
a.
To compute: The
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
b.
Adequate information:
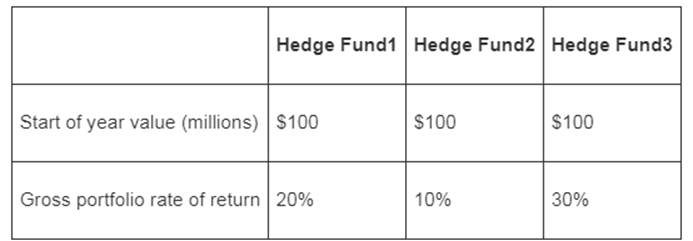
To compute: The value of the investor’s portfolio at the end of the year.
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
c.
To evaluate: The investor’s rate of return in SA fund is higher than in FF.
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
d.
To compute: The return on the portfolio held by hedge fund.
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
e.
Adequate information:
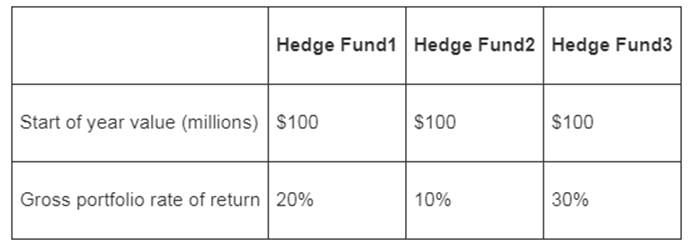
To evaluate: Whether the FF and SA funds will charge incentive fees.
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
f.
To evaluate: The reason behind the investor of FF still doing worse than the investor in SA funds.
Introduction:
Hedge Fund: Nowadays, the individual investments of different investors are collected and pooled. Later, this consolidated amount is reinvested in assets. The consolidated amount can be termed as hedge fund.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
- What are capital markets, and what is the purpose of capital markets? What is the foundation of the study on capital markets coping methods and increasing self-understanding? What are the general problems of capital markets to be addressed, and what are the consequences arising from the capital market?arrow_forwardMeticulous Drill & Reamer (MD&R) specializes in drilling and boring precise holes in hard metals (e.g., steel alloys, tungsten carbide, and titanium). The company recently contracted to drill holes with 3-centimeter diameters in large carbon-steel alloy disks, and it will have to purchase a special drill to complete this job. MD&R has eliminated all but two of the drills it has been considering: Davis Drills' T2005 and Worth Industrial Tools' AZ100. These producers have each agreed to allow MD&R to use a T2005 and an AZ100 for one week to determine which drill it will purchase. During the one-week trial, MD&R uses each of these drills to drill 31 holes with a target diameter of 3 centimeters in one large carbon-steel alloy disk, then measures the diameter of each hole and records the results. MD&R's results are provided in the table that follows and are available in the DATAfile named MeticulousDrills, Hole Diameter T2005 AZ100 3.06 2.91 3.04 3.31 3.13 2.82 3.01 3.01 2.95 2.94 3.02…arrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forward
- hello tutor:If submitted image is blurr then please comment i will write values. i will give unhelpful please.arrow_forwardLara Fredericks is interested in two mutually exclusive investments. Both investments cover the same time horizon of 5 years. The cost of the first investment is $9900, and Lara expects equal and consecutive year-end payments of $3400. The second investment promises equal and consecutive payments of $4100 with an initial outlay of $12500 required. The current required return on the first investment is 8.4 %, and the second carries a required return of 10.4 %.a. What is the net present value of the first investment?b. What is the net present value of the second investment?c. Being mutually exclusive, which investment should Lara choose? d. Which investment is relatively more risky? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat are some of the characteristics of a firm with a long operating cycle?arrow_forward
- About this Assignment For this Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes the types of organizational business structures. You will apply knowledge of business structure concepts as acquired in the course. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Project Prompts The written research paper should be at least 1,000 to 1,200 words in length and should include four sections based on the business structures studied throughout the course. Define each business structure, compare the corporate finance strategies of the four business structures, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each business structure, and how each varies in taxation. Research Paper Sections ⚫ Sole Proprietorship ⚫ Partnership • Corporation ⚫ Limited Liability Company (LLC)arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER THE COLUMN FULLY AND CORRECTLY PLEASE DO THE RIGHT CALCULATION DOUBLE CHECK AS WELL TO GIVE ME THE RIGHT ANSWER REQUIRED: Given the following information, what are the NZD/SGD currency against currency bid-ask quotations? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 4 decimal places. Bank Quotations American Terms European Terms Bid Ask Bid Ask New Zealand dollar 0.733 0.7340 1.3870 1.3884 Singapore dollar 0.6186 0.6191 1.6423 1.6436 answer Bid Ask New Zealand dollar ? ? Singapore dollar ? ?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For the Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes and discusses organizational financial risks. You will apply knowledge acquired in the course and use the concepts of multiple financial risks as the basis of research and analysis. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Audience: upper-level business students. Project Prompt Write a 1,000-1,200-word analysis discussing financial risk concepts and assess the impact of the different financial risks on an organization. For this assignment, you will structure your assignment using four research paper sections associated with corporate risk management, as studied in the course. Base your research paper on the financial statements analyzed in Corporate Finance 301 assignment 2 and apply the knowledge acquired in the analysis. Define each financial risk, discuss the risk associated components, and evaluate the financial risks and how they affect the corporation's…arrow_forward
- Bobby Nelson, made deposits of $880 at the end of each year for 6 years. Interest is 6% compounded annually. What is the value of Bobby’s annuity at the end of 6 years?arrow_forward1. Find the future value if $1,250 is invested in Simple interest account paying 6.5%: a. for 5 years b. for 20 years 2. Find the future amount $ 35,000 is invested for 30 years at 4.25% compounded: a. annually b. Quarterly c. monthly d. weekly 3. How much should be put into an account today that pays 7.75% compounded monthly if you need $10,000 in 5 years. 4. Find the effective rate for: a. 5.75% compounded quarterly b. 6.25% compounded daily. 5. $50 is invested at the end of each month into an account paying 7.5% compounded monthly. How much will be in the account after 5 years?…arrow_forwardSolve step by step no aiarrow_forward
 Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
