
Concept explainers
Figure P24.51 shows four small charged spheres arranged at the corners of a square with side d = 25.0 cm.
a. What is the electric field at the location of the sphere with charge +2.00 nC?
b. What is the total electric force exerted on the sphere with charge +2.00 nC by the other three spheres?
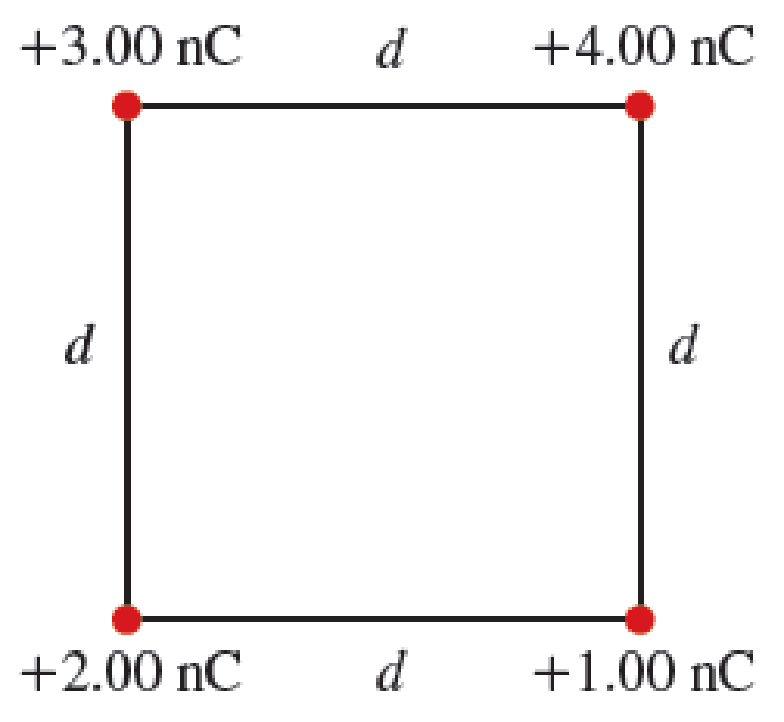
FIGURE P24.51
(a)
The electric field at the location of the sphere with charge
Answer to Problem 51PQ
The electric field at the location of the sphere with charge
Explanation of Solution
Sketch the diagram showing the electric fields and position vectors of the charges.
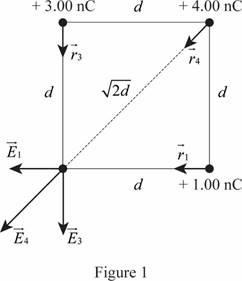
Write the equation for the electric field of a charged particle.
Here,
Use equation (I) to find the equation for the sum of the electric field at the location of the sphere with charge
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the electric field at the location of the sphere with charge
(b)
The total electric forceon the sphere with charge
Answer to Problem 51PQ
The total electric force on the sphere with charge
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the electric force.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the total electric force on the sphere with charge
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR KATZ'S PHYSICS FOR SC
- I need help with part B. I cant seem to get the correct answer. Please walk me through what youre doing to get to the answer and what that could bearrow_forwardQuestion 6: Chlorine is widely used to purify municipal water supplies and to treat swimming pool waters. Suppose that the volume of a particular sample of Cl₂ gas is 8.70 L at 895 torr and 24°C. (a) How many grams of Cl₂ are in the sample? ⚫ Atomic mass of CI = 35.453 g/mol • Molar mass of Cl₂ = 2 x 35.453 = 70.906 g/mol Solution: Use the Ideal Gas Law: Step 1: Convert Given Values • Pressure: P = 895 torr → atm PV= = nRT 1 P = 895 × = 1.1789 atm 760 • Temperature: Convert to Kelvin: T24273.15 = 297.15 K • Gas constant: R = 0.0821 L atm/mol. K Volume: V = 8.70 L Step 2: Solve for n . PV n = RT n = (1.1789)(8.70) (0.0821)(297.15) 10.25 n = = 0.420 mol 24.405 Step 3: Calculate Mass of Cl₂ Final Answer: 29.78 g of Cl₂. mass nx M mass= (0.420)(70.906) mass= 29.78 garrow_forwardE1 R₁ w 0.50 20 Ω 12 R₁₂ ww ΒΩ R₂ 60 E3 C RA w 15 Ω E2 0.25 E4 0.75 Ω 0.5 Ωarrow_forward
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





