
Campbell Biology in Focus; Modified Mastering Biology with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134433776
Author: Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 10TYU
SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE
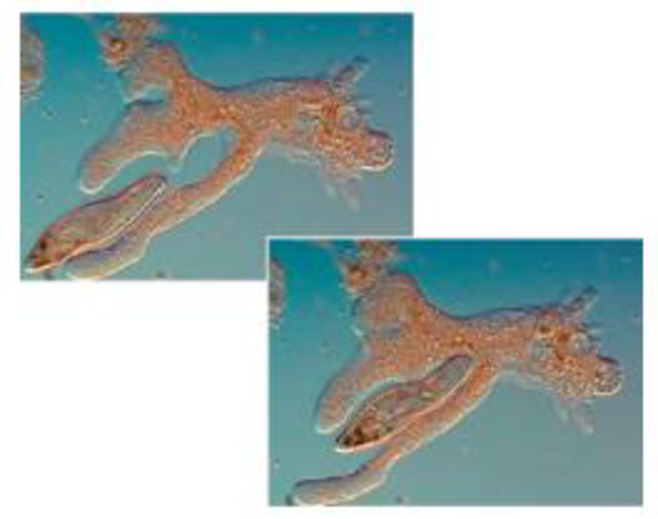
These micrographs show one single-celled eukaryote, a tubulinid amoeba, engulfing another, a ciliate. Describe a key feature of eukaryotes suggested by these images, and summarize the role of endosymbiosis in the evolutionary history of the eukaryotes. Are tubulinid amoebas more closely related to all other protists than they are to plants,
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Microscopic Images
Examine the microscopic images of protists below. Note
cell shapes, organelles, intracellular structures,
locomotory structures and other distinguishing features.
The species or taxonomic names are located under each
photo.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(0)
Multicellular algae (top row A-C, left to right) and
unicellular algae (D-F):
A. Brown kelp (seaweed) Macrocystis
B. Red algae Corallina
C. Green algae Halimeda incrassata
D. Bioluminescence (blue color) from dinoflagellates
(flagellated unicellular algae).
E. Diatoms (shelled unicellular algae)
F. Colonial green algae Volvox (bottom row)
Give an example of a protist that is:(a) a parasite of humans(b) very large and photosynthetic(c) a unicellular species with two flagella and photosynthetic(d) covered in cilia
The following groups of protists will be covered in lecture: Amoebazoa, Excavate-euglena,
Alveolata: ciliates, dinoflagellates, apicomplexan;
Stramenopiles: diatoms and brown algae, and
Plantae: chlorophytes.
How do these organisms compare in their
-general type of nutrition (autotroph, heterotroph),
-ecological roles (parasites, decomposers, importance in
food chains)
-general structures (cell walls, structures that help them
move and feed, single vs multicellular)
-reproduction (asexual, sexual)
-presence or absence of alternation of generations, -
degree of complexity of life cycles
-habitats that they are found in
Chapter 25 Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus; Modified Mastering Biology with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Ch. 25.1 - Describe major events in the evolution of early...Ch. 25.1 - Explain why eukaryotes are said to be combination...Ch. 25.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 25.2 - Summarize the evidence that choanoflagellates are...Ch. 25.2 - MAKE CONNECTlONS Describe how the origin of...Ch. 25.2 - Prob. 3CCCh. 25.3 - Briefly describe the organisms found in each of...Ch. 25.3 - MAKE CONNECTIONS Review Figures 7.2 and 8.5...Ch. 25.3 - Prob. 3CCCh. 25.4 - Justify the claim that photosynthetic protists are...
Ch. 25.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 25.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 25 - The oldest fossil eukaryote that can be resolved...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2TYUCh. 25 - Plastids that are surrounded by more than two...Ch. 25 - Prob. 4TYUCh. 25 - Prob. 5TYUCh. 25 - Based on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 25.9,...Ch. 25 - MAKE CONNECTIONS The bacterium Wolbachia is a...Ch. 25 - FOCUS ON EVOLUTION DRAW IT Medical researchers...Ch. 25 - FOCUS ON INTERACTIONS Organisms interact with each...Ch. 25 - SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE These micrographs show...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Jr. Scientist discovers a never-before-classified protist. It contains multinucleated filaments, similar to fungal hyphae however, upon closer examination the cell walls are found to be composed of cellulose rather than chitin. They do not perform photosynthesis but instead acquire nutrients by way of parasitism or decomposition. Jr. Scientist has likely discovered a rhizarian a foraminiferan an oomycete a mycetozoanarrow_forwardI don't understand this practice bio question: Despite the fact that modern taxonomists have abandoned the Kingdom Protista, the term "protist" persists in the biological literature. Explain the current meaning of the term protist and give several specific examples.arrow_forwardProtists are(a) single-celled eukaryotes.(b) multicellular eukaryotes.(c) single-celled prokaryotes.(d) single-celled akaryote. Please try to break the solutions into as many steps as practically possible and the steps should come one by one and they should be short and crisp and plagiarism-free.arrow_forward
- Algae are autotrophs and can have photosynthesis, however, evolutionary evidence suggests that plants shared a common ancestor with only green algae and are closest relatives of Charophytes. What evidences support this statement? How an algal cell is different from fungal cells, even if both are eukaryotes? Why slime mold is a protist not a fungus even if it does not have chloroplast?arrow_forwardPlease help to answer and also provide a step-by-step explanation: Movement is a type of response to stimuli. Many unicellular organisms can move in response to chemical changes outside the cell – amoeba exhibits locomotion, paramecium use cilia to get around. Protists such as the Amoeba and the Paramecium are important to our discussion of evolution because of their ability to respond to changes in the environment. These single-celled eukaryotes have this ability because a) their DNA responds to stimuli from the environment, b) they have the same germ cell layers that the Cnidaria have, c) new proteins, located in the cell membrane, have shapes and charge patterns that react to a stimulus by generating an electrical impulse. d) they have a Golgi Apparatus that measures the stimulus from the environment, e) none of these are possible.arrow_forwardPut a checkmark (1) on the group where each of the following structures are present. Cellular Structures Plantae Animalia FungiProtista Monera 1. Nucleus 2. Nucleoid 3. Nucleolus 4. Ribosomes 5. Golgi Body 6. Endoplasmic reticulum 7. Plasma membrane 8. Centriole 9. Cell wall 10. Chloroplast 11. Mitochondria 12. Cytoplasm 13. Cytoskeleton 14.Pigments 15. DNAarrow_forward
- Please help!arrow_forwardA) A major difference between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is that eukaryotic cells Group of answer choices exhibit little if any compartmentalization of function are generally smaller than prokaryotic cells have a large degree of internal organization lack organelles have little if any internal organization B) Which of the following statements about protists is false? Group of answer choices Some protists are mixotrophic Certain protists share a common ancestor with land plants Some protists are photosynthetic prokaryotes which are similar to the ancestral chloroplast Protists are a polyphyletic group of organisms that often bear little resemblance to each other Although most protists are unicellular, some protists are multicellular as wellarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not true of the protists? (a) they are unicellular, colonial, coenocytic, or simple multicellular organisms (b) their cilia and flagella have a 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules (c) they are prokaryotic, as bacteria and archaea are (d) some are free-living, and some are endosymbionts (e) most are aquatic and live in the ocean or in freshwater pondsarrow_forward
- Please briefly describe the idea of endosymbiosis and its role in protist evolution-relate to the idea of function of the group.arrow_forwardfirst 4 please and its a tablearrow_forwardClapter 4. Define and identify properties of biofilms Familiarize yourself with the following structures and what purpose(s) they se o Glycocalyx (both slime layer and capsule) Fimbriae o Flagella, distinguish the different flagella arrangements axial filament sex pili cell wall plasma membrane inclusions ribosomes plasmids nucleoid chromosome o endospores What characteristics distinguish the Domain Archaea and Domain Bacteria? Regarding cellwall hp O o 0 O O 0 0 oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
Bacterial Endospore Formation -Biology Pundit; Author: Biology Pundit;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6_sinRhE8zA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY