
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The formation of given compound from 3-methyl-1-butyne has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Addition reaction:
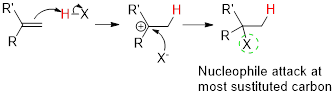
Markovnikov’s rule:
In the overall addition reaction, the hydrogen atom (electrophile) is bonded to least substituted carbon and nucleophile is bonded to the most substituted carbon. This is known as Markovnikov’s rule.
b)
Interpretation:
The formation of given compound from 3-methyl-1-butyne has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Addition reaction: Alkene reacts with polar reagent (HBr, HCl) across the double bond, leads to the product of alkyl halide.
Addition of bromine across the double bond in the presence of Lewis catalyst undergoes addition reaction leads to formation of products.
Markovnikov’s rule:
In the overall reaction, the hydrogen atom (electrophile) is bonded to least substituted carbon and nucleophile is bonded to the most substituted carbon. This is known as Markovnikov’s rule.

c)
Interpretation:
The formation of given compound from 3-methyl-1-butyne has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Addition reaction: Alkene reacts with polar reagent (HBr, HCl) across the double bond, leads to the product of alkyl halide (Or)
Hydrogenation of alkene: Addition of hydrogen molecule across the double bond in presence of catalyst undergoes hydrogenation of alkene.
Markovnikov’s rule:
In the overall reaction, the hydrogen atom (electrophile) is bonded to least substituted carbon and nucleophile is bonded to the most substituted carbon. This is known as Markovnikov’s rule.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
ALEKS 360; 18WKS F/ GEN. CHEMISTRY >I<
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forwardSynthesis of 2-metilbenzimidazol from 1,2-diaminobenceno y propanona.arrow_forward
- Predict the product of the following reaction. 1st attempt HI 1 product 50300 Jul See Periodic Table See Hint P Br 石尚 Iarrow_forwardIndicate the substitutes in one place, if they are a diazonio room.arrow_forwardIndicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forward
- Indicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
