
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119472780
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 26, Problem 11Q
Figure 26-23 gives, for three wires of radius R, the current density J(r) versus radius r, as measured from the center of a circular cross section through the wire. The wires are all made from the same material. Rank the wires according to the magnitude of the electric field (a) at the center, (b) halfway to the surface, and (c) at the surface, greatest first.
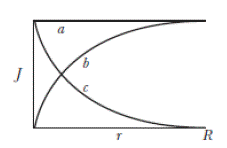
Figure 26-23 Question 11.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Point charges q1 = 50 µC and q2 = −25 µC are placed 1.0 m apart. What is the magnitude of the force on a third charge q3 = 40 µC placed midway between q1 and q2? (The prefix µ =10−6 C.)
The de-excitation of a state occurs by competing emission and relaxation processes. If the relaxation mechanisms are very effective:a) the emission of radiation is largeb) the emission of radiation is smallc) the emission occurs at a shorter wavelengthd) the de-excitation occurs only by emission processes
m
C
A block of mass m slides down a ramp of height hand
collides with an identical block that is initially at rest.
The two blocks stick together and travel around a loop of
radius R without losing contact with the track. Point A is
at the top of the loop, point B is at the end of a horizon-
tal diameter, and point C is at the bottom of the loop, as
shown in the figure above. Assume that friction between
the track and blocks is negligible.
(a) The dots below represent the two connected
blocks at points A, B, and C. Draw free-body dia-
grams showing and labeling the forces (not com
ponents) exerted on the blocks at each position.
Draw the relative lengths of all vectors to reflect
the relative magnitude of the forces.
Point A
Point B
Point C
(b) For each of the following, derive an expression in
terms of m, h, R, and fundamental constants.
i. The speed of moving block at the bottom of
the ramp, just before it contacts the stationary
block
ii. The speed of the two blocks immediately…
Chapter 26 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
Ch. 26 - Figure 26-15 shows cross sections through three...Ch. 26 - Figure 26-16 shows cross sections through three...Ch. 26 - Figure 26-17 shows a rectangular solid conductor...Ch. 26 - Figure 26-18 shows plots of the current i through...Ch. 26 - Figure 26-19 shows four situations in which...Ch. 26 - In Fig. 26-20, a wire that carries a current...Ch. 26 - Figure 26-21 gives the electric potential Vx...Ch. 26 - The following table give the lengths of three...Ch. 26 - Prob. 9QCh. 26 - Three wires, of the same diameter, are connected...
Ch. 26 - Figure 26-23 gives, for three wires of radius R,...Ch. 26 - During the 4.0 min a 5.0 A current is set up in a...Ch. 26 - An isolated conducting sphere has a 10 cm radius....Ch. 26 - A charged belt, 50 cm wide, travels at 30 m/s...Ch. 26 - The United States National Electric Code, which...Ch. 26 - SSM WWW A beam contains 2.0 108 doubly charged...Ch. 26 - A certain cylindrical wire carries current. We...Ch. 26 - A fuse in an electric circuit is a wire that is...Ch. 26 - Prob. 8PCh. 26 - The magnitude Jr of the current density in a...Ch. 26 - The magnitude J of the current density in a...Ch. 26 - What is the current in a wire of radius R = 3.40...Ch. 26 - Near Earth, the density of protons in the solar...Ch. 26 - Prob. 13PCh. 26 - A human being can be electrocuted if a current as...Ch. 26 - SSM A coil is formed by winding 250 turns of...Ch. 26 - Copper and aluminium are being considered for a...Ch. 26 - Prob. 17PCh. 26 - A wire 4.00 m long and 6.00 mm in diameter has a...Ch. 26 - SSM What is the resistivity of a wire of 1.0 mm...Ch. 26 - Prob. 20PCh. 26 - ILW A common flashlight bulb is rated at 0.30 A...Ch. 26 - Kiting during a storm. The legend that Benjamin...Ch. 26 - Prob. 23PCh. 26 - GO Figure 26-25a gives the magnitude Ex of the...Ch. 26 - SSM ILW A wire with a resistance of 6.0 is drawn...Ch. 26 - In Fig. 26-26a. a 9.00 V battery is connected to a...Ch. 26 - SSM WWW Two conductors are made of the same...Ch. 26 - GO Figure 26-27 gives the electric potential Vx...Ch. 26 - Prob. 29PCh. 26 - Prob. 30PCh. 26 - Prob. 31PCh. 26 - Prob. 32PCh. 26 - Prob. 33PCh. 26 - GO Figure 26-29 shows wire section 1 of diameter...Ch. 26 - GO In Fig. 26-30, current is set up through a...Ch. 26 - GO Swimming during a storm. Figure 26-31 shows a...Ch. 26 - Prob. 37PCh. 26 - In Fig. 26-32a, a 20 resistor is connected to a...Ch. 26 - A certain brand of hot-dog cooker works by...Ch. 26 - Thermal energy is produced in a resistor at a rate...Ch. 26 - SSM A 1220 V potential difference is applied to a...Ch. 26 - In Fig. 26-33, a battery of potential difference V...Ch. 26 - ILW An unknown resistor is connected between the...Ch. 26 - A student kept his 6.0 V, 7.0 W radio turned on at...Ch. 26 - SSM ILW A 1250 W radiant heater is constructed to...Ch. 26 - A copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.00 106 m2...Ch. 26 - A heating element is made by maintaining a...Ch. 26 - Exploding shoes. The rain-soaked shoes of a person...Ch. 26 - A 100 W lightbulb is plugged into a standard 120 V...Ch. 26 - GO The current through the battery and resistors 1...Ch. 26 - GO SSM WWW Wire C and wire D are made from...Ch. 26 - GO The current-density magnitude in a certain...Ch. 26 - A 120 V potential difference is applied to a space...Ch. 26 - Go Figure 26-36a shows a rod of resistive...Ch. 26 - SSM A Nichrome heater dissipates 500 W when the...Ch. 26 - Prob. 56PCh. 26 - An 18.0 W device has 9.00 V across it. How much...Ch. 26 - An aluminum rod with a square cross section is 1.3...Ch. 26 - A cylindrical metal rod is 1.60 m long and 5.50 mm...Ch. 26 - The chocolate crumb mystery. This story begins...Ch. 26 - SSM A steady beam of alpha particles q = 2e...Ch. 26 - A resistor with a potential difference of 200 V...Ch. 26 - A 2.0 kW heater element from a dryer has a length...Ch. 26 - cylindrical resistor of radius 5.0 mm and length...Ch. 26 - A potential difference V is applied to a wire of...Ch. 26 - The headlights of a moving car require about 10 A...Ch. 26 - A 500 W heating unit is designed to operate with...Ch. 26 - The copper windings of a motor have a resistance...Ch. 26 - How much electrical energy is transferred to...Ch. 26 - A caterpillar of length 4.0 cm crawls in the...Ch. 26 - Prob. 71PCh. 26 - A steel trolley-car rail has a cross-sectional...Ch. 26 - A coil of current-carrying Nichrome wire is...Ch. 26 - Prob. 74PCh. 26 - A certain x-ray tube operates at a current of 7.00...Ch. 26 - A current is established in a gas discharge tube...Ch. 26 - Prob. 77PCh. 26 - An insulating belt moves at speed 30 m/s and has a...Ch. 26 - In a hypothetical fusion research lab, high...Ch. 26 - When a metal rod is heated, not only its...Ch. 26 - A beam of 16 MeV deuterons from a cyclotron...Ch. 26 - A linear accelerator produces a pulsed beam of...Ch. 26 - An electric immersion heater normally takes 100...Ch. 26 - A 400 W immersion heater is placed in a pot...Ch. 26 - A 30 F capacitor is connected across a programmed...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Your microbiology lab maintains reference bacterial cultures, which are regularly transferred to new nutrient a...
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
PRACTICE 1.3 The melting point of table salt is 1474oF. What temperature is this on the Celsius and Kelvin scal...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
52. The shiny surface of a CD is imprinted with millions of tiny pits, arranged in a pattern of thousands of es...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Johnny was vigorously exercising the only joints in the skull that are freely movable. What would you guess he ...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
How does an obligate aerobe differ from a facultative aerobe?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The velocity of an elevator is given by the graph shown. Assume the positive direction is upward. Velocity (m/s) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 0 5.0 10 15 20 25 Time (s) (a) Briefly describe the motion of the elevator. Justify your description with reference to the graph. (b) Assume the elevator starts from an initial position of y = 0 at t=0. Deriving any numerical values you need from the graph: i. Write an equation for the position as a function of time for the elevator from t=0 to t = 3.0 seconds. ii. Write an equation for the position as a function of time for the elevator from t = 3.0 seconds to t = 19 seconds. (c) A student of weight mg gets on the elevator and rides the elevator during the time interval shown in the graph. Consider the force of con- tact, F, between the floor and the student. How Justify your answer with reference to the graph does F compare to mg at the following times? and your equations above. i. = 1.0 s ii. = 10.0 sarrow_forwardStudents are asked to use circular motion to measure the coefficient of static friction between two materials. They have a round turntable with a surface made from one of the materials, for which they can vary the speed of rotation. They also have a small block of mass m made from the sec- ond material. A rough sketch of the apparatus is shown in the figure below. Additionally they have equipment normally found in a physics classroom. Axis m (a) Briefly describe a procedure that would allow you to use this apparatus to calculate the coefficient of static friction, u. (b) Based on your procedure, determine how to analyze the data collected to calculate the coefficient of friction. (c) One group of students collects the following data. r (m) fm (rev/s) 0.050 1.30 0.10 0.88 0.15 0.74 0.20 0.61 0.25 0.58 i. Use the empty spaces in the table as needed to calculate quantities that would allow you to use the slope of a line graph to calculate the coefficient of friction, providing labels with…arrow_forwardPART Aarrow_forward
- answer both questionarrow_forwardOnly part A.) of the questionarrow_forwardIn general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, -3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forward
- In general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, −3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardOnly Part C.) is necessaryarrow_forwardOnly Part B.) is necessaryarrow_forward
- A (3.60 m) 30.0°- 70.0° x B (2.40 m)arrow_forwardIn general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, -3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardfine the magnitude of the vector product express in sq meters what direction is the vector product in -z or +zarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Ohm's law Explained; Author: ALL ABOUT ELECTRONICS;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PV8CMZZKrB4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY