
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of polyisobutylene is to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.21SP
The structure of polyisobutylene is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Polyisobutylene formed from the cationic polymerization of isobutylene which proceeds through the formation of tertiary cation at the carbon containing two methyl groups. Therefore, the structure of polyisobutylene polymer is,
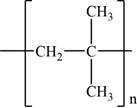
Figure 1: Structure of polyisobutylene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The polymerization of isobutylene is an addition or condensation polymerization is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Polymerization is the process of formation of a long chain polymer by the reaction of one or two monomer. The product formed in the polymerization contains the repeated units of the monomer from which it is formed.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.21SP
The polymerization of isobutylene to form butyl rubber is an addition polymerization.
Explanation of Solution
Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which polymer is formed by the addition of several monomer units to form a long chain polymer. It generally consists of one monomer unit.
Condensation polymerization is the polymerization in which two or more monomers combine to form a larger product along with the loss of water molecules. The resultant product repeatedly combines with another product to form long chain polymer.
The polymerization of isobutylene involves the addition of several monomer units to form a long chain polymer. Therefore, this is an example of addition polymerization.
(c)
Interpretation:
The polymerization of isobutylene would be most appropriate in cationic, anionic or free radical polymerization condition is to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Polymerization is the process of formation of a long chain polymer by the reaction of one or two monomer. The product formed in the polymerization contains the repeated units of the monomer from which it is formed.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.21SP
The polymerization of isobutylene to form butyl rubber proceeds in most appropriate way through cationic polymerization.
Explanation of Solution
The formation of a long chain polymer becomes favorable only due to the stability of intermediate formed in the chain propagating step. Higher is the stability of cation, anion or free radical formed in the polymerization reaction, more favorable will be the polymerization process. In case of isobutylene, one carbon atom contains two electron donating groups which increase electron density on the carbon atom. Therefore, the formation of cation is more favorable in case of isobutylene as it forms tertiary cation and stabilized by two electron donating groups. Thus, the polymerization of isobutylene occurs in the most appropriate way through cationic polymerization.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II LAB MANUAL>CUSTOM<
- CHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forwardCan anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forward
- Draw the Fischer projection of D-fructose. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Skip Part Check AP 14 tv SC F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 ! 2 # 3 CF F5 75 Ax MacBook Air 894 $ 5olo % Λ 6 > W F6 K F7 &arrow_forwardConsider this step in a radical reaction: Y What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ionization propagation initialization passivation none of the abovearrow_forward22.16 The following groups are ortho-para directors. (a) -C=CH₂ H (d) -Br (b) -NH2 (c) -OCHS Draw a contributing structure for the resonance-stabilized cation formed during elec- trophilic aromatic substitution that shows the role of each group in stabilizing the intermediate by further delocalizing its positive charge. 22.17 Predict the major product or products from treatment of each compound with Cl₁/FeCl₂- OH (b) NO2 CHO 22.18 How do you account for the fact that phenyl acetate is less reactive toward electro- philic aromatic substitution than anisole? Phenyl acetate Anisole CH (d)arrow_forward
- Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardHelp me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forward
- Is an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forwardHelp me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





