
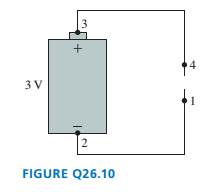
FIGURE Q26.10 shows a 3 V battery with metal wires attached to each end. What are the potential differences
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- The drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. I believe side 1 is 60 degrees but could be wrong. Thank you.arrow_forwardAfter the countdown at the beginning of a Mario Kart race, Bowser slams on the gas, taking off from rest. Bowser get up to a full speed of 25.5 m/s due to an acceleration of 10.4 m/s2.arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forward
- The drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardAccording to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forward
- According to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forwardAccording to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forwardThree point-like charges in the attached image are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 38.0 cm, and the point (C) is located half way between q1 and q3 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (C). Let q1 = −2.80 µC, q2 = −3.40 µC, and q3 = −4.50 µC. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Three point-like charges are placed as shown in the attach image, where r1 = r2 = 44.0 cm. Find the magnitude of the electric force exerted on the charge q3. Let q1 = -1.90 uC, q2 = -2.60 uC, and q3 = +3.60 uC. Thank you.arrow_forwardThe drawing attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m², while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m². The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (1 and 2 combined) if the angle theta made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardA car driving at 27m/s veers to the left to avoid a deer in the road. The maneuver takes 2.0s and the direction of travel is altered by 20 degrees. What is the average acceleration during the constant speed maneuver? Do this in accordance with the example in the chapter.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





