
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The following intermediate compound generated in the first or second cycle of the lipogenesis pathway is produced by (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) a hydrogenation reaction, or (3) a condensation reaction has to be identified.
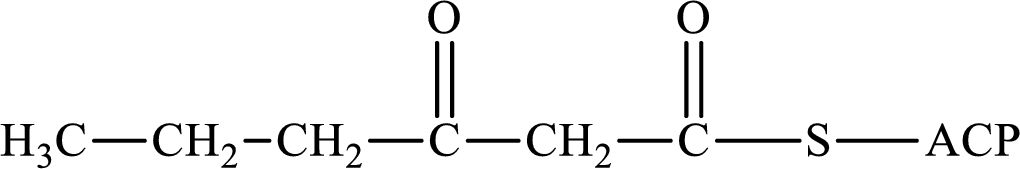
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The different reactions that are involved in the cyclic process are:

In hydrogenation reaction, a hydrogen molecule (H2) is added to an organic substance; in hydration reaction, a water molecule (H2O) is added to an unsaturated substrate; in the condensation reaction, two molecules combine to form a single product.
The first turn of the cyclic process produces four-carbon acyl group and the further turns add two carbon unit to the four-carbon acyl group. Therefore, the first turn has four carbon units and the second turn has six carbon unit in their intermediate compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
The following intermediate compound generated in the first or second cycle of the lipogenesis pathway is produced by (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) a hydrogenation reaction, or (3) a condensation reaction has to be identified.
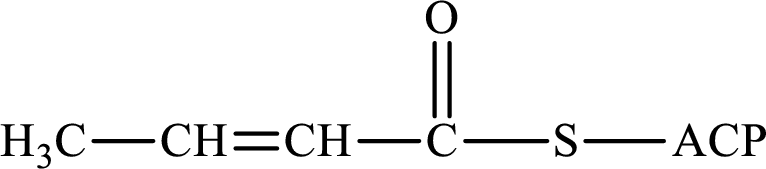
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The different reactions that are involved in the cyclic process are:

In hydrogenation reaction, a hydrogen molecule (H2) is added to an organic substance; in hydration reaction, a water molecule (H2O) is added to an unsaturated substrate; in the condensation reaction, two molecules combine to form a single product.
The first turn of the cyclic process produces four-carbon acyl group and the further turns add two carbon unit to the four-carbon acyl group. Therefore, the first turn has four carbon units and the second turn has six carbon unit in their intermediate compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
The following intermediate compound generated in the first or second cycle of the lipogenesis pathway is produced by (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) a hydrogenation reaction, or (3) a condensation reaction has to be identified.
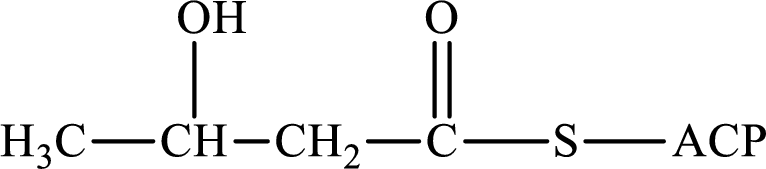
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The different reactions that are involved in the cyclic process are:

In hydrogenation reaction, a hydrogen molecule (H2) is added to an organic substance; in hydration reaction, a water molecule (H2O) is added to an unsaturated substrate; in the condensation reaction, two molecules combine to form a single product.
The first turn of the cyclic process produces four-carbon acyl group and the further turns add two carbon unit to the four-carbon acyl group. Therefore, the first turn has four carbon units and the second turn has six carbon unit in their intermediate compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The following intermediate compound generated in the first or second cycle of the lipogenesis pathway is produced by (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) a hydrogenation reaction, or (3) a condensation reaction has to be identified.
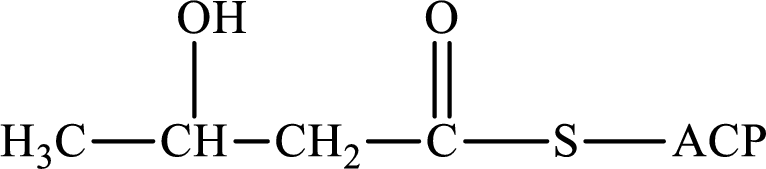
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The different reactions that are involved in the cyclic process are:

In hydrogenation reaction, a hydrogen molecule (H2) is added to an organic substance; in hydration reaction, a water molecule (H2O) is added to an unsaturated substrate; in the condensation reaction, two molecules combine to form a single product.
The first turn of the cyclic process produces four-carbon acyl group and the further turns add two carbon unit to the four-carbon acyl group. Therefore, the first turn has four carbon units and the second turn has six carbon unit in their intermediate compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
- Which of these compounds is Ester formed from the reaction of acetic acid and one propanol arrow_forwardDescribe the four labeled parts of the reaction diagram from the reaction of sucrose, breaking down with and without an enzyme.arrow_forwardHow to determine the product with mechanism showedarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



