
Concept explainers
(a)
To identify the procedure you would use to assess the effectiveness of the exercise program and check to see if the conditions allow the use of that procedure.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19E
The procedure we will use to assess the effectiveness of the exercise program is paired t -test and all the conditions are met.
Explanation of Solution
The table for the workers for the company is given in which scores of the workers are given for the job satisfaction before and after the program is mentioned. Thus, to access the effectiveness of the exercise program we will use the paired t -test as it is used if the two groups contain the same subjects or pairs related subjects. But the two-sample t -test is used if the subjects of the two groups are not related. Thus, in this case we will use the paired t -test. And the conditions for the procedure are as follows:
Random condition: It is satisfied because the ten workers were randomly selected.
Independent condition: It is satisfied assuming that the ten workers are less than the
Normal condition: It is satisfied because the distribution is symmetric and uni-modal.
Thus, all the conditions for this test are met.
(b)
To test an appropriate hypothesis and state your conclusion.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the job satisfaction improves.
Explanation of Solution
The table for the workers for the company is given in which scores of the workers are given for the job satisfaction before and after the program is mentioned. Thus, we note that,
And we will find the difference between the two samples as:
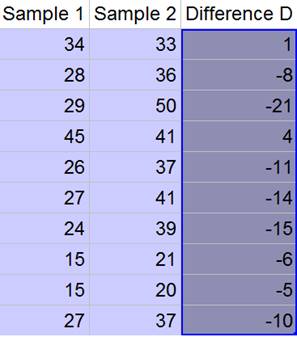
Now, the sample mean and the standard deviation of the difference are as follows:
Let us now define the hypotheses as:
Now the degree of freedom is then as:
Thus, the value of the test statistics will be then:
Thus, the P-value can be calculated using table T of appendix F as:
As we know that the P-value is less than the significance level then the null hypothesis is rejected. Thus, we have,
Thus, we conclude that there is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the job satisfaction improves.
(c)
To find out what kind of error you had commit if your conclusion turns out to be incorrect.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
If our conclusion turns out to be incorrect then it will lead to the Type I error.
Explanation of Solution
The table for the workers for the company is given in which scores of the workers are given for the job satisfaction before and after the program is mentioned. From part (b) we have that,
As we know that the P-value is less than the significance level then the null hypothesis is rejected. Thus, we have,
Thus, we conclude that there is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the job satisfaction improves. Thus,
Type I error: Reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
Type II error: Fail to reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
Thus, if our conclusion turns out to be incorrect then it will lead to the Type I error.
Chapter 25 Solutions
Stats: Modeling the World Nasta Edition Grades 9-12
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra (7th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- 21. find the mean. and variance of the following: Ⓒ x(t) = Ut +V, and V indepriv. s.t U.VN NL0, 63). X(t) = t² + Ut +V, U and V incepires have N (0,8) Ut ①xt = e UNN (0162) ~ X+ = UCOSTE, UNNL0, 62) SU, Oct ⑤Xt= 7 where U. Vindp.rus +> ½ have NL, 62). ⑥Xn = ΣY, 41, 42, 43, ... Yn vandom sample K=1 Text with mean zen and variance 6arrow_forwardA psychology researcher conducted a Chi-Square Test of Independence to examine whether there is a relationship between college students’ year in school (Freshman, Sophomore, Junior, Senior) and their preferred coping strategy for academic stress (Problem-Focused, Emotion-Focused, Avoidance). The test yielded the following result: image.png Interpret the results of this analysis. In your response, clearly explain: Whether the result is statistically significant and why. What this means about the relationship between year in school and coping strategy. What the researcher should conclude based on these findings.arrow_forwardA school counselor is conducting a research study to examine whether there is a relationship between the number of times teenagers report vaping per week and their academic performance, measured by GPA. The counselor collects data from a sample of high school students. Write the null and alternative hypotheses for this study. Clearly state your hypotheses in terms of the correlation between vaping frequency and academic performance. EditViewInsertFormatToolsTable 12pt Paragrapharrow_forward
- A smallish urn contains 25 small plastic bunnies – 7 of which are pink and 18 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X = 5) ≈ (b) P(X<6) ≈ The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a) The probability that the Grinch gets exactly 6 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.054", "≈ 0.043", "≈ 0.061"] . (b) The probability that the Grinch gets at least 7 blue marbles is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.922", "≈ 0.905", "≈ 0.893"] . (c) The probability that the Grinch gets between 8 and 12 blue marbles (inclusive) is [ Select ] ["≈ 0.801", "≈ 0.760", "≈ 0.786"] . The Whoville small urn contains 100 marbles – 60 blue and 40 orange. The Grinch sneaks in one night and grabs a simple random sample (without replacement) of 15 marbles. (a)…arrow_forwardSuppose an experiment was conducted to compare the mileage(km) per litre obtained by competing brands of petrol I,II,III. Three new Mazda, three new Toyota and three new Nissan cars were available for experimentation. During the experiment the cars would operate under same conditions in order to eliminate the effect of external variables on the distance travelled per litre on the assigned brand of petrol. The data is given as below: Brands of Petrol Mazda Toyota Nissan I 10.6 12.0 11.0 II 9.0 15.0 12.0 III 12.0 17.4 13.0 (a) Test at the 5% level of significance whether there are signi cant differences among the brands of fuels and also among the cars. [10] (b) Compute the standard error for comparing any two fuel brands means. Hence compare, at the 5% level of significance, each of fuel brands II, and III with the standard fuel brand I. [10] �arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forward
- What would you say about a set of quantitative bivariate data whose linear correlation is -1? What would a scatter diagram of the data look like? (5 points)arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forwardAnalyze the residuals of a linear regression model and select the best response. yes, the residual plot does not show a curve no, the residual plot shows a curve yes, the residual plot shows a curve no, the residual plot does not show a curve I answered, "No, the residual plot shows a curve." (and this was incorrect). I am not sure why I keep getting these wrong when the answer seems obvious. Please help me understand what the yes and no references in the answer.arrow_forward
- a. Find the value of A.b. Find pX(x) and py(y).c. Find pX|y(x|y) and py|X(y|x)d. Are x and y independent? Why or why not?arrow_forwardAnalyze the residuals of a linear regression model and select the best response.Criteria is simple evaluation of possible indications of an exponential model vs. linear model) no, the residual plot does not show a curve yes, the residual plot does not show a curve yes, the residual plot shows a curve no, the residual plot shows a curve I selected: yes, the residual plot shows a curve and it is INCORRECT. Can u help me understand why?arrow_forwardYou have been hired as an intern to run analyses on the data and report the results back to Sarah; the five questions that Sarah needs you to address are given below. please do it step by step on excel Does there appear to be a positive or negative relationship between price and screen size? Use a scatter plot to examine the relationship. Determine and interpret the correlation coefficient between the two variables. In your interpretation, discuss the direction of the relationship (positive, negative, or zero relationship). Also discuss the strength of the relationship. Estimate the relationship between screen size and price using a simple linear regression model and interpret the estimated coefficients. (In your interpretation, tell the dollar amount by which price will change for each unit of increase in screen size). Include the manufacturer dummy variable (Samsung=1, 0 otherwise) and estimate the relationship between screen size, price and manufacturer dummy as a multiple…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





