
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the two isomeric propyl radicals that are formed on hydrogen abstraction from propane by
Concept introduction:
Radicals are species containing an unpaired electron, i.e., they are electron-poor species. Being electron-poor, they are highly unstable, and therefore, highly reactive species. They react with any other species present.
In the case of
Answer to Problem 25.42P
The two alkyl radicals produced when
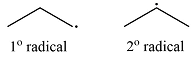
Explanation of Solution
Propane has two types of hydrogens, one attached to a primary carbon and one to a secondary carbon. The abstraction of the two types of hydrogens will produce two radicals – a primary propyl radical and a secondary propyl radical.
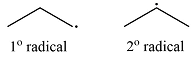
The type of radical produced when
(b)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow notation for the formation of the two isomeric propyl radicals that are formed on hydrogen abstraction from propane by
Concept introduction:
In the case of alkanes, a radical like
Curved arrow notation represents the movement of electron(s) in a reaction or resonance. Movement of a single electron is represented by a curved arrow with a half arrowhead. The arrow starts at the electron and ends on the atom or the region where it moves.
Answer to Problem 25.42P
The curved arrow notation for the formation of the two alkyl radicals produced when
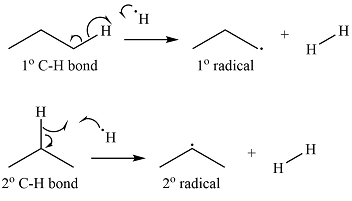
Explanation of Solution
Propane has two types of hydrogens, one attached to a primary carbon and one to a secondary carbon. The abstraction of the two types of hydrogens will produce two radicals – a primary propyl radical and a secondary propyl radical.
The
Thus, the curved arrow representation of the formation of the two radicals can be shown as

The curved arrow representation of the formation of the two radicals is drawn using half arrows on the basis of the type of hydrogen abstracted.
(c)
Interpretation:
The percentage of each propyl radical formed is to be calculated taking into account the different numbers of each type of hydrogen in propane.
Concept introduction:
The ease with which a hydrogen is abstracted from an alkane in its reaction with a radical depends on the relative stability of the type of alkyl radical that is produced. The relative stability of alkyl radicals changes as
The likelihood of abstraction of a particular type of hydrogen from an alkane also increases with the number of hydrogens of that type present in the molecule.
The percentage of formation of a particular type of alkyl radical is calculated from the product of the number of that type of hydrogens present in the molecule and its reactivity.
Answer to Problem 25.42P
The percentages of the
Explanation of Solution
The percentage of formation of each type of alkyl radical is calculated from the product of the number of that type of hydrogens present in the molecule and its reactivity.
There are six primary hydrogens and two secondary hydrogens in propane, and the reactivities of the two types are 1 and 5 respectively.
Thus, the percentages of the
The percentage of each type of radical produced is calculated from the number of hydrogens of each type and their relative reactivities.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism 1) Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalin 2) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerol 3) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided provide the correct letter that corresponds with the Carboxylic acid that is formed in the reaction below. 6 M NaOH Acid-workup WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES A) Pool of Reagents for Part B CI B) OH C) E) CI J) racemic F) K) OH N) OH P) G) OH D) HO H) L) M) HO Q) R) CI Aarrow_forwardIn the table below, the exact chemical structures for Methyl salicylate can be represented by the letter WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES CI B) A) E) Cl racemic F) J) CI K) N) OH P) Pool of Reagents for Part B OH OH G) L) OH D) HO H) M) HO Q) R) CIarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





