
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
A reaction that leads to the formation of triglyceride, starting with glycerol and carboxylic acids has to be suggested.
Concept introduction:
Ester formation reaction: Reaction of alcohol and

a)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxyl group act as nucleophile and the carboxylic group act as electrophile in presence of acid catalyst; the nucleophile attack at electrophilic carbon of carboxylic acid leads to the formation of ester with the elimination of water molecule.
Mechanism of condensation reaction:
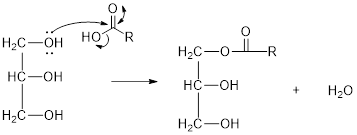
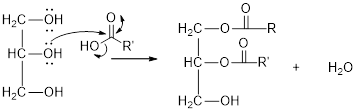
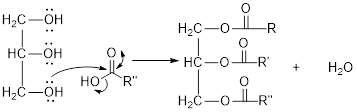
As shown above, the successive steps lead to the formation of triglycerides containing three ester group with the elimination of three water molecules.
b)
Interpretation:
An equation for the base hydrolysis of ester has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Ester formation reaction: Reaction of alcohol and carboxylic acid using acid catalyst results the ester formation with the elimination of water molecule.
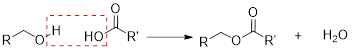
b)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxyl group acts as nucleophile and the carbonyl carbon act as electrophile; the nucleophile attack at electrophilic carbon of ester leads to the formation of alcohol with the elimination of fatty acid salts (soap).
Base hydrolysis of Esters:
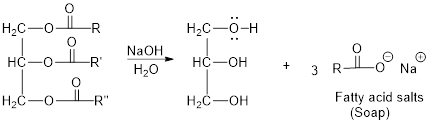
c)
Interpretation:
Difference between fats and oils has to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Melting point: At temperature begins the solid to melt.
Unsaturation bonds: The presence of double or triple bonds in the molecules.
c)
Explanation of Solution
The presence of unsaturated bonds in the molecules tight close packing will be less due to bend of double bonds and the intermolecular attraction between them is less and less energy is required to overcome the interaction. More the double bonds lower the intermolecular interaction. Hence, the melting point decreases.
d)
Interpretation:
Reagent and catalyst used in hydrogenation process has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Hydrogenation of
Homogeneous catalyst: Catalyst used is in same phase as the reactants.
Heterogeneous catalyst: Catalyst used is in different phase as the reactants.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Liquid oil is obtained from plants, having double bonds the presence of reactive double bond is converted into single bonds in order to solidify. Hydrogenation of double bonds is the process in which hydrogen molecule is added across the double bond forming alkane product. The alkane is highly facilitated for close packing and solidifies the oil.
Reaction carried out is hydrogenation reaction; hydrogen molecule is the reagent used in presence of either heterogeneous or homogeneous catalyst.
e)
Interpretation:
Iodine number has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Iodine number: number of grams of Iodine that react with given quantity of oil is called Iodine number.
Number of moles = Molarity
e)
Explanation of Solution
Given: molarity of
Number of moles of
The mol ratio between
Number of grams of
The iodine number is the number of grams of iodine that reacts with 100 g of corn oil.
Hence, Iodine number calculated is 123
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
AVC LOOSELEAF CHEMISTRY W/CONNECT 2 SEM
- Name the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- Provide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





