and halides having
a. c.
c. e.
e.
b.![]() d.
d.![]() f.
f.
(a)
Interpretation: The synthesis of the given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Lithium aluminum hydride is a strong reducing agent. Treatment of carbonyl compounds with lithium aluminum hydride yields alcohols. It reduces ketone into secondary alcohol.
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of the given compound is,
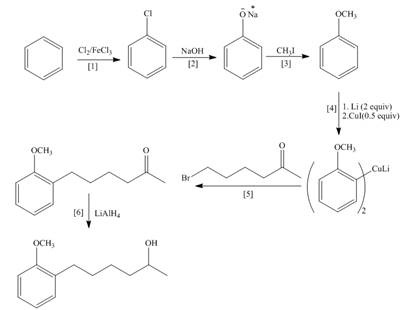
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of given compound is follows:
Step-1 Chlorination of benzene takes place in the presence of ferric chloride and gives chlorobenzene.
Step-2 Chlorobenzene is treated with base and undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction and gives phenol.
Step-3 Phenol is treated with methyl iodide and gives anisole.
Step-4 Anisole is treated with
Step-5 Organocuprate compound is treated with
Step-6 The substituted product is treated with
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
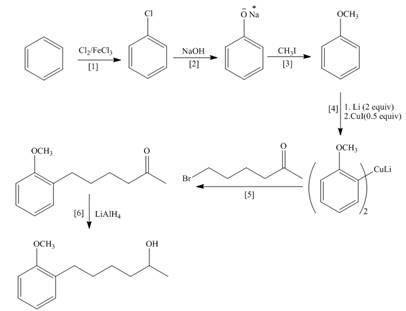
Figure 1
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The synthesis of the given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Gilman reagents are organometallic compounds which are a source of nucleophiles. These nucleophiles give
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of the given compound is,
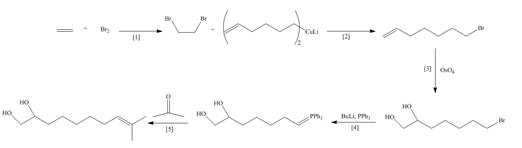
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of the given compound is follows:
Step-1 Alkene is treated with
Step-2
Step-3The
Step-4 The compound obtained from step-4 is treated with
Step-5 The Wittig reagent is treated with acetone to give a desired product.
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 2
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The synthesis of the given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Suzuki reaction is a type of substitution reaction. It involves the palladium coupling between organic halide with organoborane in the presence of base. It is a stereospecific reaction.
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of the given compound is,
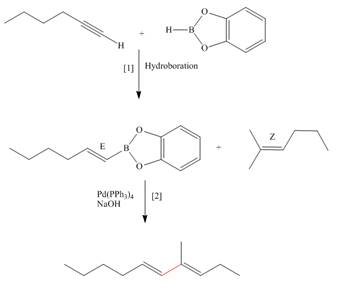
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of the given compound is follows:
Step-1 Hydroboration of hex
Step-2 The
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
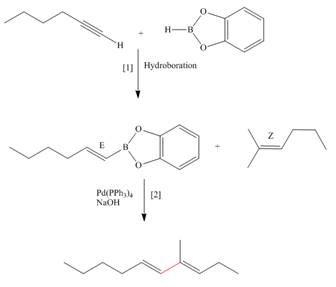
Figure 3
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The synthesis of the given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Heck reaction is a type of substitution reaction. It involves the palladium coupling between aryl or vinyl halide with alkene which leads to the formation of trans alkene at less substituted carbon.
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of the given compound is,
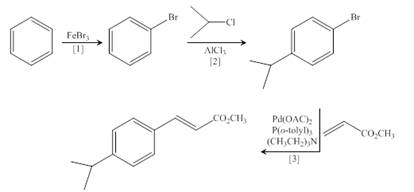
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of the given compound is follows:
Step-1 Bromination of benzene takes place in the presence of ferric chloride and gives bromobenzene.
Step-2 Friedelcraft alkylation of bromobenzene takes place in the presence of isopropyl chloride.
Step-3The
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
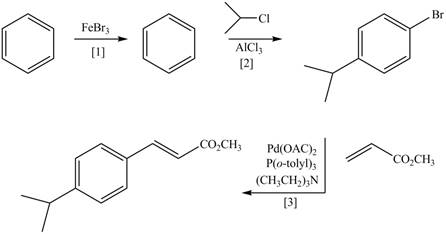
Figure 4
The synthesis of the given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The synthesis of the given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Heck reaction is a type of substitution reaction. It involves the palladium coupling between aryl or vinyl halide with alkene which leads to the formation of trans alkene at less substituted carbon. The nonhalogenated cyclopropanes are synthesized by the treatment of an alkene with
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of given compound is,
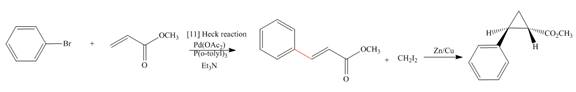
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of given compound is as follows:
Step-1 Bromobenzene is treated with
Step-2 The compound formed in step-1 undergoes Simmons-Smith reaction and forms a desired product.
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
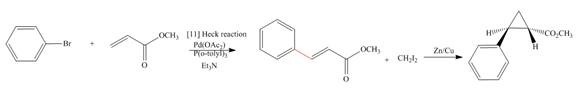
Figure 5
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Heck reaction is a type of substitution reaction. It involves the palladium coupling between aryl or vinyl halide with alkene which leads to the formation of trans alkene at less substituted carbon.
Answer to Problem 26.49P
The synthesis of given compounds is,
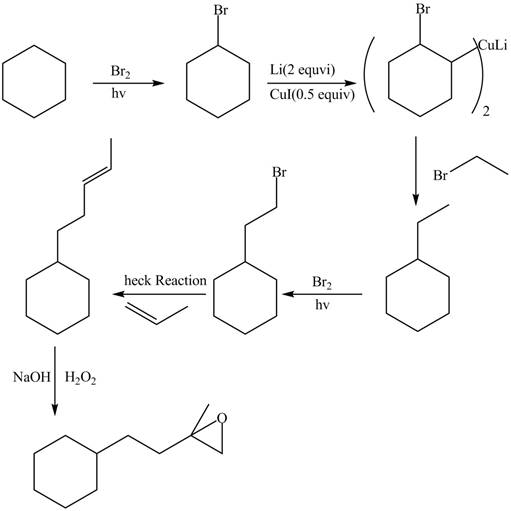
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of given compounds is as follows:
Step-1 Cyclohexane is treated with
Step-2 The brominated compound then treated with
Step-3 The organocuprate compound then treated with organic bromide to form ethylcyclohexane.
Step-4 Then ethylcyclohexane undergoes heck reaction in the presence of 1-propene to form substituted alkene compound.
Step-5 The substituted alkene compound reacts with hydrogen peroxide in the sodium hydroxide to form the desired oxirane product.
The synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
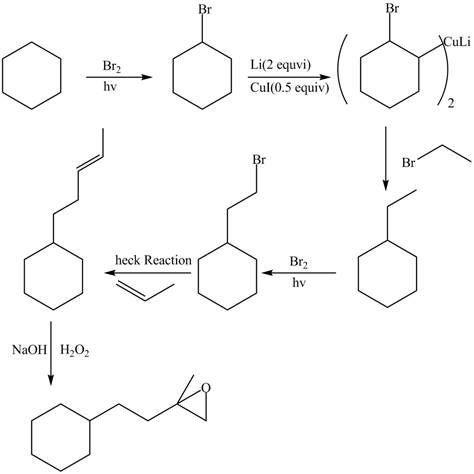
Figure 6
The synthesis of given compound is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
