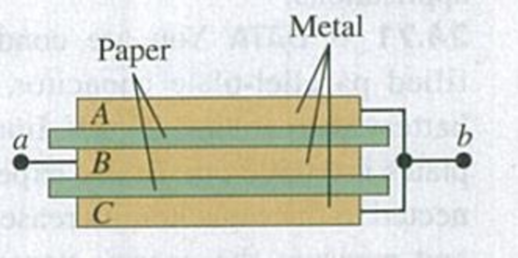
Problem 24.1DQ: Equation (24.2) shows that the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor becomes larger as the plate... Problem 24.2DQ: Suppose several different parallel-plate capacitors are charged up by a constant-voltage source.... Problem 24.3DQ: Suppose the two plates of a capacitor have different areas. When the capacitor is charged by... Problem 24.4DQ: To store the maximum amount of energy in a parallel-plate capacitor with a given battery (voltage... Problem 24.5DQ: In the parallel-plate capacitor of Fig. 24.2, suppose the plates are pulled apart so that the... Problem 24.6DQ: A parallel-plate capacitor is charged by being connected to a battery and is kept connected to the... Problem 24.7DQ: A parallel-plate capacitor is charged by being connected to a battery and is then disconnected from... Problem 24.8DQ: Two parallel-plate capacitors, identical except that one has twice the plate separation of the... Problem 24.9DQ: The charged plates of a capacitor attract each other, so to pull the plates farther apart requires... Problem 24.10DQ: You have two capacitors and want to connect them across a voltage source (battery) to store the... Problem 24.11DQ: As shown in Table 24.1, water has a very large dielectric constant K = 80.4. Why do you think water... Problem 24.12DQ: Is dielectric strength the same thing as dielectric constant? Explain any differences between the... Problem 24.13DQ: A capacitor made of aluminum foil strips separated by Mylar film was subjected to excessive voltage,... Problem 24.14DQ: Suppose you bring a slab of dielectric close to the gap between the plates of a charged capacitor,... Problem 24.15DQ: The freshness of fish can be measured by placing a fish between the plates of a capacitor and... Problem 24.16DQ: Electrolytic capacitors use as their dielectric an extremely thin layer of nonconducting oxide... Problem 24.17DQ: In terms of the dielectric constant K, what happens to the electric flux through the Gaussian... Problem 24.18DQ: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a power supply that maintains a fixed potential... Problem 24.19DQ: Liquid dielectrics that have polar molecules (such as water) always have dielectric constants that... Problem 24.20DQ: A conductor is an extreme case of a dielectric, since if an electric field is applied to a... Problem 24.21DQ: The two plates of a capacitor are given charges Q. The capacitor is then disconnected from the... Problem 24.1E: The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are 2.50 mm apart, and each carries a charge of magnitude... Problem 24.2E: The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are 3.28 mm apart, and each has an area of 9.82 cm2. Each... Problem 24.3E: A parallel-plate air capacitor of capacitance 245 pF has a charge of magnitude 0.148 C on each... Problem 24.4E: Cathode-ray-tube oscilloscopes have parallel metal plates inside them to deflect the electron beam.... Problem 24.5E: A 10.0-F parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates is connected to a 12.0-V battery. (a) What is... Problem 24.6E: A 5.00-F parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a 12.0-V battery. After the capacitor is fully... Problem 24.7E: A parallel-plate air capacitor is to store charge of magnitude 240.0 pC on each plate when the... Problem 24.8E: A 5.00-pF, parallel-plate, air-filled capacitor with circular plates is to be used in a circuit in... Problem 24.9E: A capacitor is made from two hollow, coaxial, iron cylinders, one inside the other. The inner... Problem 24.10E: A cylindrical capacitor consists of a solid inner conducting core with radius 0.250 cm, surrounded... Problem 24.11E: A spherical capacitor contains a charge of 3.30 nC when connected to a potential difference of 220... Problem 24.12E: A cylindrical capacitor has an inner conductor of radius 2.2 mm and an outer conductor of radius 3.5... Problem 24.13E: A spherical capacitor is formed from two concentric, spherical, conducting shells separated by... Problem 24.14E: Figure E24.14 shows a system of four capacitors, where the potential difference across ab is 50.0 V.... Problem 24.15E: BIO Electric Eels. Electric eels and electric fish generate large potential differences that are... Problem 24.16E: For the system of capacitors shown in Fig. E24.16, Find the equivalent capacitance (a) between b and... Problem 24.17E: In Fig. E24.17, each capacitor has C = 4.00 F and Vab = +28.0 V. Calculate (a) the charge on each... Problem 24.18E: In Fig. 24.8a, let C1 = 3.00 F, C2 = 5.00F, and Vab = +64.0 V. Calculate (a) the charge on each... Problem 24.19E: In Fig. 24.9a, let C1 = 3.00 F, C2 = 5.00 F, and Vab = +52.0 V. Calculate (a) the charge on each... Problem 24.20E: In Fig. E24.20, C1 = 6.00 F, C2 = 3 00 F, and C3 = 5.00 F. The capacitor network is connected to an... Problem 24.21E: For the system of capacitors shown in Fig. E24.21, a potential difference of 25 V is maintained... Problem 24.22E: Suppose the 3-F capacitor in Fig. 24.10a were removed and replaced by a different one, and that this... Problem 24.23E: 5.80-F, parallel-plate, air capacitor has a plate separation of 5.00 mm and is charged to a... Problem 24.24E: A parallel-plate air capacitor has a capacitance of 920 pF. The charge on each plate is 3.90 C. (a)... Problem 24.25E: An air capacitor is made from two flat parallel plates 1.50 mm apart. The magnitude of charge on... Problem 24.26E: A parallel-plate vacuum capacitor has 8.38 J of energy stored in it. The separation between the... Problem 24.27E: You have two identical capacitors and an external potential source, (a) Compare the total energy... Problem 24.28E: For the capacitor net-work shown in Fig. E24.28, the potential difference across ab is 48 V. Find... Problem 24.29E: For the capacitor net-work shown in Fig. E24.29, the potential difference across ab is 220 V. Find... Problem 24.30E: A 0.350-m-long cylindrical capacitor consists of a solid conducting core with a radius of 1.20 mm... Problem 24.31E: A cylindrical air capacitor of length 15.0 m stores 3.20 109 J of energy when the potential... Problem 24.32E: A capacitor is formed from two concentric spherical conducting shells separated by vacuum. The inner... Problem 24.33E: A 12.5-F capacitor is connected to a power supply that keeps a constant potential difference of 24.0... Problem 24.34E: A parallel-plate capacitor has capacitance C0 = 8.00 pF when there is air between the plates. The... Problem 24.35E: Two parallel plates have equal and opposite charges. When the space between the plates is evacuated,... Problem 24.36E: A budding electronics hobbyist wants to make a simple 1.0-nF capacitor for tuning her crystal radio,... Problem 24.37E: The dielectric to be used in a parallel-plate capacitor has a dielectric constant of 3.60 and a... Problem 24.38E: BIO Potential in Human Cells. Some cell walls in the human body have a layer of negative charge on... Problem 24.39E: A constant potential difference of 12 v is maintained between the terminals of a 0.25-F,... Problem 24.40E: Polystyrene has dielectric constant 2.6 and dielectric strength 2.0 107 V/m. A piece of polystyrene... Problem 24.41E: When a 360-nF air capacitor (1 nF = 109F) is connected to a power supply, the energy stored in the... Problem 24.42E: A parallel-plate capacitor has capacitance C = 12.5 pF when the volume between the plates is filled... Problem 24.43E: A parallel-plate capacitor has the volume between its plates filled with plastic with dielectric... Problem 24.44E: A parallel-plate capacitor has plates with area 0.0225 m2 separated by 1.00 mm of Teflon. (a)... Problem 24.45P: Electronic flash units for cameras contain a capacitor for storing the energy used to produce the... Problem 24.46P: A parallel-plate air capacitor is made by using two plates 12 cm square, spaced 3.7 mm apart. It is... Problem 24.47P: In one type of computer keyboard, each key holds a small metal plate that serves as one plate of a... Problem 24.48P: BIO Cell Membranes. Cell membranes (the walled enclosure around a cell) are typically about 7.5 nm... Problem 24.49P: A 20.0-F capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 800 V. The terminals of the charged... Problem 24.50P: In Fig. 24.9a, let C1 = 9.0 F, C2 = 4.0 F, and Vab = 64 V. Suppose the charged capacitors are... Problem 24.51P: For the capacitor network shown in Fig. P24.51, the potential difference across ab is 12.0 V. Find... Problem 24.52P: In Fig. E24.17, C1 = 6.00 F, C2 = 3.00 F, C3 = 4.00 F, and C4 = 8.00 F. The capacitor network is... Problem 24.53P: In Fig. P24.53, C1 = C5 = 8.4 F and C2 = C3 = C4 = 4.2 F. The applied potential is Vab = 220 V. (a)... Problem 24.54P: Current materials-science technology allows engineers to construct capacitors with much higher... Problem 24.55P: In Fig. E24.20, C1 = 3.00 F and Vab = 150 V. The charge on capacitor C1 is 150 C and the charge on... Problem 24.56P: The capacitors in Fig. P24.56 are initially uncharged and are connected, as in the diagram, with... Problem 24.57P: Three capacitors having capacitances of 8.4, 8.4, and 4.2 F are connected in series across a 36-V... Problem 24.58P: Capacitance of a Thundercloud. The charge center of a thundercloud, drifting 3.0 km above the earths... Problem 24.59P: In Fig. P24.59, each capacitance C1 is 6.9 F, and each capacitance C2 is 4.6 F. (a) Compute the... Problem 24.60P: Each combination of capacitors between points a and b, in Fig. P24.60 is first connected across a... Problem 24.61P: A parallel-plate capacitor with only air between the plates is charged by connecting it to a... Problem 24.62P: An air capacitor is made by using two flat plates, each with area A, separated by a distance d. Then... Problem 24.63P: A potential difference Vab = 48.0 V is applied across the capacitor network of Fig. E24.17. If C1 =... Problem 24.64P: CALC The inner cylinder of a long, cylindrical capacitor has radius ra and linear charge density +.... Problem 24.65P: A parallel-plate capacitor has square plates that are 8.00 cm on each side and 3.80 mm apart. The... Problem 24.66P: A parallel-plate capacitor is made from two plates 12,0 cm on each side and 4.50 mm apart. Half of... Problem 24.67P: Three square metal plates A, B, and C, each 12.0 cm on a side and 1.50 mm thick, are arranged as in... Problem 24.68P: A fuel gauge uses a capacitor to determine the height of the fuel in a tank. The effective... Problem 24.69P: DATA Your electronics company has several identical capacitors with capacitance C1 and several... Problem 24.70P: DATA You are designing capacitors for various applications. For one application, you want the... Problem 24.71P: DATA You are conducting experiments with an air-filled parallel-plate capacitor. You connect the... Problem 24.72CP: Two square conducting plates with sides of length L are separated by a distance D. A dielectric slab... Problem 24.73PP: BIO THE ELECTRIC EGG. Upon fertilization, the eggs of many species undergo a rapid change in... Problem 24.74PP: Suppose that the egg has a diameter of 200 m. What fractional change in the internal Na+... Problem 24.75PP: Suppose that the change in Vm was caused by the entry of Ca2+ instead of Na+. How many Ca2+ ions... Problem 24.76PP: What is the minimum amount of work that must be done by the cell to restore Vm to 70 mV? (a) 3 mJ;... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




