
(a)
Interpretation:
The amino acid formed when
Concept introduction:
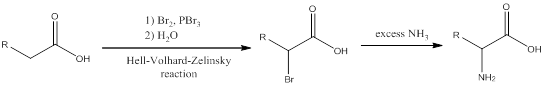
To identify: the amino acid formed when the given carboxylic acid is treated with bromine, phosphorous tribromide and followed by excess ammonia,
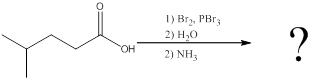
(b)
Interpretation:
The amino acid formed when carboxylic acid is treated with bromine and phosphorous tribromide, followed by water and the resulting
Concept introduction:

To identify: the amino acid formed when the given carboxylic acid is treated with bromine, phosphorous tribromide and followed by excess ammonia,
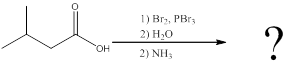
(c)
Interpretation:
The amino acid formed when carboxylic acid is treated with bromine and phosphorous tribromide, followed by water and the resulting
Concept introduction:

To identify: the amino acid formed when the given carboxylic acid is treated with bromine, phosphorous tribromide and followed by excess ammonia,
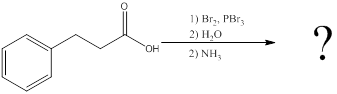
(d)
Interpretation:
The amino acid formed when carboxylic acid is treated with bromine and phosphorous tribromide, followed by water and the resulting
Concept introduction:

To identify: the amino acid formed when the given carboxylic acid is treated with bromine, phosphorous tribromide and followed by excess ammonia,
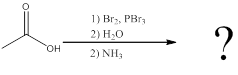
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/WILEYPLUS
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





