
Concept explainers
(a)
The angle of the reflected and refracted rays when light ray incident from the air at angle of incidence
(a)
Answer to Problem 40P
The angle of reflection is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The index of refraction of glass is
From, law of reflection, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Thus, angle of reflection is
From Snell’s law,
Here,
Substitute
The figure below shows the angle of incidence, the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction.
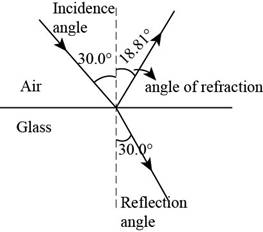
Figure (1)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is
(b)
The angle of the reflected and refracted rays when light ray incident from the glass at angle of incidence
(b)
Answer to Problem 40P
The angle of reflection is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The index of refraction of glass is
From, law of reflection, angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Thus, angle of reflection is
From, Snell’s law,
Here,
Substitute
The figure below shows the angle of incidence, the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction.
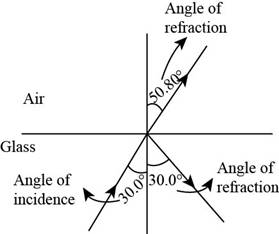
Figure (2)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is
(c)
The angles of reflection and refraction for all angles of incidence at
(c)
Answer to Problem 40P
The angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for rays incident from air onto the air-glass surface is increasing as angle of incidence is increasing. The table for different values of angles is,
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Explanation of Solution
From, law of reflection, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. So for all value of angles between
The formula to calculate the angle of refraction is,
From, Snell’s law,
Substitute
Substitute
The remaining values of the angle of refraction can be calculated by the same method.
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the of angle of refraction for rays incident from air onto the air-glass surface is increasing as angle of incidence is increasing.
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d)
The angles of reflection and refraction for all angles of incidence at
(d)
Answer to Problem 40P
The angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the of angle of refraction for rays coming up to the interface through the glass will increase up to angle of incidence
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Explanation of Solution
From, the law of reflection, angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. So, for all value of angles between
The formula to calculate the angle of refraction is,
From, Snell’s law,
Substitute
Substitute
The remaining values of the angle of refraction can be calculated by the same method.
The formula to calculate the critical angle is,
Here,
Substitute
The angle of incidence is greater than
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the of angle of refraction for rays coming up to the interface through the glass will increase up to angle of incidence
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax





