
Concept explainers
Concept Introduction:
Capital budgeting is a planning process used to know whether a long term investment or options like to keep the old machine will be profitable or not involving factors like present value factors.
There are many capital budgeting techniques. The two techniques that will be discussed here is –
1. Payback period of the investment
2.
1. Payback period –
Payback period of the investment is calculated as under –
This is how we calculate payback period in case of even annual net cash inflows.
2. Net present value –
The net present value is calculated as under –
Initial investment can be defined as the cash outlay incurred at the beginning of the product and total present value of cash inflows is computed as under (in case of even cash inflows) –
This is how we calculate net present value of an investment.
Requirement 1
To compute:
Payback period of Investment
Answer to Problem 29QS
Solution:
Payback period of Investment = 5 years
Explanation of Solution
Payback period of the investment is calculated as under –
Given,
• Initial investment = $ 80 million
• Annual net
Thus, the payback period of the investment = 5 years.
Requirement 2
To compute:
Net present value of the investment.
Answer to Problem 29QS
Solution:
Net present value of the investment = $11.952 million
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Initial investment = $ 80 million
Total present value of cash inflows will be calculated as under –
Now, for present value of cash inflows –
Given –
• Annual net
• Number of years = 8 years
• Interest rate or required rate = 8%
Total present value of cash inflows =
Net present value of the investment will be calculated as under –
Initial investment = $ 80 million
Total present value of cash inflows = $ 91.952 million
Thus, the net present value of the investment = $ 11.952 million.
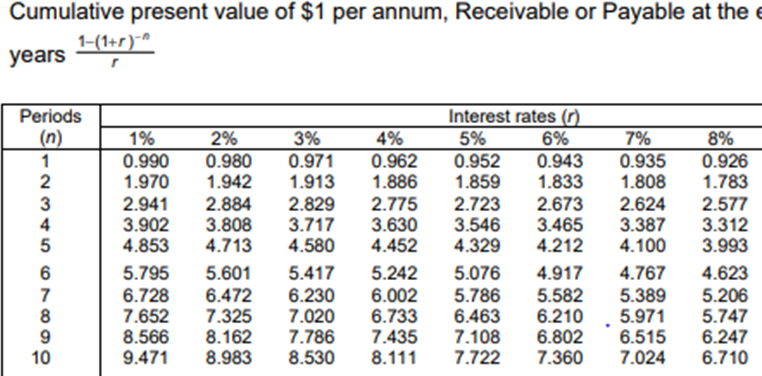
Note – The following PVAF table has been used for referring PVAF @ 8 % for 8 years.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Fundamental Accounting Principles
- Nordica Chemicals produces joint products M and N from Compound Z in a single operation. 800 liters of Compound Z, costing $2,400, produce 500 liters of Product M, selling for $3.50 per liter, and 300 liters of Product N, selling for $6.00 per liter. The portion of the $2,400 cost that should be allocated to Product M using the value basis of allocation is____.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardCan you explain the correct approach to solve this general accounting question?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





