
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
How to produce the given compound from an
Concept introduction:
In each of these reactions, the
Answer to Problem 24.56P
The starting compound and the reaction condition are given below.
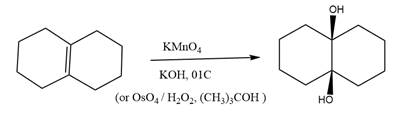
Explanation of Solution
The product from this reaction is a syn 1, 2-
The given reaction is explained as when
(b)
Interpretation:
How to produce the given compound from an alkene or alkyne is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In each of these reactions, the
Answer to Problem 24.56P
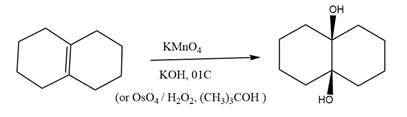
The starting compound and the reaction condition are given below.
Explanation of Solution
The product from this reaction is a syn 1, 2-diol. A
The given reaction is explained as when
(c)
Interpretation:
How to produce the given compound from an alkene or alkyne is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In each of these reactions, the
Answer to Problem 24.56P
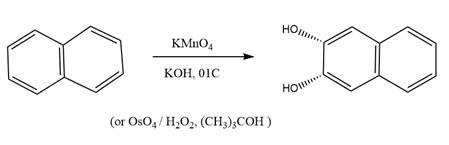
The starting compound and the reaction condition are given below.
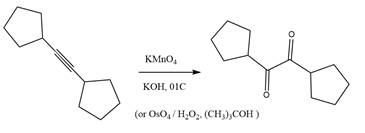
Explanation of Solution
The product from this reaction is a
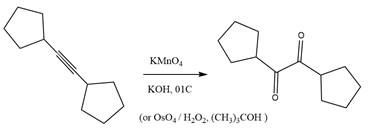
The given reaction is explained as when
(d)
Interpretation:
How to produce the given compound from an alkene or alkyne is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In each of these reactions, the
Answer to Problem 24.56P
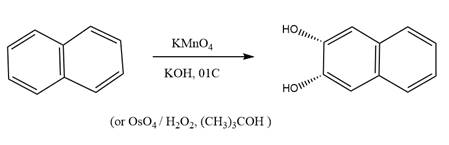
The starting compound and the reaction condition are given below.
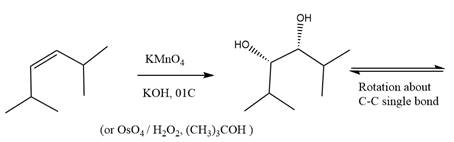
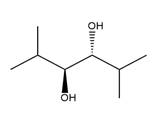
Explanation of Solution
The product from this reaction is a syn 1, 2-diol. A
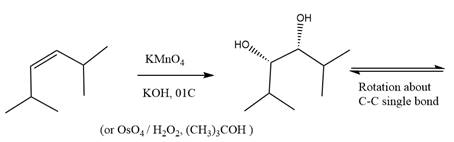
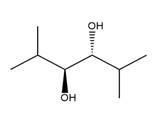
The given reaction is explained as when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


