
Concept explainers
Solve the following problem over the interval from
(a) Analytically.
(b) Euler's method.
(c) Heun's method without iteration.
(d) Ralston's method.
(e) Fourth-order RK method.
(a)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solution to the initial value problem is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
To solvean initial value problem of the form
Calculation:
Rewrite the provided differential equation as,
Integrate both sides to get,
Now use the initial condition
Hence, the analytical solution of the initial value problem is
(b)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: For
| t | y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 0.25 | 1.25 |
| 0.5 | 1.809017 |
| 0.75 | 2.817765 |
| 1 | 4.496385 |
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solvean initial value problem of the form
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
Further,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Euler’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
| T | y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 0.25 | 1.25 |
| 0.5 | 1.809017 |
| 0.75 | 2.817765 |
| 1 | 4.496385 |
(c)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
And,
Thus,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Heun’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
Theresults thus obtained aretabulated as,
(d)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
And,
Thus,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Ralston’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
(e)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Ans,
And,
And,
Therefore,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement RK method of order four, solve the differential equation, and compare the results obtained from part (a) to part (e) on a single plot.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
Plot for all the methods along with the analytical solution
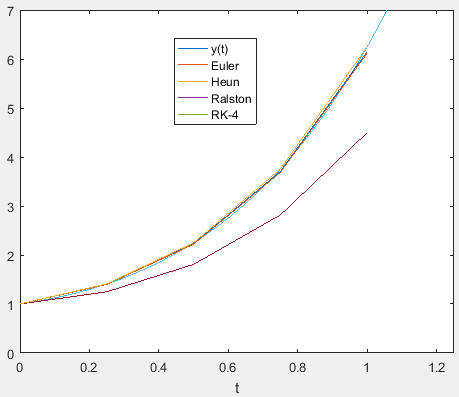
From the graph, it is inferred that the RK method of order 4 is the best approximation to the solution.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Note: A waiting line model solver computer package is needed to answer these questions. The Kolkmeyer Manufacturing Company uses a group of six identical machines, each of which operates an average of 18 hours between breakdowns. With randomly occurring breakdowns, the Poisson probability distribution is used to describe the machine breakdown arrival process. One person from the maintenance department provides the single-server repair service for the six machines. Management is now considering adding two machines to its manufacturing operation. This addition will bring the number of machines to eight. The president of Kolkmeyer asked for a study of the need to add a second employee to the repair operation. The service rate for each individual assigned to the repair operation is 0.50 machines per hour. (a) Compute the operating characteristics if the company retains the single-employee repair operation. (Round your answers to four decimal places. Report time in hours.) La = L = Wa = W =…arrow_forwardUse the Euclidean algorithm to find two sets of integers (a, b, c) such that 55a65b+143c: Solution = 1. By the Euclidean algorithm, we have: 143 = 2.65 + 13 and 65 = 5.13, so 13 = 143 – 2.65. - Also, 55 = 4.13+3, 13 = 4.3 + 1 and 3 = 3.1, so 1 = 13 — 4.3 = 13 — 4(55 – 4.13) = 17.13 – 4.55. Combining these, we have: 1 = 17(143 – 2.65) - 4.55 = −4.55 - 34.65 + 17.143, so we can take a = − −4, b = −34, c = 17. By carrying out the division algorithm in other ways, we obtain different solutions, such as 19.55 23.65 +7.143, so a = = 9, b -23, c = 7. = = how ? come [Note that 13.55 + 11.65 - 10.143 0, so we can obtain new solutions by adding multiples of this equation, or similar equations.]arrow_forward- Let n = 7, let p = 23 and let S be the set of least positive residues mod p of the first (p − 1)/2 multiple of n, i.e. n mod p, 2n mod p, ..., p-1 2 -n mod p. Let T be the subset of S consisting of those residues which exceed p/2. Find the set T, and hence compute the Legendre symbol (7|23). 23 32 how come? The first 11 multiples of 7 reduced mod 23 are 7, 14, 21, 5, 12, 19, 3, 10, 17, 1, 8. The set T is the subset of these residues exceeding So T = {12, 14, 17, 19, 21}. By Gauss' lemma (Apostol Theorem 9.6), (7|23) = (−1)|T| = (−1)5 = −1.arrow_forward
- Let n = 7, let p = 23 and let S be the set of least positive residues mod p of the first (p-1)/2 multiple of n, i.e. n mod p, 2n mod p, ..., 2 p-1 -n mod p. Let T be the subset of S consisting of those residues which exceed p/2. Find the set T, and hence compute the Legendre symbol (7|23). The first 11 multiples of 7 reduced mod 23 are 7, 14, 21, 5, 12, 19, 3, 10, 17, 1, 8. 23 The set T is the subset of these residues exceeding 2° So T = {12, 14, 17, 19, 21}. By Gauss' lemma (Apostol Theorem 9.6), (7|23) = (−1)|T| = (−1)5 = −1. how come?arrow_forwardShading a Venn diagram with 3 sets: Unions, intersections, and... The Venn diagram shows sets A, B, C, and the universal set U. Shade (CUA)' n B on the Venn diagram. U Explanation Check A- B Q Search 田arrow_forwardWhat is the area of this figure? 5 mm 4 mm 3 mm square millimeters 11 mm Submit 8 mm Work it out 9 mmarrow_forward
- Please explain how come of X2(n).arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardFind all solutions of the polynomial congruence x²+4x+1 = 0 (mod 143). (The solutions of the congruence x² + 4x+1=0 (mod 11) are x = 3,4 (mod 11) and the solutions of the congruence x² +4x+1 = 0 (mod 13) are x = 2,7 (mod 13).)arrow_forward
- Determine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.The notation Z_(n) refers to the set {0,1,2,...,n-1}. For example, Z_(4)={0,1,2,3}. f: Z_(6) -> Z_(6) defined by f(x)=x^(2)+4(mod6). g: Z_(5) -> Z_(5) defined by g(x)=x^(2)-11(mod5). h: Z*Z -> Z defined by h(x,y)=x+2y. j: R-{3} -> R defined by j(x)=(4x)/(x-3).arrow_forwardDetermine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.arrow_forwardLet A = {a, b, c, d}, B = {a,b,c}, and C = {s, t, u,v}. Draw an arrow diagram of a function for each of the following descriptions. If no such function exists, briefly explain why. (a) A function f : AC whose range is the set C. (b) A function g: BC whose range is the set C. (c) A function g: BC that is injective. (d) A function j : A → C that is not bijective.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage


 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





