
Concept explainers
Figure 26-15 shows cross sections through three long conductors of the same length and material, with square cross sections of edge lengths as shown. Conductor B fits snugly within conductor A, and conductor C fits snugly within conductor B. Rank the following according to their end-to-end resistances, greatest first: the individual conductors and the combinations of A + B (B inside A), B + C(C inside B), and A + B + C(B inside A inside C).
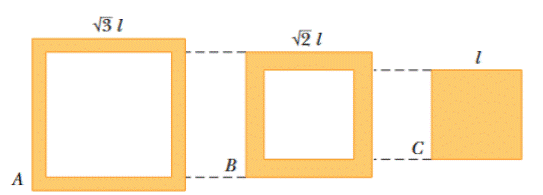
Figure 26-15 Question 1.
To find:
Ranking of resistances from greatest to lowest.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
Ranking of resistances from greatest to lowest is
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
We use the formula of resistance related to resistivity, length, and area. Here, we have given the material and length as same for the given conductors, so the resistivity and length are same for all. So, the resistance will be proportional to only the area of cross section of the conductor. Using the proportionality relation, we can rank the resistances for given combinations.
2) Formula:
3) Given:
Figure 26-15 is the cross sections of conductors.
4) Calculation:
We can calculate the area of cross section of each conductor as,
Area of conductor C is
Similarly, area of conductor A is
We know the formula,
Here, the given conductors are of same material and length so the resistivity and length are the same for each conductor, so the resistance depends on only the area of cross section of the conductor as,
The resistancesof given combination of conductors are,
For combination of
For
For
From this, we can rank the resistances from greatest to lowest as follows,
Conclusion:
We can rank the combination of conductors of same material and length according to the resistance from their area of cross section.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS V.1
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- The character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forwarda) What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless. T = b) If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg? mm =arrow_forward
- Curve Fitter CURVE FITTER Open Update Fit Save New Exclusion Rules Select Validation Data Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic Auto Fourier Fit Fit Duplicate Data Manual FILE DATA FIT TYPE FIT Harmonic Motion X us 0.45 mi ce 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 Residuals Plot Contour Plot Plot Prediction Bounds None VISUALIZATION Colormap Export PREFERENCES EXPORT Fit Options COA Fourier Equation Fit Plot x vs. t -Harmonic Motion a0+ a1*cos(x*w) + b1*sin(x*w) Number of terms Center and scale 1 ▸ Advanced Options Read about fit options Results Value Lower Upper 0.15 a0 0.1586 0.1551 0.1620 a1 0.0163 0.0115 0.0211 0.1 b1 0.0011 -0.0093 0.0115 W 1.0473 0.9880 1.1066 2 8 10 t 12 14 16 18 20 Goodness of Fit Value Table of Fits SSE 0.2671 Fit State Fit name Data Harmonic Motion x vs. t Fit type fourier1 R-square 0.13345 SSE DFE 0.26712 296 Adj R-sq 0.12467 RMSE 0.030041 # Coeff Valic R-square 0.1335 4 DFE 296.0000 Adj R-sq 0.1247 RMSE 0.0300arrow_forwardWhat point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?arrow_forwardLet's assume that the brightness of a field-emission electron gun is given by β = 4iB π² d²α² a) Assuming a gun brightness of 5x108 A/(cm²sr), if we want to have an electron beam with a semi-convergence angle of 5 milliradian and a probe current of 1 nA, What will be the effective source size? (5 points) b) For the same electron gun, plot the dependence of the probe current on the parameter (dpa) for α = 2, 5, and 10 milliradian, respectively. Hint: use nm as the unit for the electron probe size and display the three plots on the same graph. (10 points)arrow_forward
- i need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearlyarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardReview the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle. Equation: SF=ma Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





