
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of polyoxetane via anionic
Concept introduction:
Oxetane is a four membered ether ring and is highly strained. Anionic polymerization is a type of chain growth polymerization in which polymerization is initiated by anions. In the propagation step, the reactive intermediates are anions and not free radicals. Termination occurs in anionic polymerization when an acid is added to the reaction mixture. The anion is neutralized in the resulting proton transfer, which ends the propagation cycle. The anionic polymerization mechanism is an
Answer to Problem 26.44P
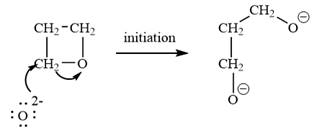
The oxetane is a four membered ether ring and is highly strained. It can undergo anionic ring-opening polymerization to relieve the strain. The anionic polymerization is initiated by an oxide ion which acts as a nucleophile. This is an
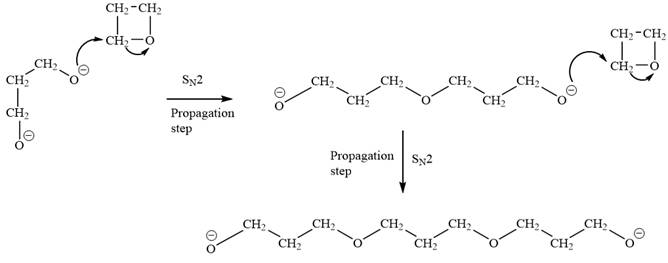
Explanation of Solution
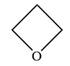
The structure of oxetane is as below:
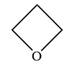
The oxetane is a four membered ether ring and is highly strained. It can undergo anionic ring-opening polymerization to relieve the strain. The anionic polymerization is initiated by an oxide ion which acts as a nucleophile. This is an
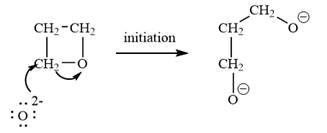
The oxygen atom of oxetane gains a negative charge and thus acts as a nucleophile. This acts as a site of chain growth. The propagation step can be shown as below:
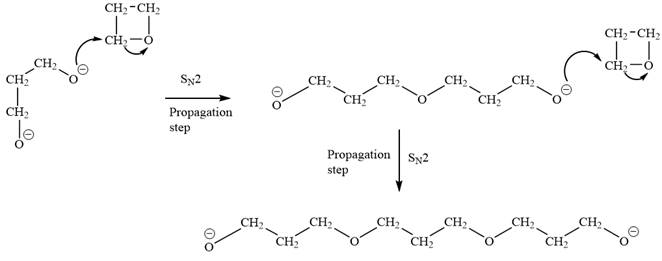
The anionic polymerization mechanism is an
(b)
Interpretation:
The condensed formula for polyoxetane is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In a condensed formula, each nonhydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Adjacent nonhydrogen atoms in the condensed formula are interpreted as being covalently bonded to each other. Parentheses in a condensed formula denote that the group is attached to the previous C. Lone pairs are not shown explicitly in the condensed formula.
Answer to Problem 26.44P
The condensed formula for polyoxetane is
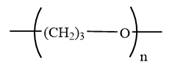
Explanation of Solution
The structure of oxetane is as below:
The oxetane is a four membered ether ring and is highly strained. It can undergo anionic ring-opening polymerization to relieve the strain. The anionic polymerization is initiated by an oxide ion which acts as a nucleophile. This is an
In a condensed formula, each nonhydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Adjacent nonhydrogen atoms in the condensed formula are interpreted as being covalently bonded to each other. Parentheses in a condensed formula denote that the group is attached to the previous C. Lone pairs are not shown explicitly in the condensed formula. Thus, the condensed formula of oxetane is:
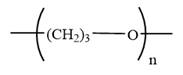
In a condensed formula, each nonhydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined if polyoxetane is expected to be more or less soluble in water than poly(ethelene oxide).
Concept introduction:
The solubility of a
Answer to Problem 26.44P
Polyoxetane (PO) is expected to be less soluble in water than poly(ethelene oxide) (PEO), as the extent of hydrogen bonding is less along the chain of polyoxetane than in polyethelene oxide.
Explanation of Solution
The condensed structures of polyoxetane and poly(ethelene oxide) are shown below:
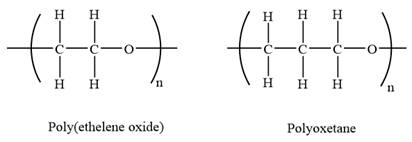
The repeating units in both are shown in the parenthesis. Poly(ethelene oxide) has two carbon atoms while polyoxetane has three carbon atoms in the repeating unit. As the number of carbon atoms increases the solubility of the polymer decreases. Both the repeating units have an oxygen atom in it. Due to which hydrogen bonding is possible. The number of carbon atoms in polyoxetane is more so, oxygen occurs less frequently in polymer chain in than in polyethelene oxide. As a result, there will be less hydrogen bonding with water along the chain of polyoxetane than in polyethelene oxide. Hence, it is expected that polyoxetane (PO) will be less soluble in water than poly(ethelene oxide) (PEO).
As the strength of intermolecular forces increases, the solubility of a polymer in a given solvent increase.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined if polyoxetane is expected to have a higher or lower melting point than poly(ethelene oxide).
Concept introduction:
The melting point of a polymer depends on the strength of intermolecular forces present in that particular polymer. Among two polymers, a more polar polymer has stronger intermolecular forces than a less polar polymer. The polarity depends on the asymmetric distribution of electrons and the presence of electronegative atoms. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force present in covalent compounds.
Answer to Problem 26.44P
Polyoxetane (PO) is expected to have a lower melting point than poly(ethelene oxide) (PEO), as the extent of hydrogen bonding is less along the chain of polyoxetane than in polyethelene oxide. Also, as the number of carbon atoms in poyoxetane is more, it is slightly less polar than polyethelene oxide.
Explanation of Solution
The condensed structures of polyoxetane and poly(ethelene oxide) are shown below:

The repeating units in both are shown in the parenthesis. Poly(ethelene oxide) has two carbon atoms while polyoxetane has three carbon atoms in the repeating unit. As the number of carbon atoms increases the polarity decreases. Polyoxetane is slightly less polar than polyethelene oxide.
Both the repeating units have an oxygen atom in it. Due to which hydrogen bonding is possible. The number of carbon atoms in polyoxetane is more so, oxygen occurs less frequently in polymer chain in than in polyethelene oxide. As a result, there will be less hydrogen bonding. Hence, polyoxetane (PO) is expected to have a lower melting point than poly(ethelene oxide) (PEO).
As the strength of intermolecular forces increases, the melting point increase.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forwardDraw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forward
- 3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forward
- What is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





