
ANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY MEASURES Based on the financial statement data in Exercise 24-1B, compute the following activity measures for 20-2 (round all calculations to two decimal places):
- (a)
Accounts receivable turnover - (b) Merchandise inventory turnover
- (c) Asset turnover
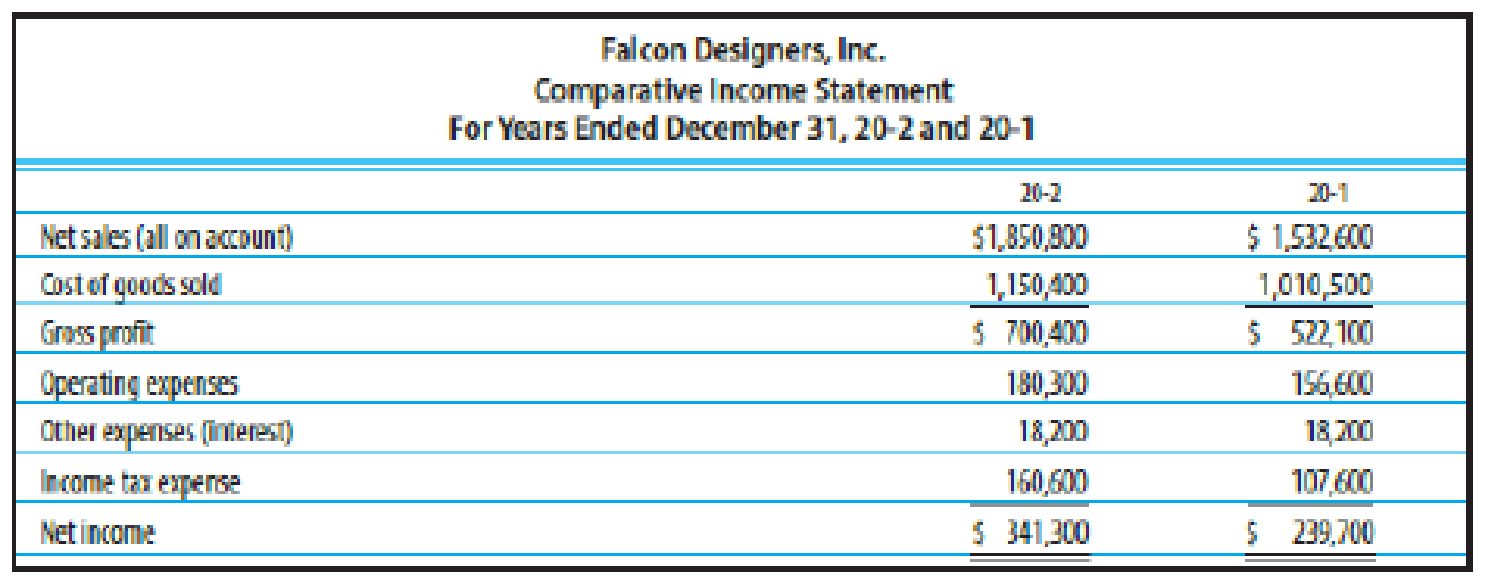
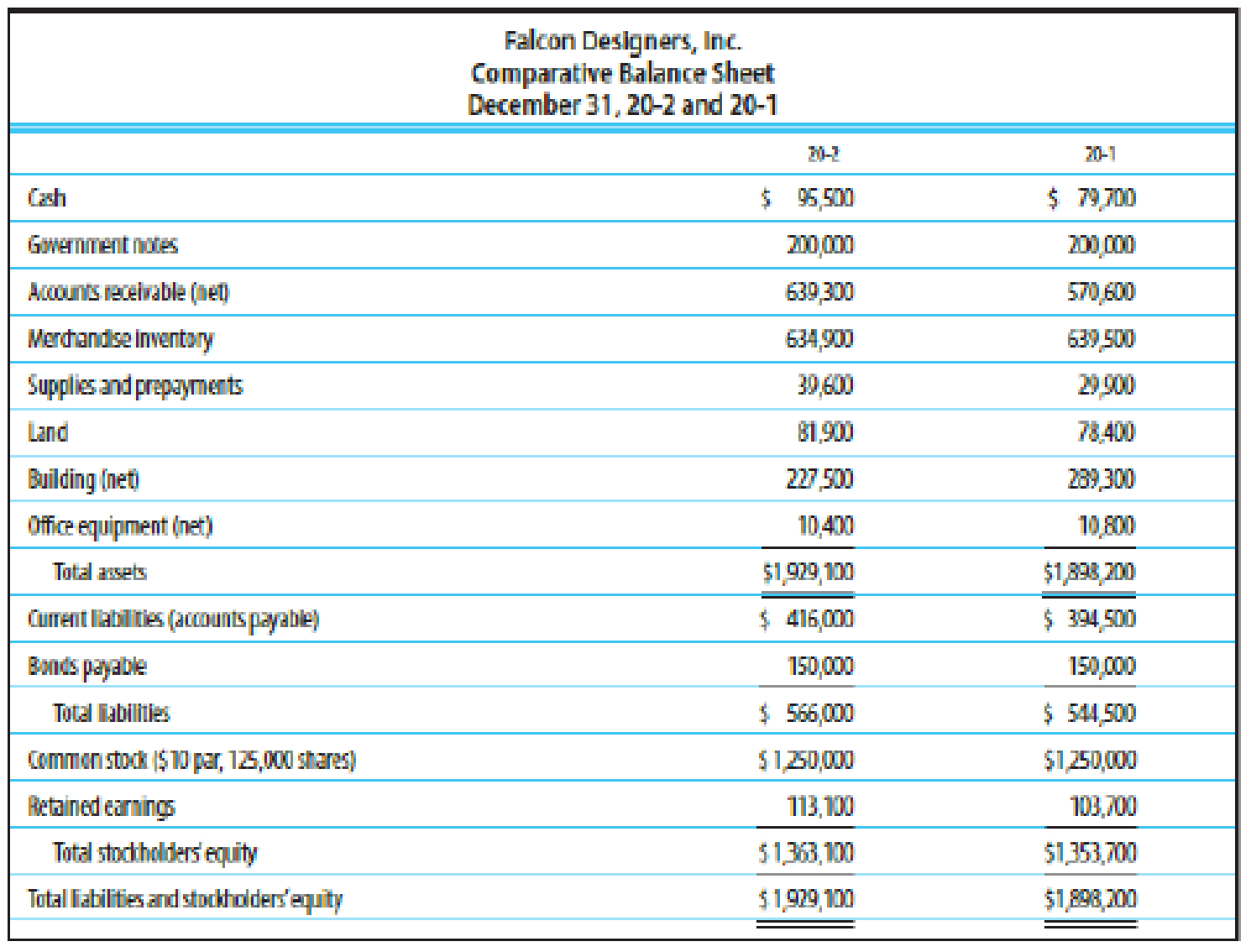
(a)
Calculate accounts receivable turnover and average collection period for the period 20-2.
Explanation of Solution
Accounts receivable turnover:
Accounts receivable turnover is a liquidity measure of accounts receivable in times, which is calculated by dividing the net credit sales by the average amount of net accounts receivables. In other words, it indicates the number of times the average amount of net accounts receivables collected during a particular period.
Calculate accounts receivable turnover ratio for the period 20-2 as follows:
Therefore, accounts receivable turnover ratio for the period 20-2 is 3.06 times.
Average collection period:
Average collection period indicates the number of days taken by a business to collect its outstanding amount of accounts receivable on an average.
Calculate average collection period for the period 20-2.
Therefore, average collection period for the period 20-2 is 119.28 days.
b.
Calculate merchandise inventory turnover and average number of days to sell inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Inventory turnover ratio:
Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period.
Calculate merchandise inventory for the period 20-2.
Therefore, inventory turnover ratio for the period 20-2 is 1.81 times.
Days’ sales in inventory:
Days’ sales in inventory are used to determine number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them.
Calculate average number of days to sell inventory for the period 20-2.
Therefore, average number of days to sell inventory during the period 20-2 is 201.66 days.
(c)
Calculate asset turnover ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Asset turnover:
Asset turnover is a ratio that measures the productive capacity of the fixed assets to generate the sales revenue for the company. Thus, it shows the relationship between the net sales and the average total fixed assets.
Calculate assets turnover ratio for the period 20-2.
Therefore, assets turnover ratio is 0.97 to 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
COLLEGE ACCOUNTING, CHAPTERS 1-27 2T
- PLEASE HELP ME WITH THIS ACCOUNTING PROBLEMarrow_forwardLet's say that Dr. Tim’s Company purchased a heavy-duty truck on July 1, 2021, for $30,000. It was estimated that it would have a useful life of 10 years and then would have a trade-in value of $6,000. The company uses the straight-line method. It was traded on August 1, 2026, for a similar truck costing $42,000; $16,000 was allowed as trade-in value (also fair value) on the old truck and $26,000 was paid in cash. A comparison of expected cash flows for the trucks includes the exchange lacks commercial substance. What is the entry to record the trade-in? Truck (new) $42,000 Accumulated Depreciation $12,200 ($30,000 - $6,000) x (61 months / 120 months) Loss on Disposal of Trucks $1,800 ($30,000 - $12,200 - $16,000 [trade-in] Trucks (old)…arrow_forward16. Candy Company projects the following sales: BB (Click on the icon to view the projected sales.) Candy collects sales on account in the month after the sale. The Accounts Receivable balance on January 1 is $12,300, which represents December's sales on account. Candy projects the following cash receipts from customers: BEE (Click on the icon to view the cash receipts from customers.) Recalculate cash receipts from customers if total sales remain the same but cash sales are only 5% of the total. Begin by computing the cash sales and sales on account for each month if cash sales are only 5% of the total. January February March Cash sales (5%) Sales on account (95%) Total sales $ 31,000 $ 27,000 $ 33,000 Data table X I Data table - X January February March January February March Cash sales (10%) $ 3,100 $ 27,900 Sales on account (90%) 2,700 $ 24,300 3,300 29,700 Cash receipts from cash sales Cash receipts from sales on account $ 3,100 $ 2,700 $ 12,300 27,900 3,300 24,300 $ 31,000 $…arrow_forward
- 11. Kapper Company projects 2025 first quarter sales to be $35,000 and increase by 15% per quarter. Determine the projected sales for 2025 by quarter and in total. Round answers to the nearest dollar. 12. Fagg Company manufactures and sells bicycles. A popular model is the XC. The company expects to sell 2,100 XCs in 2024 and 2,000 XCs in 2025. At the beginning of 2024, Friedman has 380 XCs in Finished Goods Inventory and desires to h of the next year's sales available at the end of the year. How many XCs will Fagg need to produce in 2024? 11. Kapper Company projects 2025 first quarter sales to be $35,000 and increase by 15% per quarter. Determine the projected sales for 2025 by quarter and in total. Round answers to the nearest dollar. Determine the projected sales for each quarter, then compute the projected sales for 2025. Base sale amount Quarter 1 Multiplier for sales increase = Projected sales for the quarter Larrow_forward15. Callarman Company began operations on January 1 and has projected the following selling and administrative expenses: (Click on the icon to view the selling and administrative expenses.) Determine the cash payments for selling and administrative expenses for the first three months of operations. (Complete all answer boxes. Enter a "0" for zero amounts.) Rent Expense Utilities Expense Depreciation Expense Insurance Expense Total cash payments for selling and administrative expenses Data tables January February March Rent Expense Utilities Expense Depreciation Expense Insurance Expense $1,400 per month, paid as incurred 800 per month, paid in month after incurred 1,000 per month 50 per month, 9 months prepaid on January 1 Print Donearrow_forwardMatch the budget types to the definitions. Budget Types 5. Financial 6. Flexible 7. Operating 8. Operational 9. Static 10. Strategic Definitions a. Includes sales, production, and cost of goods sold budgets b. Long-term budgets c. Includes only one level of sales volume d. Includes various levels of sales volumes e. Short-term budgets f. Includes the budgeted financial statementsarrow_forward
- 14. Cain Company is a sporting goods store. The company sells a tent that sleeps six people. The store expects to sell 280 tents in 2024 and 360 tents in 2025. At the beginning of 2024, Cain Company has 30 tents in Merchandise Inventory and desires to have 60% of the next year's sales available at the end of the year. How many tents will Cain Company need to purchase in 2024? Begin by selecting the labels, then enter the amounts to compute the budgeted tents to be purchased. Plus: Total tents needed Less: Budgetec Budgeted tents returned Budgeted tents to be sold Desired tents in ending inventory Tents in beginning inventory Zarrow_forwardCalculate Airbnb inventory turnover for the year 2024. ( (COGS) was $1.829 billion for the previous 12 months)(average inventory for 2024 is showing a significant increase, with the company reporting over $491 million) What does inventory turnover tells an investor?arrow_forwardCariman Company manufactures and sells three styles of door Handles: Gold, Bronze and Silver. Production takes 50, 50, and 20 machine hours to manufacture 1,000-unit batches of Gold, Bronze, and Silver Handles, respectively. The following additional data apply: Projected sales in units Per Unit data: Gold Bronze Silver 60,000 100,000 80,000 2. Determine the activity cost driver rate for setup costs and inspection costs? 3. Using the ABC system, for the Gold style of Handle: a. Calculate the estimated overhead costs per unit? b. Calculate the estimated operating profit per unit? 4. Explain the difference between the profits obtained from the traditional system and the ABC system. Which system provides a better estimate of profitability? Selling price $80 $40 $60 Direct materials $16 $8 $16 Direct labour $30 $6 $18 Overhead cost based on direct labour hours (traditional system) $24 $6 $18 Hours per 1,000-unit batch: Direct labour hours Machine hours Setup hours Inspection hours 80 20 60…arrow_forward
- I need some help with problem B. I have done the work, but I'd like to make sure if I have done the calculations correctly. If you see anything else that is wrong, please let me know.arrow_forwardModule 6 Discussion Discuss the significance of recognizing the time value of money in the long-term impact of the capital budgeting decision. 60 Replies, 59 Unread Σarrow_forwardHow many weeks of supply does summit logistics Inc. Hold ?arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning





