
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from pyridine is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis for the given product from pyridine is shown below.
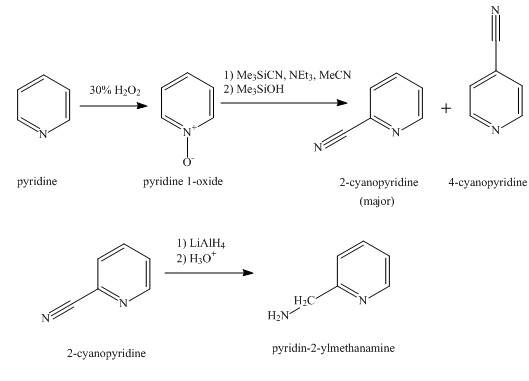
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, pyridine undergoes oxidation on nitrogen atom to form
In the second step, the treatment of
In the final step, the reduction of

Figure 1
The synthesis for the given product from pyridine is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from pyridine is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The formation of diazonium salt from aromatic
The addition of the nitro group is known as nitration.
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis for the given product from pyridine is shown below.
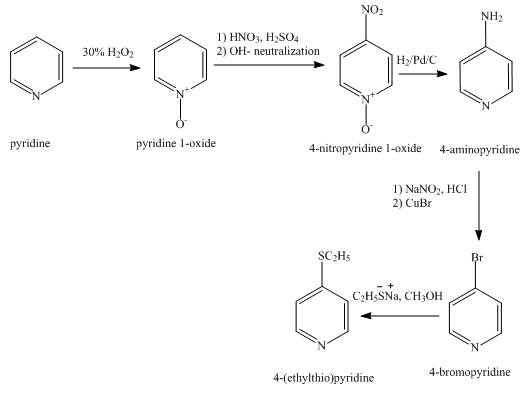
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, pyridine undergoes oxidation on nitrogen atom to form
In the third step, the reduction of
In the fourth step,
In the fifth step,
The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 2
The synthesis for the given product from pyridine is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is shown below.
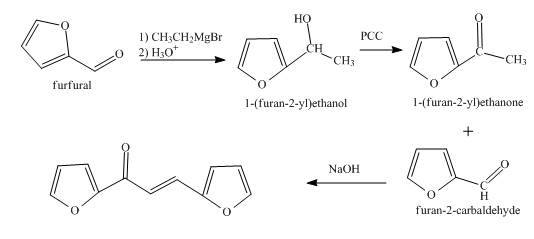
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, the treatment of fufural with
In the second step, the product obtained with the help of pyridinium chlorochromate undergoes oxidation to form the corresponding
In the final step, methyl ketone reacts with the furfural in the presence of
The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is shown below.
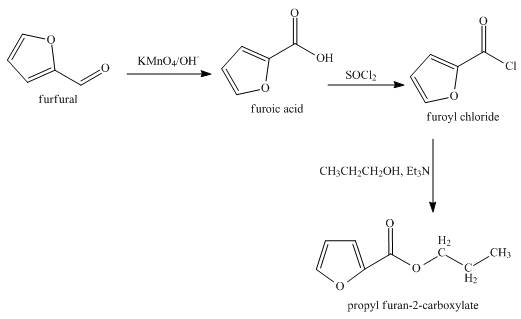
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, the reaction of furfural with
In the second step, furoic reacts acid with thionyl chloride to form furoyl chloride. The type of reaction is nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
In the third step, furoyl chloride with
The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
The synthesis of the given product from furfural is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increasing in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis of the given product from
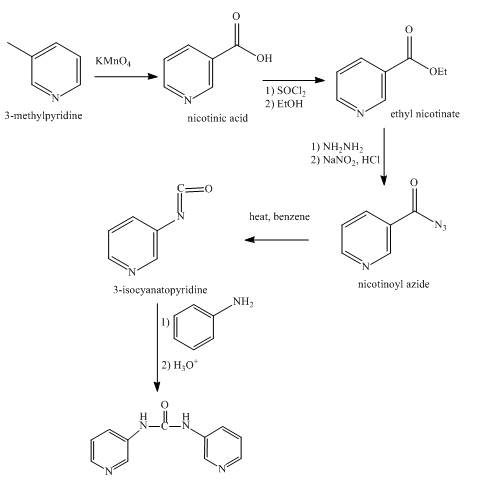
Explanation of Solution
In the first step,
In the second step, the reaction between nicotinic acid and thionyl chloride takes place in the presence of ethanol and gives the corresponding methyl ester as product.
In the third step, the reaction between methyl ester with hydrazine in the presence of
In the fourth step, the acyl azide on heating with benzene gives isocyanate as the product.
In the fifth step, the isocyanate is treated with

Figure 5
The synthesis of the given product from
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis of the given product from
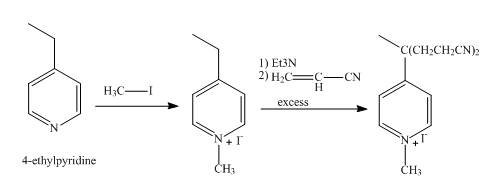
Explanation of Solution
In the first step, the reaction of
In the second step,
The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The synthesis of the given product from
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the given product from
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 26.39AP
The synthesis of the given product from
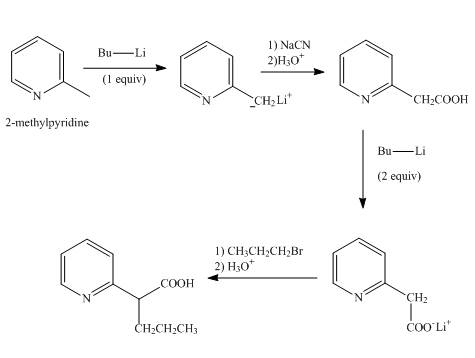
Explanation of Solution
In the first step,
In the second step, the treatment of resonance stabilized anion with sodium cyanide followed by hydrolysis gives a
In the third step, the treatment of
In the final step, the resonance stabilized anion undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction with propyl bromide to form the desired product.
The overall reaction is shown below.

Figure 7
The synthesis of the given product from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Can I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forward
- I'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





